

World Kidney Day (WKD) is a global campaign which aims at spreading worldwide awareness about the importance of kidneys, kidney health and the diseases associated with kidneys. It is a joint initiative which was launched in 2006 by the mutual efforts of the International Society of Nephrology (ISN) and the International Federation of Kidney Foundations (IFKF).
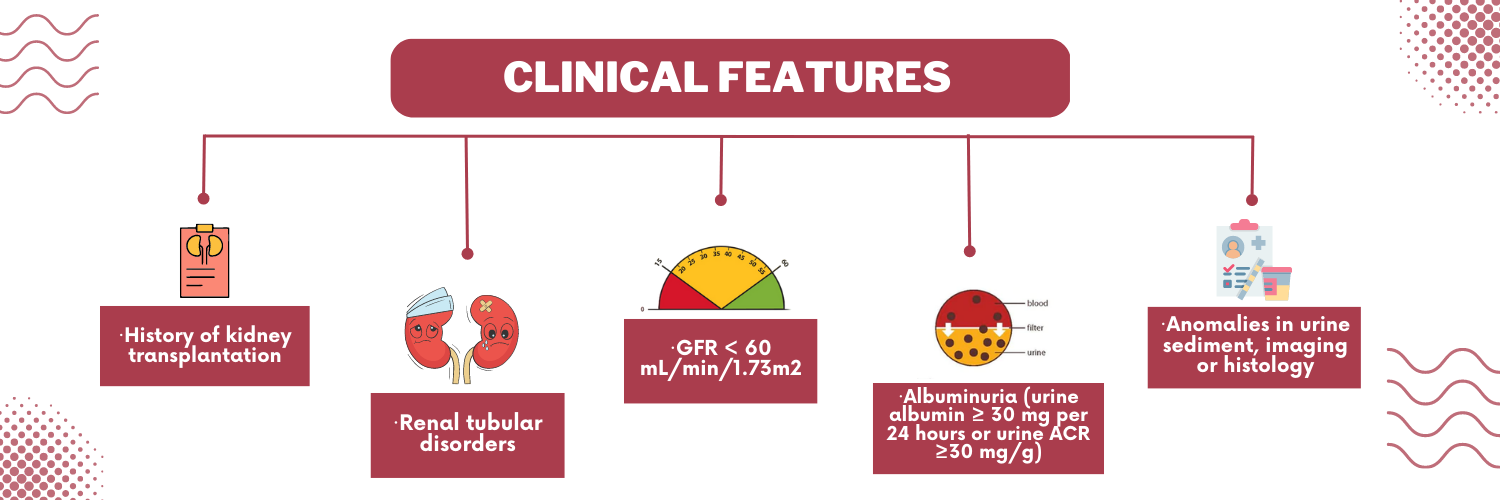
The most prevalent form of kidney disease is Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD). Chronic Kidney Disease also known as Chronic Kidney Failure or Chronic Renal Disease is a permanent and progressive damage in kidneys over months or years, consequent to which the kidneys become incapacitated to filter blood efficiently. CKD has multiple stages of seriousness and gets more and more severe over time. The last stage is called Renal Failure in which the kidneys ultimately stop working where dialysis or kidney transplant is indispensable for survival. CKD includes one or more of the following features:
Usually, kidney disease starts slowly and silently, and progresses over anumber of years. Not everyone progresses from Stage 1 to Stage 5. Stage 5 is also known as End-Stage Renal Disease (ESRD).
| Stage | Description | Glomerular Filtration Rate (GFR) level |
|---|---|---|
| Normal Kidney Function | Healthy Kidneys | 90mL/min or more |
| Stage 1 | Kidney damage with normal or high GFR | 90mL/min or more |
| Stage 2 | Kidney damage and mild decrease in GFR | 60-89mL/min |
| Stage 3 | Moderate decrease inGFR | 30-59mL/min |
| Stage 4 | Severe decrease in GFR | 15-29mL/min |
| Stage 5 | Established kidney failure | Less than 15mL/min or on dialysis |
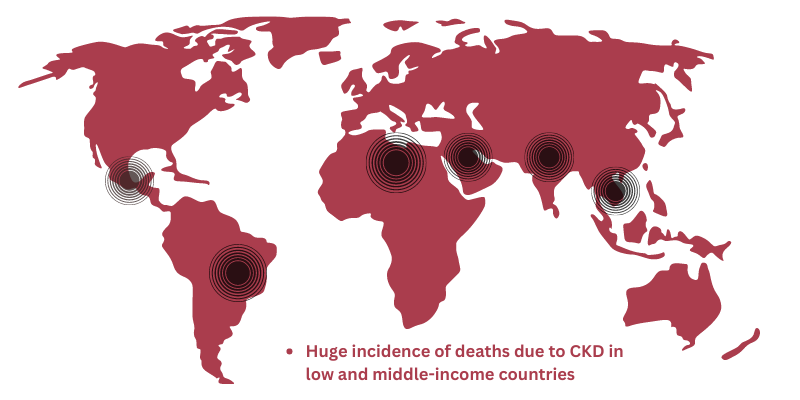
Chronic kidney disease (CKD) has emerged as one of the most prominent causes of death and suffering in the 21st century. Chronic kidney disease is a particularly significant burden in low- and middle-income countries Being one of the leading causes of years of life lost, CKD affects 8% to 16% of the population worldwide, out of which only 5% of patients report with early CKD.




Today in India, more than 1.3 Lakh people are receiving dialysis while the number is going up by 232 per 10 Lakh of population. The etiology of CKD extends throughout India.
As per the estimates, as little as 10-20 percent of End Stage Renal Disease patients, in India continue long term renal replacement therapy (RRT).
According to the reports, limited medical facilities and resources; and risk factors being poorly controlled and managed are few of the many factors leading to rapid progression of CKD to Renal Failure (ESRD) in the patients.
More than 90 percent of all the patients in need of Renal Replacement Therapy (RRT) lose their lives due to inability to meet patient care expenses, and even out of those, about 60 percent of the patients discontinue due to financial causes.
In the Union Budget 2016, the Government of India introduced a plan for standalone haemodialysis centers for End Stage Renal Disease patients.Today in India, more than 1.3 Lakh people are receiving dialysis while the number is going up by 232 per 10 Lakh of population. The etiology of CKD extends throughout India.
Most people do not notice any grave symptoms or are asymptomatic until the disease has reached advanced stage. Common Symptoms of CKD include








Most people do not notice any grave symptoms or are asymptomatic until the disease has reached advanced stage. Common Symptoms of CKD include

Diabetes: Extreme levels of blood sugar can cause damage to multiple organs including the kidneys.

Hypertension: High blood pressure can be both, a cause and a result of CKD.
Some other causes/risk factors include:

To keep the kidneys healthy and protect them, following preventive measures can be taken:
