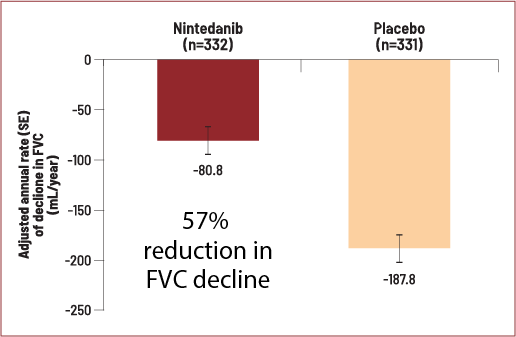
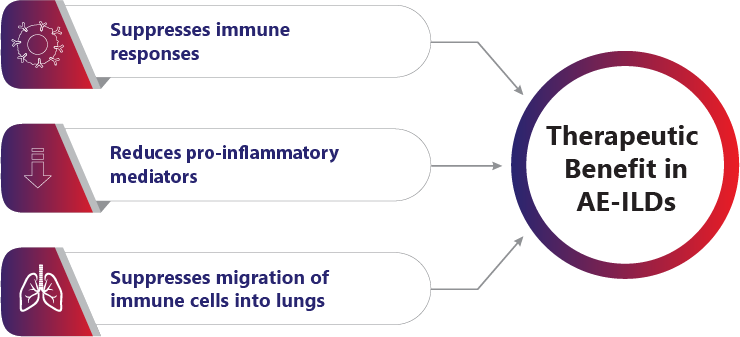
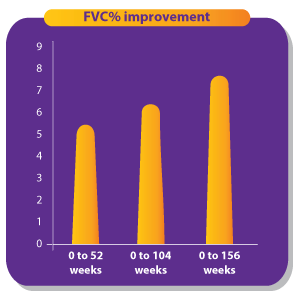
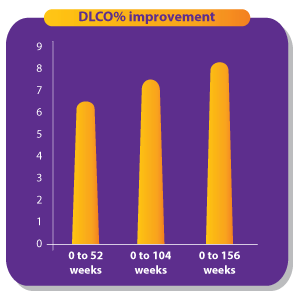
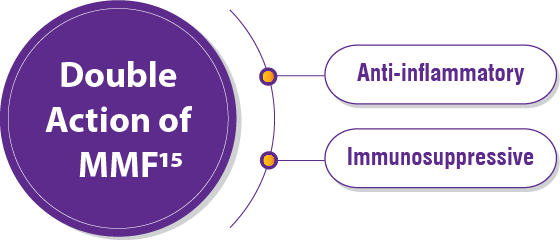
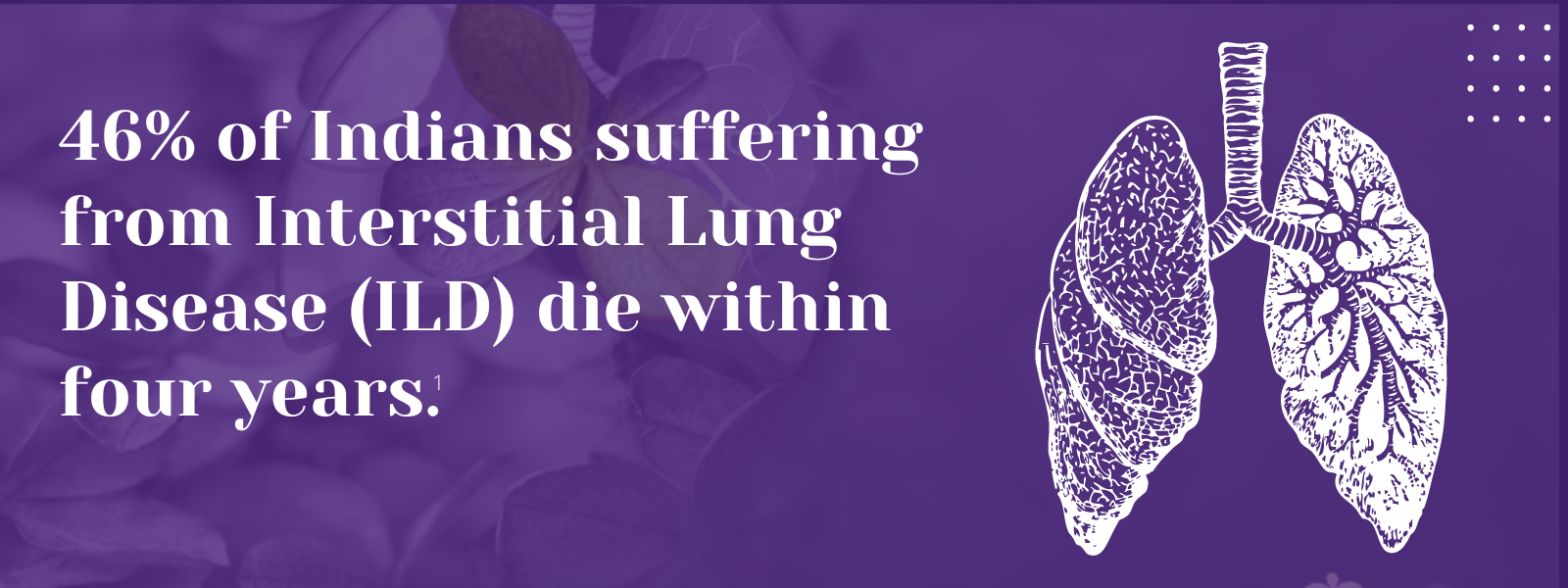
1. Singh S, Bairwa M, Collins BF, et.al, Survival predictors of interstitial lung disease in India: Follow-up of Interstitial Lung Disease India registry. Lung India: Jan–Feb 2021 doi: 10.4103/lungindia.lungindia_414_20 2. Ma X, Zhu L, Kurche JS, et al Global and regional burden of interstitial lung disease and pulmonary sarcoidosis from 1990 to 2019: results from the Global Burden of Disease study 2019Thorax 2022;77:596-605. 3. https://www.lung.org/lung-health-diseases/lung-disease-lookup/interstitial-lung-disease#:~:text=Interstitial%20lung%20disease%20(ILD)%20is,and%20gets%20worse%20over%20time. 4. Singh S, Collins BF, Sharma BS Interstitial Lung Disease in India. Results of a Prospective Registry. American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine. 2017. https://doi.org/10.1164/rccm.201607-1484OC 5. Oldham, J. M., & Noth, I. (2014). Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: early detection and referral. Respiratory medicine, 108(6), 819–829. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rmed.2014.03.008 6. King, Talmadge E Jr et al. “A phase 3 trial of pirfenidone in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis.” The New England journal of medicine vol. 370,22 (2014): 2083-92. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1402582 7. Richeldi L, Cottin V, du Bois RM, et al. Nintedanib in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: Combined evidence from the TOMORROW and INPULSIS(®) trials. Respir Med. 2016;113:74-79. doi:10.1016/j.rmed.2016.02.001 8. Wollin, Lutz et al. “Antifibrotic and anti-inflammatory activity of the tyrosine kinase inhibitor nintedanib in experimental models of lung fibrosis.” The Journal of pharmacology and experimental therapeutics vol. 349,2 (2014): 209-20. doi:10.1124/jpet.113.208223 9. Vasarmidi, E., Tsitoura, E., Spandidos, D. A., Tzanakis, N., & Antoniou, K. M. (2020). Pulmonary fibrosis in the aftermath of the COVID-19 era (Review). Experimental