




Handles the pressure whatever the level
For Hypertensive patients, SBP 160mm Hg
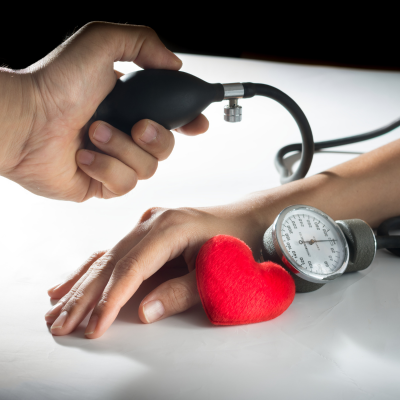

Resistant hypertension (RH) is defined as above-goal elevated blood pressure (BP) in a patient despite the concurrent use of 3 antihypertensive drug classes, commonly including a long-acting calcium channel blocker, a blocker of the renin-angiotensin system (angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor or angiotensin receptor blocker), and a diuretic.
Resistant hypertension was associated with an adjusted hazard ratio2 of





Older Age

Obesity

Diabetes
Chronic Kidney Diseases

High baseline Blood Pressure






Blunted peak concentration

Twice/Thrice daily dosing

Allows 24hr slow and sustained release of drug

Once daily dosing



1) Bharatia, R., Chitale, M., et. al Management Practices in Indian Patients with Uncontrolled Hypertension. The Journal of the Association of Physicians of India, 64(7), 14–21.
2) Pathan MK, Cohen DL. Resistant Hypertension: Where are We Now and Where Do We Go from Here?. Integr Blood Press Control. 2020;13:83-93. Published 2020 Aug 5. doi:10.2147/IBPC.S223334
3) AHA scientific statement on September 13, 2018
4) J Hypertens Suppl. 1994 Nov; 12(8) S97-10
5) Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1985 Aug; 20(2): 155–158
Copyright ©Nicardia, All Right Reserved.