- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
BP lowering effects of renal denervation maintained upto 1 year with fewer medicines: JACC
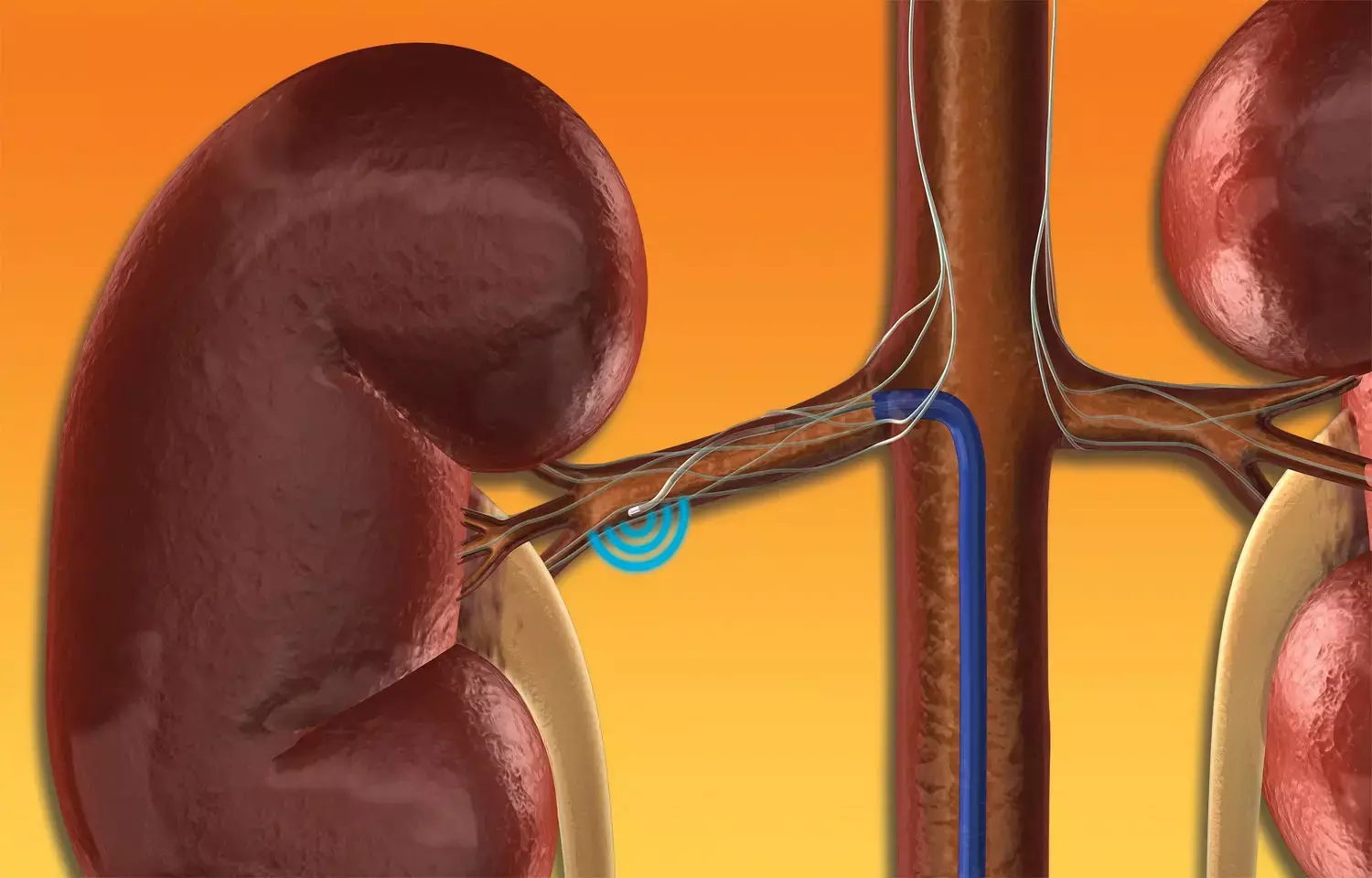
Delhi: With fewer prescribed antihypertensive medications, the BP lowering effect of endovascular ultrasound renal denervation (RDN) was maintained at 12 months compared to sham, according to a recent study in the journal JACC: Cardiovascular Interventions.
Previous RCTs have shown the blood pressure (BP)–lowering efficacy and safety of endovascular ultrasound renal denervation in the absence and presence of antihypertensive medications. This study by Michel Azizi , Hypertension Department and DMU Carte, Paris, France, and colleagues reports the 12-month results of the RADIANCE-HTN (A Study of the ReCor Medical Paradise System in Clinical Hypertension) SOLO trial following unblinding of patients at 6 months.
It included patients with daytime ambulatory BP ≥135/85 mm Hg after 4 weeks off medication. They were randomized to receive RDN (n = 74) or sham (n = 72) and maintained off medication for 2 months. A standardized medication escalation protocol was instituted between 2 and 5 months (blinded phase). Between 6 and 12 months (unblinded phase), patients received antihypertensive medications at physicians' discretion.
Outcomes at 12 months included medication burden, change in daytime ambulatory systolic BP (dASBP) and office or home systolic BP (SBP), visit-to-visit variability in SBP, and safety.
Key findings of the study include:
- Sixty-five of 74 RDN patients and 67 of 72 sham patients had 12-month dASBP measurements.
- The proportion of patients on ≥2 medications (27.7% vs. 44.8%), the number of medications (0 vs. 1.4), and defined daily dose (1.4 vs. 2.2) were less with RDN versus sham.
- The decrease in dASBP from baseline in the RDN group (−16.5 ± 12.9 mm Hg) remained stable at 12 months.
- The RDN versus sham adjusted difference at 12 months was −2.3 mm Hg for dASBP, −6.3 mm Hg for office SBP, and −3.4 mm Hg for home SBP.
- Visit-to-visit variability in SBP was smaller in the RDN group.
- No renal artery injury was detected on computed tomographic or magnetic resonance angiography.
"The decrease in BP with a treatment strategy including RDN followed by subsequent addition of antihypertensive medications was associated with a lower VVV of BP than a treatment strategy including stepped-care intensified antihypertensive treatment only," wrote the authors.
"Despite unblinding, the BP-lowering effect of RDN was maintained at 12 months with fewer prescribed medications compared with sham." they concluded.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


