




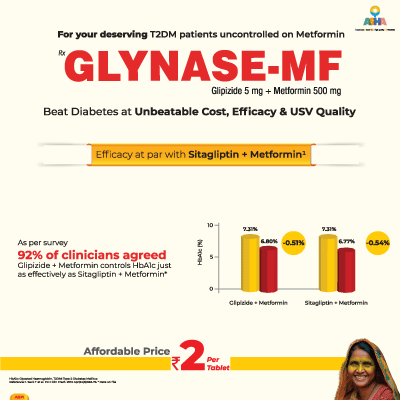
Summary: The study evaluated affordable treatment strategies for managing type 2 diabetes in resource-challenged patients. In a study involving 590 clinicians and 60 experts, the majority agreed that the fixed-dose combination of glipizide and metformin is effective, safe, and cost-efficient—especially suitable for patients with limited financial resources. About 90% supported its use due to its affordability (monthly cost < ₹120), and over 65% considered it a first-line option. Clinicians emphasized the importance of improving awareness, access, and availability of such treatments to enhance outcomes in underserved populations.
Citation: DOI: 10.69605/ijlbpr_13.11.2024.26
Summary: The study built a consensus among Indian clinicians on managing type 2 diabetes in financially constrained patients. Surveying 590 clinicians and interviewing 60 experts, the study found that most doctors regularly treat resource-challenged T2DM patients who struggle with follow-ups and medication adherence due to cost. Over 80% of clinicians cited affordability as a key barrier, and a majority supported using low-cost combinations like glipizide plus metformin to improve adherence and outcomes. Experts also highlighted financial, lifestyle, and psychological challenges in this population.
Citation: Unnikrishnan, Ambika G.1; Patel, Abji B.2; Kannan, Alagarsamy3; Bagchi, Ananda4; Laway, Bashir A.5; Selvaraj, Chandrasekar6; Sanyal, Debmalya7; Dutta, Deep8; Bandyopadhyay, Dipanjan9; Chilakala, Gopinath R.10; Shinde, Jaydeep S.11; Vadgama, Jimit12; Reddy, Kora Chandra O.13; Kundan, Kunal14; Chitle, Manoj15; Lakhani, Om16; Devarbhavi, Praveen K.17; Bhake, Ragini1; Deshmane, Rajesh18; Chandrashekar, Sadashivappa19; Kumar, Senthil20; Kota, Sunil K.21; Shivane, Vyankatesh22; Subramaniyan, Vaithi G.23; Revankar, Santosh Y.24. Understanding Knowledge, Attitude, and Perception of Indian Clinicians in the Management of Resource-challenged Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients in India - DESERVE India Expert Opinion: Part 1. Chronicle of Diabetes Research and Practice 4(1):p 4-13, Jan–Jun 2025.
DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.4103/cdrp.cdrp_8_24

Summary: Review presented simplified guidelines for managing post-transplant diabetes mellitus (PTDM), a common issue after organ transplants.
Glipizide is preferred SU in patients with T2DM and CKD as it is metabolized in liver
Citation: Chowdhury TA, Wahba M, Mallik R, Peracha J, Patel D, De P, Fogarty D, Frankel A, Karalliedde J, Mark PB, Montero RM, Pokrajac A, Zac-Varghese S, Bain SC, Dasgupta I, Banerjee D, Winocour P, Sharif A. Association of British Clinical Diabetologists and Renal Association guidelines on the detection and management of diabetes post solid organ transplantation. Diabet Med. 2021 Jun;38(6):e14523. Epub 2021 Feb 11.
PMID: 33434362. https://doi.org/10.1111/dme.14523
Summary: This review assessed diabetes treatments and the impact of tight glycemic control in patients with diabetic kidney disease. As kidney function declines, impaired drug clearance and altered insulin signaling increase the risk of both hyper- and hypoglycemia, requiring frequent therapy adjustments. With limited specific guidelines, individualized treatment and close monitoring are essential. Among sulfonylureas, glipizide is preferred for CKD patients due to its safer renal profile.
Citation: Betônico CC, Titan SM, Correa-Giannella ML, Nery M, Queiroz M. Management of diabetes mellitus in individuals with chronic kidney disease: therapeutic perspectives and glycemic control. Clinics (Sao Paulo). 2016 Jan;71(1):47-53.
PMID: 26872083; PMCID: PMC4732385. https://doi.org/10.6061/clinics/2016(01)08
Summary: This review highlighted the importance of individualized diabetes management in patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD). Diabetes is the leading cause of kidney failure, and CKD increases cardiovascular risk. As CKD progresses, glycemic targets and medication choices must be carefully adjusted. Although some drugs, like insulin and sulfonylureas, raise the risk of hypoglycemia, in CKD, glipizide and gliclazide are preferable. Glipizide and gliclazide do not have active metabolites that are cleared by the kidney, so dose adjustments are not needed.
Citation: Hahr, A. J., & Molitch, M. E. (2022). Management of diabetes mellitus in patients with CKD: core curriculum 2022. American Journal of Kidney Diseases, 79(5), 728-736.

Summary: The article suggested that in elderly individuals, malnourished or severely ill patients, and those with compromised liver, adrenal, or kidney function, glipizide should be started at a reduced dose, with higher doses generally avoided to minimize the risk of hypoglycemia. Additionally, patients taking beta-blockers may have a diminished ability to detect the symptoms of low blood sugar. While glipizide can be used alongside insulin, it is usually necessary to use the lower end of the dosing range to reduce the likelihood of hypoglycemic episodes.
Citation: Correa R, Quintanilla Rodriguez BS, Nappe TM. Glipizide. [Updated 2023 Jul 3]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan-
Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK459177/
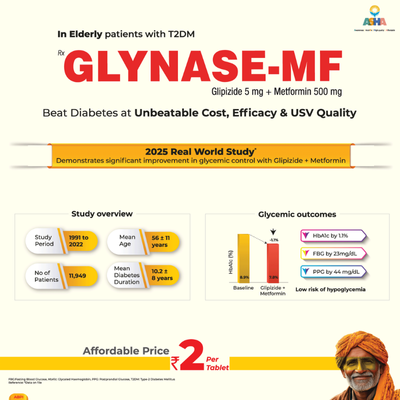
Summary: The article concluded that glipizide, which lacks active metabolites and carries the lowest risk of hypoglycemia in patients with reduced kidney function, is the preferred sulfonylurea for use in older adults. For elderly patients already on metformin but not meeting their A1C targets, adding a second medication should be considered if there are no contraindications. Suitable options include a GLP-1 receptor agonist, an SGLT-2 inhibitor, a DPP-4 inhibitor, or a short-acting sulfonylurea such as glipizide.
Citation: Keber B, Fiebert J. Diabetes in the elderly: Matching meds to needs. J Fam Pract. 2018 Jul;67(7):408;410;412;415.
PMID: 29989611. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29989611/

USV Private Limited, Arvind Vithal Gandhi Chowk, B.S.D Marg, Govandi, Mumbai - 400 088