- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Macintosh laryngoscope effective tool to align I-gel to secure airway in patients under GA
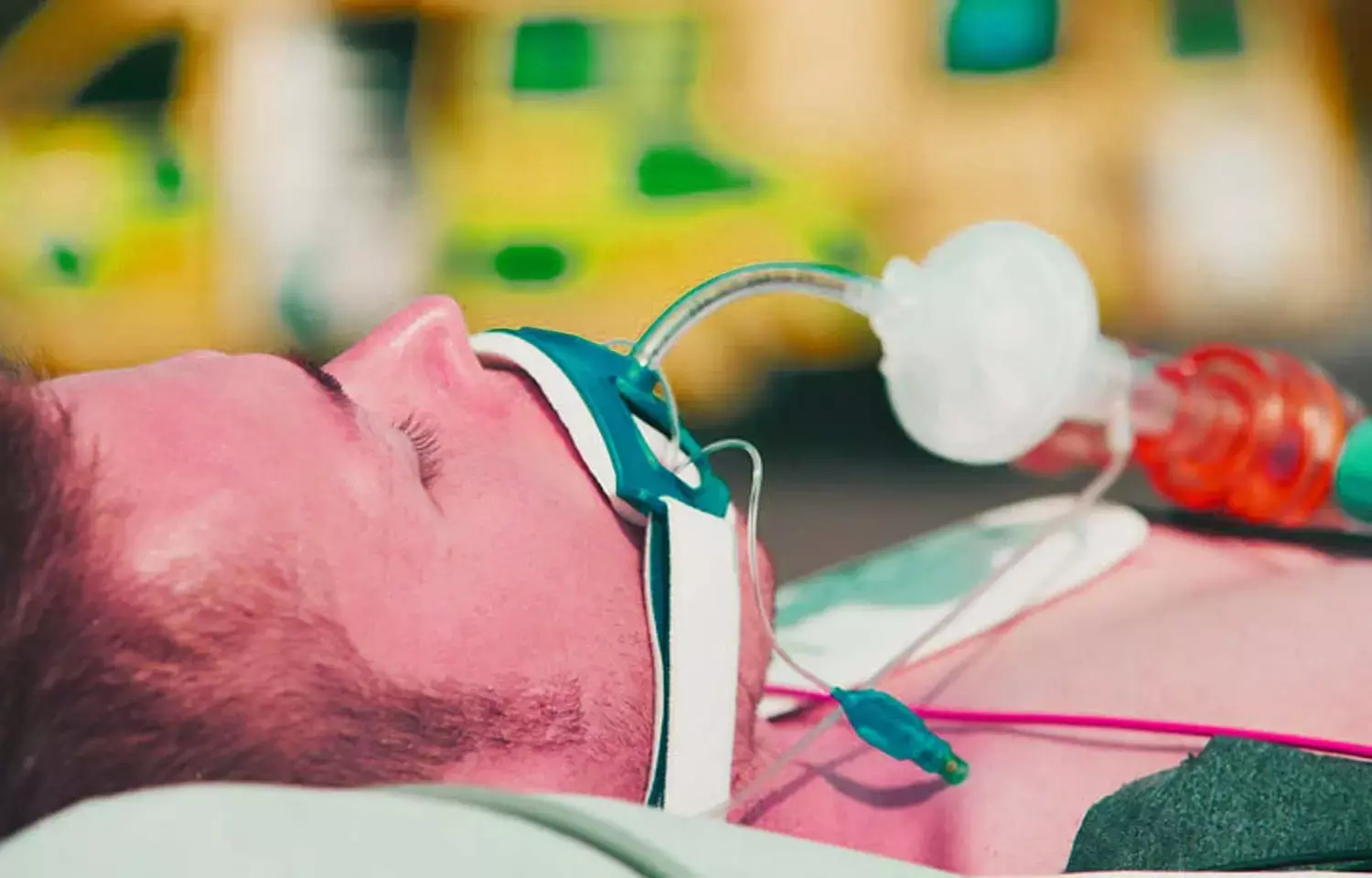
Researchers have found in a new study that compared to the conventionally used blind insertion technique, the readily available Macintosh laryngoscope could be used as a clinically useful and cost effective tool to ensure proper alignment and function of I-gel™ , when used to secure the airway in patients under general anaesthesia.
