- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Age and Blood Pressure Drive Arterial Stiffness Progression in Japanese Adults: New Risk Score Developed
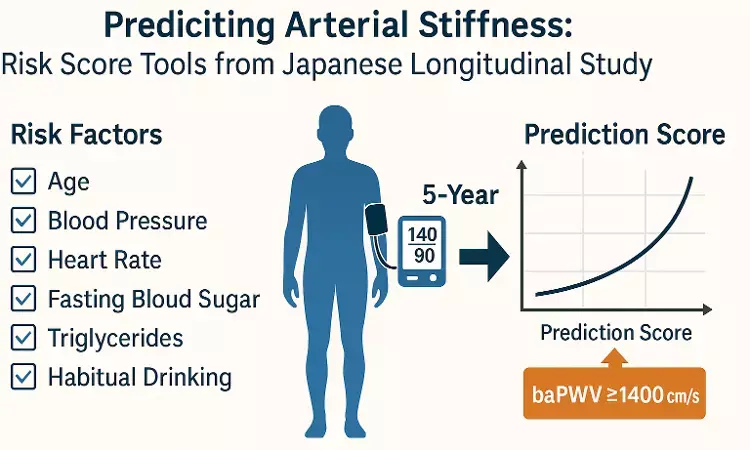
Age, blood pressure, and metabolic risk factors can predict arterial stiffness progression over five years, a recent study has reported.
Published in Hypertension Research, a peer-reviewed journal under the Nature portfolio, this large-scale longitudinal analysis was conducted in Japan and involved 10,284 participants aged 30–69 years. The study aimed to identify predictors of increased brachial-ankle pulse wave velocity (baPWV ≥1400 cm/s), a validated surrogate for arterial stiffness.
Study Design and Cohort Details
This retrospective cohort study utilized data from health examinations conducted at Kagoshima Kouseiren Hospital between 2005 and 2019. From the original cohort, 6104 individuals (3394 men, 2710 women) with baseline baPWV <1400 cm/s and no history of cardiovascular medication were followed over five years. The primary outcome was progression to baPWV ≥1400 cm/s—a threshold indicating elevated arterial stiffness.
Key Findings
- Incidence: 32.6% of men and 24.8% of women developed baPWV ≥1400 cm/s over five years.
- Men: Significant predictors included age, systolic and diastolic blood pressure (SBP, DBP), heart rate (HR), fasting blood sugar (FBS), triglycerides (TG), and habitual drinking.
- Women: Significant predictors were age, SBP, DBP, HR, and smoking history.
- A risk score based on these factors achieved moderate predictive accuracy (Area Under the Curve [AUC]: 0.68 in men, 0.71 in women).
- A logistic regression-based equation provided higher predictive discrimination (AUC: 0.71 in men, 0.77 in women), outperforming the simpler score-based model.
By combining accessible clinical parameters into a validated predictive model, this study bridges a critical gap in the early identification of subclinical atherosclerosis risk.
Reference: Inadome N, Kawasoe S, Miyata M, et al. Risk prediction score and equation for progression of arterial stiffness using Japanese longitudinal health examination data. Hypertens Res. 2025;48:1690–1701. doi:10.1038/s41440-024-02057-z
Meghna A Singhania is the founder and Editor-in-Chief at Medical Dialogues. An Economics graduate from Delhi University and a post graduate from London School of Economics and Political Science, her key research interest lies in health economics, and policy making in health and medical sector in the country. She is a member of the Association of Healthcare Journalists. She can be contacted at meghna@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


