- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
PENG block provides better analgesia than FICB in hip fractures analgesia
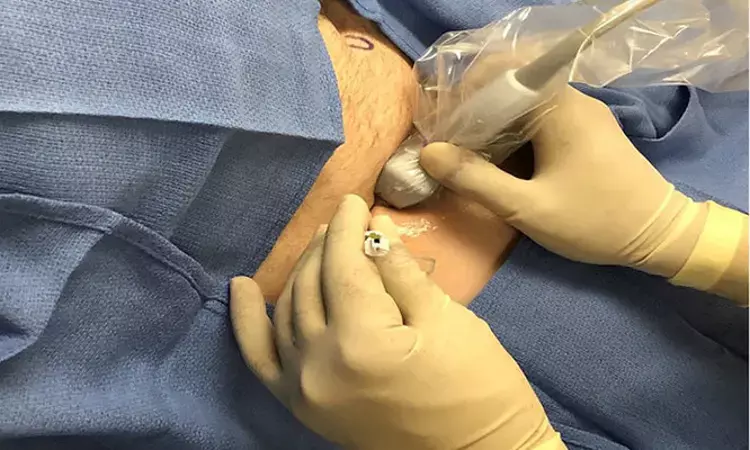
PENG block provides better analgesia than FICB in hip fractures analgesia, finds an OTSR study. Fascia iliaca compartment block (FICB) is a common regional analgesic strategy in hip fracture surgery but, recently it has been suggested that FICB may not provide enough analgesia. Pericapsular nerve group block (PENG) is a novel method for hip analgesia which its efficacy is not well established yet.
F.Mosaffa, M. Taheri, A.Manafi Rasi et al. conducted a study to document the effect of the PENG block in the control of the hip fracture pain as well as to compare the effectiveness of the PENG compared with FICB.
This randomized controlled clinical trial was conducted in a hospital in Iran. Hip fracture patients were randomly divided into two groups; Group A (n = 22) received FICB and Group B (n = 30) received PENG block.
Results:
• There was no significant difference in age (p = 0.75), sex (p = 0.96), weight (p = 0.053), type of fractures (p = 0.94) and surgical methods (p = 0.94) between the two groups.
• There was no significant difference between VAS score before blocks procedure between two groups (p = 0.37).
• After 15 minutes of blocks and after 12 hours of post-surgery, VAS score significantly reduced in the PENG block group compared with the FICB group (p = 0.031; p = 0.021, respectively).
• The first time of the analgesic consumption after surgery was significantly longer in the PENG block compared with the FCIB (p = 0.007).
• Compared with the FICB group, the total dose of morphine consumption during 24 hours significantly reduced in the PENG block (p = 0.008).
The authors concluded that - PENG block is a good method in hip fractures analgesia and provides better analgesia than FICB. However, further studies with larger sample sizes are required to validate the efficacy and superiority of the PENG blocks over conventional techniques.
Further reading:
Comparison of pericapsular nerve group (PENG) block with fascia iliaca compartment block (FICB) for pain control in hip fractures: A double-blind prospective randomized controlled clinical trial
Faramarz Mosaffa, Mehrdad Taheri, Alireza Manafi Rasi, Hamidreza Samadpour, Elham Memarya, Alireza Mirkheshti.
Orthopaedics & Traumatology: Surgery & Research 108 (2022) 103135
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.otsr.2021.103135
MBBS, Dip. Ortho, DNB ortho, MNAMS
Dr Supreeth D R (MBBS, Dip. Ortho, DNB ortho, MNAMS) is a practicing orthopedician with interest in medical research and publishing articles. He completed MBBS from mysore medical college, dip ortho from Trivandrum medical college and sec. DNB from Manipal Hospital, Bengaluru. He has expirence of 7years in the field of orthopedics. He has presented scientific papers & posters in various state, national and international conferences. His interest in writing articles lead the way to join medical dialogues. He can be contacted at editorial@medicaldialogues.in.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


