Overview of BP Right Karo
Ensuring precise blood pressure (BP) measurement is key to diagnosing hypertension accurately and implementing effective management protocols.
In the world full of modern health technology, the array of devices for measuring blood pressure seems endless, from sleek smartwatches and fitness trackers to wearable blood pressure monitors. Yet, amidst this abundance, the reliability of such devices can sometimes be uncertain. That's where "BP Right Karo" comes in. Designed to empower individuals with accurate blood pressure management, "BP Right Karo" not only raises awareness about the importance of monitoring blood pressure but also provides expert guidance from doctors.
Through BP Right Karo, leaders in hypertension treatment in India, JB Pharma is making efforts to assist doctors and educate patients on measuring BP at home. This initiative aims to empower individuals to embark on a journey towards better health, arming them with the knowledge to manage blood pressure effectively.








Alcohol: Reducing or eliminating alcohol consumption can significantly lower your blood pressure and improve your overall health. If you choose to drink alcohol, do so in moderation. This means limiting your intake to no more than one drink per day for women and no more than two drinks per day for men. If you find it di cult to moderate your alcohol consumption, seek support from friends, family, or a healthcare professional.
Smoking: Smoking cigarettes not only damages your lungs but also increases your blood pressure and damages your blood vessels, making you more susceptible to hypertension and its complications. Quitting smoking is one of the best things you can do for your cardiovascular health. There are many resources available to help you quit, including nicotine replacement therapy, counselling, and support groups. Talk to your doctor about creating a plan to quit smoking and improve your blood pressure. Quitting smoking may help in BP reduction by 10-20mmHg


Dr Dilip Kumar
Senior Consultant Interventional Cardiologist & Electrophysiologist, Media Insitute of Cardiac Sciences
Dr. H.K Chopra
Senior Consultant Cardiologist Moolchand Medicity, New Delhi
Dr Rajiv Karnik
Director- Heart Failure Clinic & Interventional Cardiologist, Fortis Hospital, Mumbai.
BP कैसे Right Karo?
Dr. Ajay Kumar Pandey, Cardiologist, Varanasi
Dr. Pradeep Kumar, Senior Nephrologist, Meerut

-
 Accurate measurement of BP is essential for both estimating cardiovascular disease risk and management of high BP.
Accurate measurement of BP is essential for both estimating cardiovascular disease risk and management of high BP. -
 The diagnosis and management of hypertension depend on the accurate measurement of BP.
The diagnosis and management of hypertension depend on the accurate measurement of BP. -
 Avoiding common errors can lead to correct diagnosis, timely treatment, and improving BP control rates.
Avoiding common errors can lead to correct diagnosis, timely treatment, and improving BP control rates.
In the 30 minutes before your BP is measured
Avoid caffeinated beverages2

May increase BP by about 3-15 mm Hg in systolic and 4-13 mm Hg in diastolic
Avoid smoking3
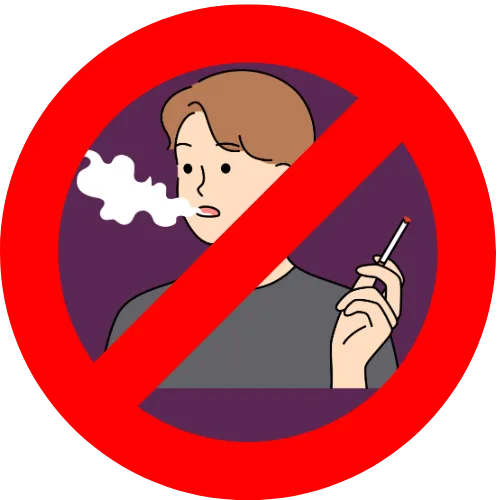

May elevate BP by 5 to 10 mm Hg temporarily
Avoid alcohol1
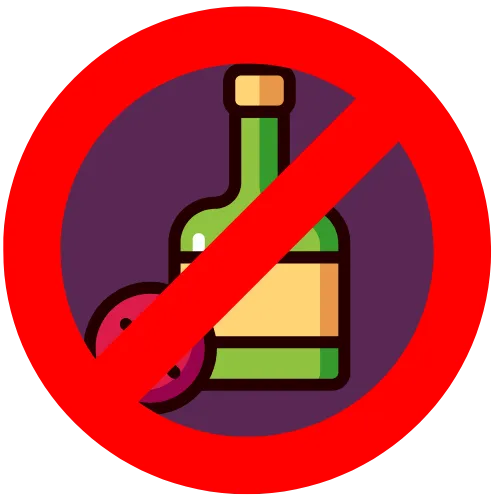

May cause acute increasing of BP by 5 to 10 mm Hg
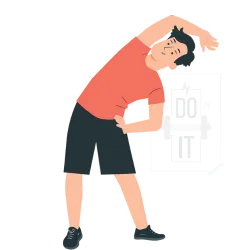
Avoid exercise1

Exercise can increase blood pressure for a short term
In the 5 minutes before your BP is measured
Empty the bladder4