and therapeutic medicine, 20(3), 2557–2560. https://doi.org/10.3892/etm.2020.8980 10. Flaherty KR, Wells AU, Cottin V, Devaraj A, Walsh SLF, Inoue Y, et al., Nintedanib in Progressive Fibrosing Interstitial Lung Diseases, N Engl J Med. 2019 Oct 31;381(18):1718-1727 11. . G, Collard HR, Egan JJ, et al. An official ATS/ERS/JRS/ALAT statement: idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: evidence-based guidelines for diagnosis and management. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2011; 183: 788–824 12. Juarez MM, Chan AL, Norris AG, Morrissey BM, Albertson TE. Acute exacerbation of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis-a review of current and novel pharmacotherapies. J Thorac Dis. 2015 Mar;7(3):499-519 13. Cassone, G., Sebastiani, M., Vacchi, C., Erre, G., Salvarani, C. and Manfredi, A., 2021. Ecacy and safety of mycophenolate mofetil in the treatment of rheumatic disease-related interstitial lung disease: a narrative review.Drugs in Context, 10, pp.1-17 14. Fischer, A., Brown, K., Du Bois, R., Frankel, S., Cosgrove, G., Fernandez-Perez, E., Huie, T., Krishnamoorthy, M., Meehan, R., Olson, A., Solomon, J. and Swigris, J., 2013. 15. .Brown, K., Rajan, S., Shenoy, P., Mehta, M., Lopez, M., Hegde, R. and Gogtay, J., 2021. The emerging role of mycophenolate mofetil in interstitial lung diseases.Expert Review of Respiratory Medicine, 15(12), pp.1539-1549. 16. .Adegunsoye, A., Oldham, J., Fernández Pérez, E., et al., 2017. Outcomes of immunosuppressive therapy in chronic hypersensitivity pneumonitis.ERJ Open Research, 3(3), pp.00016-2017 17. Tashkin, D., Roth, M., Clements, P., Furst, D., et al., 2016. Mycophenolate mofetil versus oral cyclophosphamide in scleroderma-related interstitial lung disease (SLS II): a randomised controlled, double-blind, parallel group trial.The Lancet Respiratory Medicine, 4(9), pp.708-719. 18. Brown, K., Rajan, S., Shenoy, P., Mehta, M., Lopez, M., Hegde, R. and Gogtay, J., 2021. The emerging role of mycophenolate mofetil in interstitial lung diseases.Expert Review of Respiratory Medicine, 15(12), pp.1539-1549






 Introducing A Comprehensive ILD portfolio
Introducing A Comprehensive ILD portfolio