Vertigo is a symptom of vestibular dysfunction and described as a sensation of motion, most commonly rotational motion
Most common causes of Vertigo are:
-
 Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo (BPPV)
Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo (BPPV) -
 Meniere's disease
Meniere's disease
Dosage and benefits of 

In Vertigo

For better vestibular recovery1
In the frequency of Vertigo attacks2 & its intensity3
Facilitates the body’s natural compensation4
Only non sedating anti vertigo drug4
In BPPV, to manage Post Maneuver Dizziness

Decrease in the symptoms5

3x improvement in residual dizziness6

Reduced recurrence with sustained symptom relief5


In Meniere’s disease
1st line drug in Meniere’s disease8
Significantly improves clinical outcomes9
OTHER DOSAGE
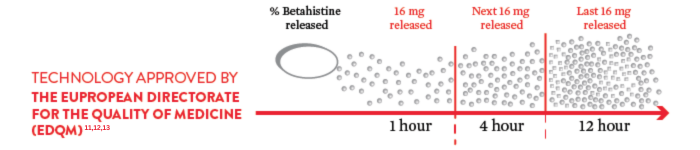
UNIQUE HYDROPHILIC MATRIX TECHNOLOGY10,11,12

Benefits of 

Reduces pill burden13

Suitable for elderly13

Well tolerated13
EVIDENCE SUGGEST 48 MG/DAY IS THE MOST EFFICACIOUS DOSE2



Distegrates in the mouth - doesn't need water*

Orange mint flavour*
Videos
Betaserc - Professor Michel Lacour_Compensation
Vertin vestibular compensation
Betaserc - Professor Michel Lacour_Treatment duration
Journal Links
References
* Data on file.
1) Parfenov VA, Golyk VA, Matsnev EI, Morozova SV, Melnikov OA, Antonenko LM, Sigaleva EE, Situkho MI, Asaulenko OI, Popovych VI, Zamergrad MV. Effectiveness of betahistine (48 mg/day) in patients with vestibular vertigo during routine practice: The VIRTUOSO study. PLoS One. 2017 Mar 30;12(3):e0174114. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0174114. PMID: 28358888; PMCID: PMC5373561
2) Albera R. Betahistine in the treatment of Meniere’s disease and other balance disturbances. Review of its e cacy and safety. Otorinolaringol. 2005;55:115-21.
3) Mira E, et al. Betahistine dihydrochloride in the treatment of peripheral vestibular vertigo. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2003;260(2):73-7
4) Lacour M. Betahistine treatment in managing vertigo and improving vestibular compensation: clarification. J Vestib Res. 2013;23(3):139-51
5) Guneri EA, et al. The effects of betahistine in addition to epley maneuver in posterior canal benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2012;146(1):104-8
6) Banerjee TK, et al. Repositioning maneuvers in benign paroxysmal positional vertigo: how do we improve outcomes? Int J Res Med Sci. 2021;9(12):3764-3768
7) Kaur J. et al. Management of Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo: A Comparative Study between Epleys Manouvre and Betahistine. International Tinnitus Journal. 2017;21(1):30-34
8) International consensus (ICON) on treatment of Ménière's disease. J Nevox et al, Eur Ann Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Dis 2018 Feb;135(1S):S29-S32.
9) Strupp M. et al. Acta Otolaryngol 2008; 128:520-48.
10) www.pharmatech.com, Modulation of drug release from hydrophilic matrices as accessed on April 2012.
11) Levina et al. the influence of excipients in Drug release from Hydroxypropyl methylcellulose matrices. J Pharm Sci 2004; 93: 2746 – 54
12) Maderuelo et al. Critical factors in the release of drugs from sustained release hydrophilic matrices. J control release 2011 ; 154 : 2-19.
13) Adrion C, Fischer CS, Wagner J, Gürkov R, Mansmann U, Strupp M; BEMED Study Group. Efficacy and safety of betahistine treatment in patients with Meniere's disease: primary results of a long term, multicentre, double blind, randomised, placebo controlled, dose defining trial (BEMED trial). BMJ. 2016 Jan 21;352:h6816. doi: 10.1136/bmj.h6816. PMID: 26797774; PMCID: PMC4721211
1) Parfenov VA, Golyk VA, Matsnev EI, Morozova SV, Melnikov OA, Antonenko LM, Sigaleva EE, Situkho MI, Asaulenko OI, Popovych VI, Zamergrad MV. Effectiveness of betahistine (48 mg/day) in patients with vestibular vertigo during routine practice: The VIRTUOSO study. PLoS One. 2017 Mar 30;12(3):e0174114. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0174114. PMID: 28358888; PMCID: PMC5373561
2) Albera R. Betahistine in the treatment of Meniere’s disease and other balance disturbances. Review of its e cacy and safety. Otorinolaringol. 2005;55:115-21.
3) Mira E, et al. Betahistine dihydrochloride in the treatment of peripheral vestibular vertigo. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2003;260(2):73-7
4) Lacour M. Betahistine treatment in managing vertigo and improving vestibular compensation: clarification. J Vestib Res. 2013;23(3):139-51
5) Guneri EA, et al. The effects of betahistine in addition to epley maneuver in posterior canal benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2012;146(1):104-8
6) Banerjee TK, et al. Repositioning maneuvers in benign paroxysmal positional vertigo: how do we improve outcomes? Int J Res Med Sci. 2021;9(12):3764-3768
7) Kaur J. et al. Management of Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo: A Comparative Study between Epleys Manouvre and Betahistine. International Tinnitus Journal. 2017;21(1):30-34
8) International consensus (ICON) on treatment of Ménière's disease. J Nevox et al, Eur Ann Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Dis 2018 Feb;135(1S):S29-S32.
9) Strupp M. et al. Acta Otolaryngol 2008; 128:520-48.
10) www.pharmatech.com, Modulation of drug release from hydrophilic matrices as accessed on April 2012.
11) Levina et al. the influence of excipients in Drug release from Hydroxypropyl methylcellulose matrices. J Pharm Sci 2004; 93: 2746 – 54
12) Maderuelo et al. Critical factors in the release of drugs from sustained release hydrophilic matrices. J control release 2011 ; 154 : 2-19.
13) Adrion C, Fischer CS, Wagner J, Gürkov R, Mansmann U, Strupp M; BEMED Study Group. Efficacy and safety of betahistine treatment in patients with Meniere's disease: primary results of a long term, multicentre, double blind, randomised, placebo controlled, dose defining trial (BEMED trial). BMJ. 2016 Jan 21;352:h6816. doi: 10.1136/bmj.h6816. PMID: 26797774; PMCID: PMC4721211
This information here in is meant for the awareness and for enhancement of medical knowledge. Although due care has been taken to ensure the accuracy and completeness of the information, Abbott India Limited shall not be liable in any manner whatsoever for any action on the basis of this patient information material and does not hold itself liable for any consequences, legal or otherwise, arising out of information in this material.
Please refer to full prescribing information for complete details of the product.
Images used in the information material are for representation purposes only
Please refer to full prescribing information for complete details of the product.
Images used in the information material are for representation purposes only