In the arsenal of anesthesiologists engaged in airway management, supraglottic airway (SGA) devices are a well-established device. I-gel (Intersurgical, Wokingham, Berkshire, United Kingdom) is a second-generation supraglottic airway device that has a cuffless perilaryngeal sealing mechanism. It is simple to implant with low danger of tissue stress, and its biting block and strengthened tip create a more patent airway. I-gel and other SGAs are most often inserted using the blind insertion method described by Brain. Malpositioning of the SGA may result in a number of problems, including stomach insufflation, increased risk of aspiration, inadequate tidal volume, air leak, airway blockage, blood staining of the device, tissue damage, and nerve injury.
A recently published research investigated the effectiveness of the Macintosh laryngoscope in increasing the success rate when I-gel is used to secure the airway.
Included were 156 adult patients who were scheduled to have elective surgery under general anesthesia. All subjects were randomly split into two groups; I-gel was placed using a blind method in group A and a Macintosh-guided approach in group B. The major purpose of the research was to assess the incidence of ideal placement in both groups based on the glottic view score obtained with a fiberoptic bronchoscope. Also compared were the oropharyngeal leak pressure, hemodynamic parameters, and insertion characteristics. Categorical data were shown as ratios or percentages, whereas continuous data were displayed as means standard deviations or medians (95 percent confidence interval). The relative risk ratio was used to determine the degree of relationship between insertion method and the anatomical fit of the device. The laryngoscope-guided insertion group had considerably higher fiberoptic scores than the blind insertion group (P 0.0001). The incidence of malposition was 3.85% in the laryngoscopic insertion group and 39.4% in the blind insertion group (P 0.0001), respectively. Oropharyngeal leak pressure was significantly greater in the laryngoscope-guided insertion group compared to the blind insertion group (P 0.0001): 26.89 3.37 cm H2O against 24.50 3.00 cm H2O. Other insertion features, except insertion time, were similar across the two groups.
The results of our study indicate that there is a 39.74 percent risk of suboptimal positioning of I-gel when I-gel is inserted using the standard blind insertion technique, compared to only 3.85 percent when the same is inserted under vision using a Macintosh laryngoscope, indicating a relative risk of less than 1, or an 86.98 percent reduction in the risk of suboptimal positioning.
Moreover, the laryngoscope-guided approach generates higher OPLP values, indicating a substantial improvement in the anatomic fit and airway seal of the device. The easily accessible Macintosh laryngoscope might be utilized as a therapeutically helpful and cost-effective instrument to guarantee appropriate alignment and function of I-gel when used to secure the airway in patients undergoing general anesthesia.
Reference –
Vyas, Ankit; Bihani, Pooja; Jaju, Rishabh1; Paliwal, Naveen,; Tak, Mathura L.; Choudhary, Usha Comparison of the efficacy of Macintosh laryngoscope-guided insertion of I-gel™ with the conventional blind insertion technique – A randomised study, Indian Journal of Anaesthesia: June 2022 - Volume 66 - Issue 6 - p 449-455
doi: 10.4103/ija.ija_192_22
MBBS, MD (Anaesthesiology), FNB (Cardiac Anaesthesiology)
Dr Monish Raut is a practicing Cardiac Anesthesiologist. He completed his MBBS at Government Medical College, Nagpur, and pursued his MD in Anesthesiology at BJ Medical College, Pune. Further specializing in Cardiac Anesthesiology, Dr Raut earned his FNB in Cardiac Anesthesiology from Sir Ganga Ram Hospital, Delhi.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


