- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Vitamin C reduces cortisol suppressant effect of etomidate in trauma patients undergoing RSI
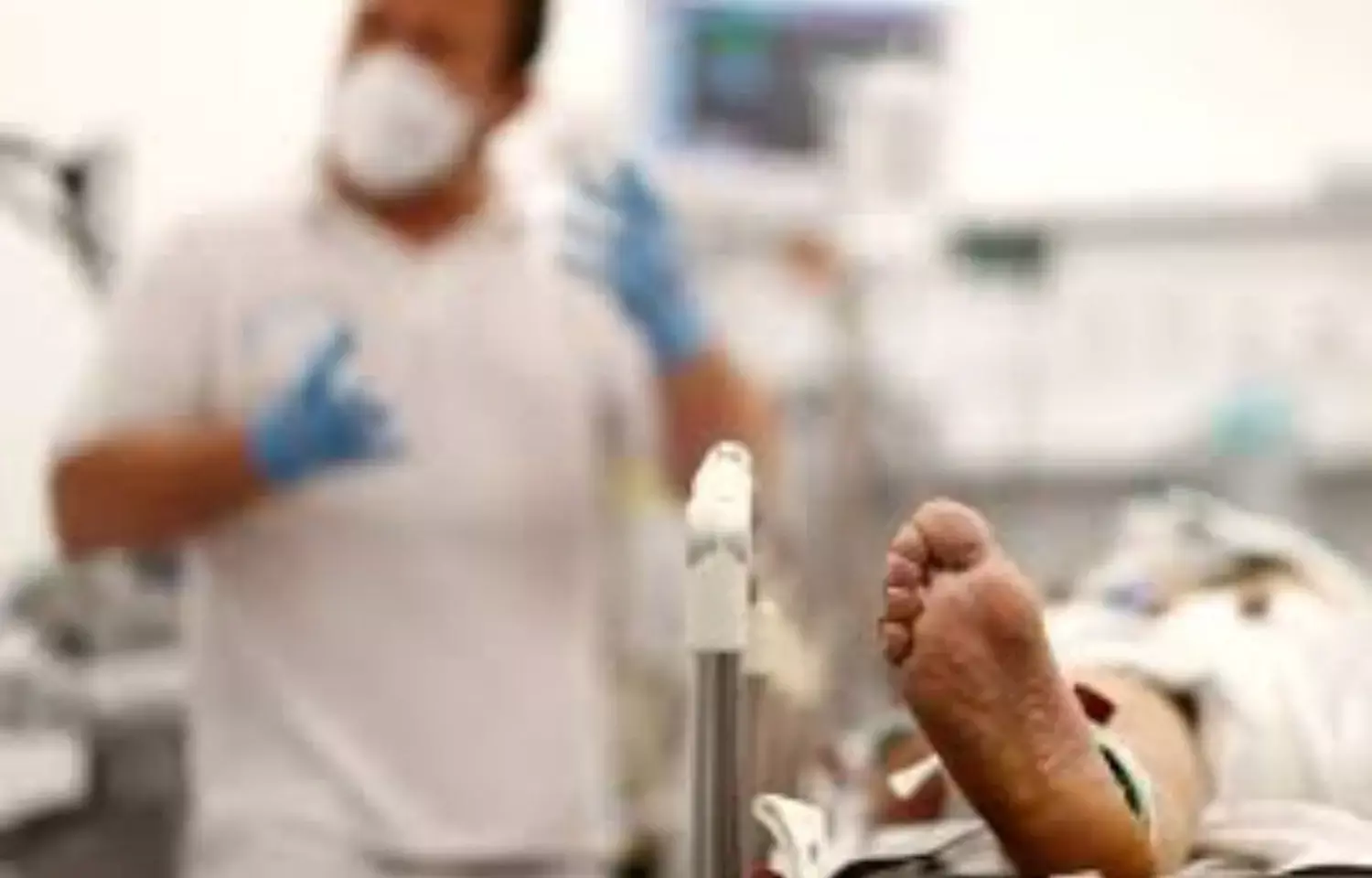
When trauma victims experience Rapid Sequence Intubation (RSI), etomidate can lower their cortisol levels. Vitamin C supplementation reduces cortisol suppressant effect of etomidate in trauma patients undergoing RSI, according to a new study.
The study has been published in BMC Anesthesiology.
The usual procedure for airway care and intubation in the emergency room is rapid sequence induction/intubation (ED). By utilizing an anesthetic medication and a neuro-muscular blocking agent, this approach can lower the chance of aspiration and intubation failure. Etomidate is a common induction agent for RSI in EDs and is an imidazole derivative. Due to this medication's rapid start of action, safe hemodynamic profile, low histamine generation, and limited impact on respiratory depression, it was chosen as a therapy for RSI. There are some reservations concerning its suppressive effects on the adreno-cortical axis, despite the fact that it has a safe hemodynamic profile. Antioxidants like vitamin C can offer protection in this situation. Therefore, to find out how vitamin C affects cortisol levels in trauma patients who undergo RSI with etomidate, Jafar Rahimi Panahi and crew undertook this clinical experiment.
The researchers looked at adult trauma patients who need RSI with etomidate in a controlled clinical study. Three hours after the RSI with etomidate in one group, cortisol levels were assessed. In the second group, we gave one gram of vitamin C before giving etomidate, and three hours later we assessed the cortisol level.
The key findings of this study were:
51 patients have been examined.
After RSI with etomidate, the blood cortisol level was considerably reduced in both groups.
After RSI, the cortisol level in the vitamin C group was significantly greater than in the control group.
Several studies, including this one, have shown that administering vitamin C before administering etomidate during the induction stage of intubation can prevent adrenal inhibition and lessen the amount of blood cortisol level suppression brought on by etomidate. Although some studies have suggested midazolam as an option to etomidate, this drug is still the first choice for patients with unstable injuries because of the low risk of side effects from etomidate.
Reference:
Panahi, J. R., Paknezhad, S. P., vahedi, A., Shasavainia, K., Laleh, M. R., & Soleimanpour, H. (2023). Effect of vitamin C on adrenal suppression following etomidate for rapid sequence induction in trauma patients: a randomized clinical trial. In BMC Anesthesiology (Vol. 23, Issue 1). Springer Science and Business Media LLC. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12871-023-02065-5
Neuroscience Masters graduate
Jacinthlyn Sylvia, a Neuroscience Master's graduate from Chennai has worked extensively in deciphering the neurobiology of cognition and motor control in aging. She also has spread-out exposure to Neurosurgery from her Bachelor’s. She is currently involved in active Neuro-Oncology research. She is an upcoming neuroscientist with a fiery passion for writing. Her news cover at Medical Dialogues feature recent discoveries and updates from the healthcare and biomedical research fields. She can be reached at editorial@medicaldialogues.in
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


