


Clostridium Butyricum
(4 million)
Streptococcus Faecalis
(60 million)
Lactobacillus Sporogenes
(100 Million)
Genetically Modified
Bacillus Mesentericus (GMBM)
(2 million)
An Indian Diabetologist, presented his valuable opinion on IPROCON the first-ever Indian probiotic consensus at European Association...
One of the renowned Diabetologists, presented his valuable opinion on IPROCON the first-ever Indian probiotic consensus at the European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD) conference, 2023...
Co-prescribing pre-and probiotics mitigates the potential side effects of long-term PPI use, survey on 1000 plus doctors concludes...
Published in the latest December issue of JAPI, the survey included 1007 health care professionals (HCPs) from across India. Based on consensus results...
Co-prescription of probiotics with proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) decreases the potential side effects associated with...
 /
/

1 Million Spores: Genetically Modified Bacillus Mesentericus
2 Million Spores: Clostridium Butyricum
30 Million Spores: Streptococcus Faecalis
50 Million Spores: Lactobacillus Sporogenes
Dosage: Co Rx with PPI.
One capsule three times a day.

2 Million Spores: Genetically Modified Bacillus Mesentericus
4 Million Spores: Clostridium Butyricum
60 Million Spores: Streptococcus Faecalis
100 Million Spores: Lactobacillus Sporogenes
Dosage: Co Rx. With PPI & antibiotic.
One capsule three times a day.



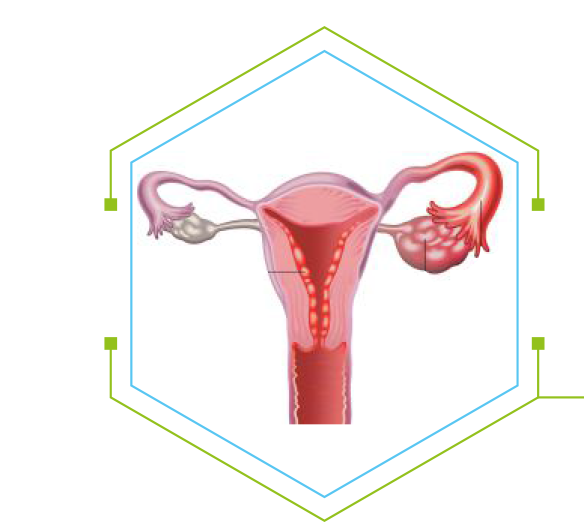
Studies show Probiotic Usage leads to 81 % reduction in Vaginal Infections*. Probiotics are recommended in various conditions including Bacterial Vaginosis, Vaginal Candidiasis, Pruritis, Vaginal Odor, White discharge.
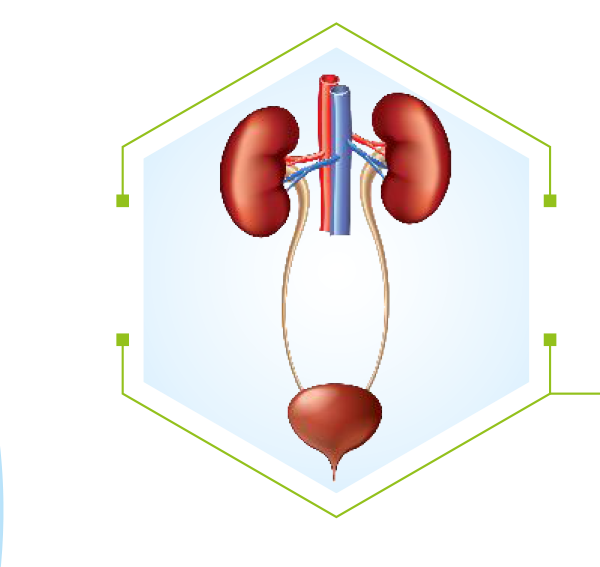
Probiotics are recommended as a first step in regulating the urinary microbiota and hence help in dealing with Urinary Tract Infections. Probiotics are also recommended as a tool for prevention of Recurrent UTIs.
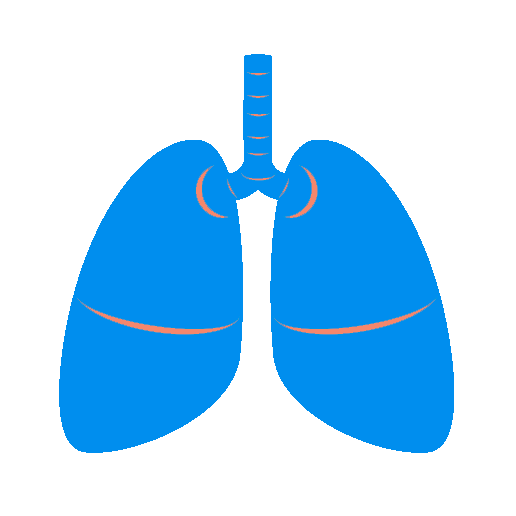
Probtiocs are effective in modulation of gut microbial patterns and hence have an effect in containing respiratory tract infections ( URTI) by modulating the gut-lung microtbiota axis.
*WGO Global Guideline Probiotics and prebiotics. 1) Guinane CM, et. al. Role of the gut microbiota in health and chronic gastrointestinal disease: understanding a hidden metabolic organ. Therap Adv Gastroenterol. 2013 Jul;6(4):295-308. doi: 10.1177/1756283X13482996. PMID: 23814609; PMCID: PMC3667473. 2) Săsăran MO, Mărginean CO, Adumitrăchioaiei H, Meliț LE. Pathogen-Specific Benefits of Probiotic and Synbiotic Use in Childhood Acute Gastroenteritis: An Updated Review of the Literature. Nutrients. 2023 Jan 27;15(3):643. doi: 10.3390/nu15030643. PMID: 36771350; PMCID: PMC9919199. 3) Li W, Xu B, Wang L, Sun Q, Deng W, Wei F, Ma H, Fu C, Wang G, Li S. Effects of Clostridium butyricum on Growth Performance, Gut Microbiota and Intestinal Barrier Function of Broilers. Front Microbiol. 2021 Dec 8;12:777456. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.777456. PMID: 34956140; PMCID: PMC8692979. 4) Inatomi T, Otomaru K. Effects of heat-killed Enterococcus faecalis T-110 supplementation on gut immunity, gut flora, and intestinal infection in naturally aged hamsters. PLoS One. 2020 Dec 30;15(12):e0240773. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0240773. PMID: 33378402; PMCID: PMC7773277. 5) A AJ, Suresh A. Oral microbial shift induced by probiotic Bacillus coagualans along with its clinical perspectives. J Oral Biol Craniofac Res. 2023 May-Jun;13(3):398-402. doi: 10.1016/j.jobcr.2023.03.013. Epub 2023 Apr 17. PMID: 37124834; PMCID: PMC10131115. 6) Antibiotics 2021,10,408