As a full, one can temporarily raise BP by 10 to 15 mm Hg
Sit still5
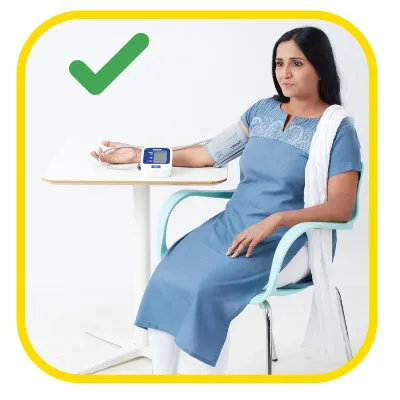
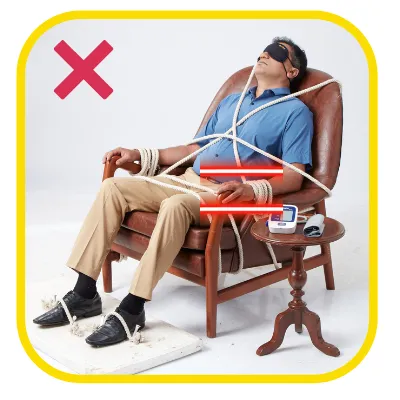
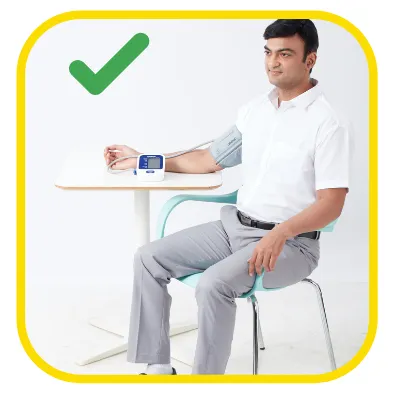
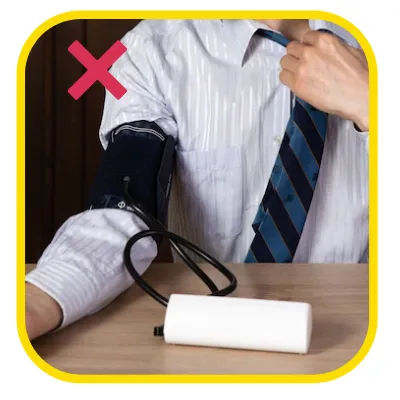
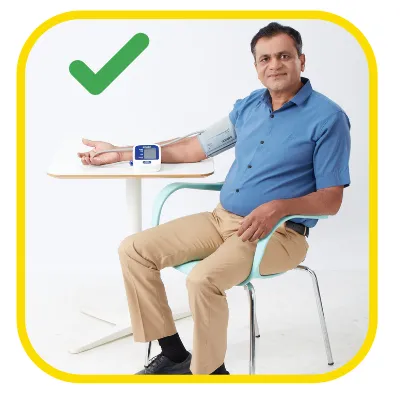
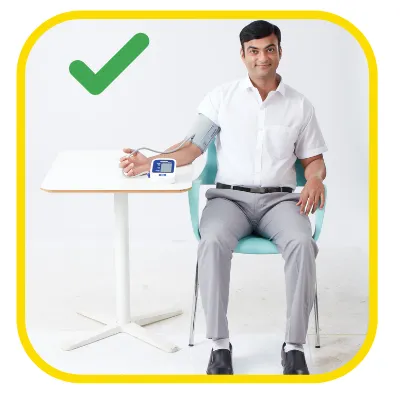










Dr. Johann Christopher Cardiologist, Hyderabad on the eve of World Hypertension Day speaks all about hypertension & how to check BP at home
Dr. Rajeev Garg Cardiologist, Hyderabad on the eve of World Hypertension Day speaks all about hypertension & how to check BP at home
Dr. E. Saravanan Cardiologist, Coimbatore on the eve of World Hypertension Day speaks all about hypertension & how to check BP at home
Prof. Dr. Nagaraj Desai Cardiologist, Bengaluru on the eve of World Hypertension Day speaks all about hypertension & how to check BP at home
Dr. Mahesh K. Shah Cardiologist, Mumbai on the eve of World Hypertension Day speaks all about hypertension & how to check BP at home
Dr. Praneeth Polamuri Cardiologist, Hyderabad on the eve of World Hypertension Day speaks all about hypertension & how to check BP at home
Dr. Anoop Agrawal Cardiologist, Hyderabad on the eve of World Hypertension Day speaks all about hypertension & how to check BP at home
Dr. Asha Mahilmaran Cardiologist, Chennai on the eve of World Hypertension Day speaks all about hypertension & how to check BP at home
Dr. Zakia Khan Cardiologist, Mumbai on the eve of World Hypertension Day speaks all about hypertension & how to check BP at home
Dr. Sanjeev Gulati Nephrologist, New Delhi on the eve of World Hypertension Day speaks all about hypertension & how to check BP at home
Dr. Manish Ganwani Nagpur explains what is blood pressure and how to check BP at home
Dr. Parag Hemant Rahatekar Nagpur explains what is blood pressure and how to check BP at home
Dr. A. Vamsidhar Kadapa explains what is blood pressure and how to check BP at home
Dr. Pln Kapardhi Hyderabad explains what is blood pressure and how to check BP at home
Dr. Satyajit Govindrao Mehetre Hyderabad explains what is blood pressure and how to check BP at home
Dr. A. George Koshy Trivandrum explains what is blood pressure and how to check BP at home
Dr. Mohammed Hidayathulla Hyderabad explains what is blood pressure and how to check BP at home
Dr. Nirmal Kumar Hyderabad explains what is blood pressure and how to check BP at home
Dr. Himanshu Verma New Delhi explains what is blood pressure and how to check BP at home
Dr. V S R Bhupal Vijayawada explains what is blood pressure and how to check BP at home
Dr. P. Sudarshan Vijayawada explains what is blood pressure and how to check BP at home
Dr. Hemanshu Bhatia Hyderabad explains what is blood pressure and how to check BP at home
Dr. Deepak Raju Kannur explains what is blood pressure and how to check BP at home
Dr. Nitin S. Patki Pune explains what is blood pressure and how to check BP at home