- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Fluoroquinolones use linked to sudden cardiac death in dialysis patients: JAMA
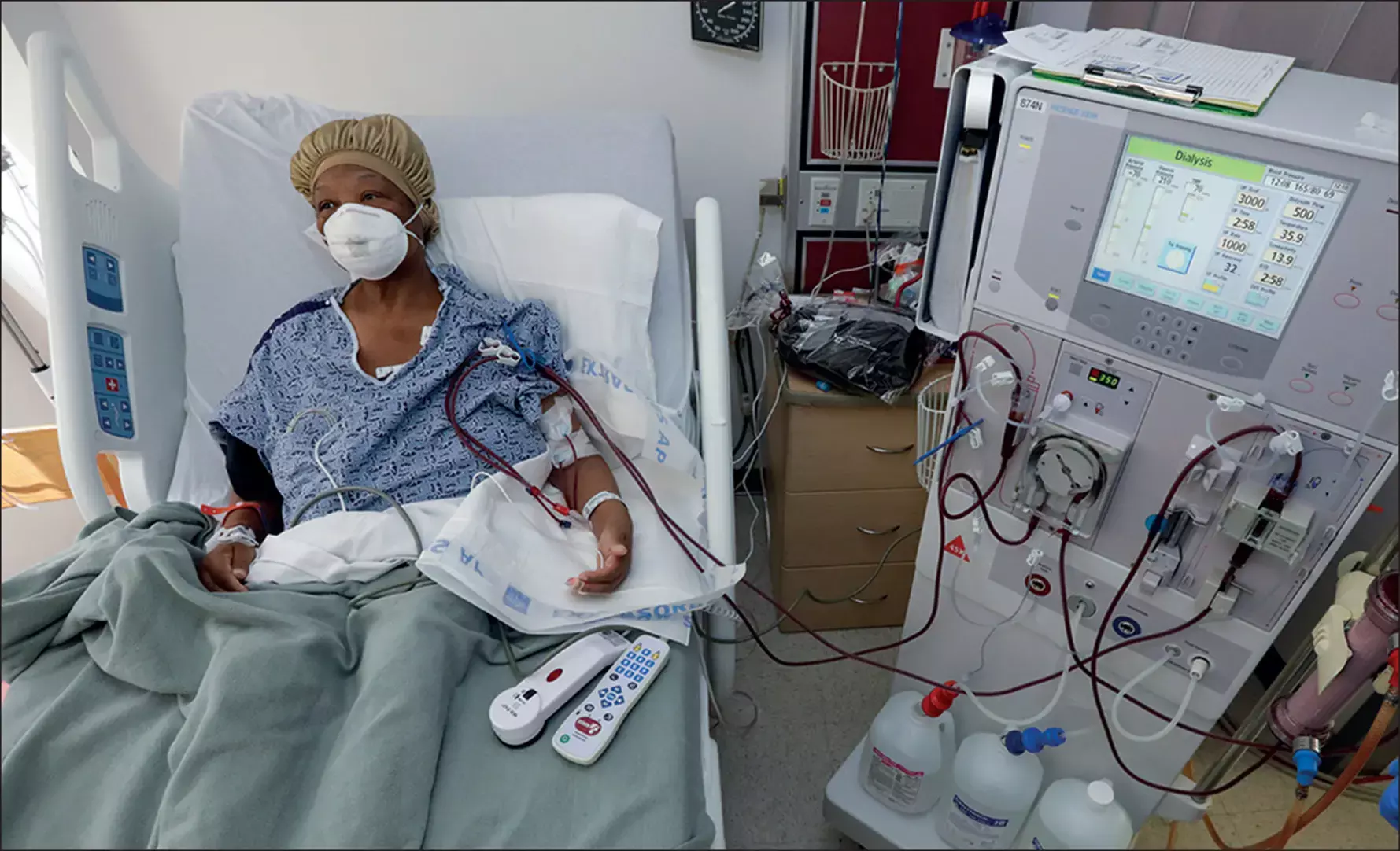
A recent study published in the JAMA Cardiology finds the link between fluoroquinolone use with cardiac complications in the general population. Respiratory fluoroquinolone antibiotics are some of the most common medications with QT interval–prolonging potential prescribed to patients with hemodialysis-dependent kidney failure—individuals who have a very high risk of sudden cardiac death (SCD). To date, there have been no large-scale, population-specific studies evaluating the cardiac safety of respiratory fluoroquinolones in the hemodialysis population.
A team of researchers conducted a study to investigate the cardiac safety of respiratory fluoroquinolones among individuals with hemodialysis-dependent kidney failure.
A retrospective cohort study examining safety using an active comparator new-user design was conducted using administrative claims data from a US-wide kidney failure registry from January 1, 2007, to December 31, 2016, including 264 968 Medicare beneficiaries receiving in-centre maintenance hemodialysis. Data analysis was performed from January 4 to August 16, 2021.
They were exposed to Respiratory fluoroquinolone (levofloxacin or moxifloxacin) vs amoxicillin-based (amoxicillin or amoxicillin with clavulanic acid) antibiotic treatment.
The results of the study are as follows:
- The study cohort included 264 968 unique in-centre hemodialysis patients and 626 322 study antibiotic treatment episodes: 251 726 respiratory fluoroquinolone treatment episodes (40.2%) and 374 596 amoxicillin-based treatment episodes (59.8%). Of the 264 968 patients, 135 236 (51.0%) were men, and the mean (SD) age was 61 (15) years.
- Respiratory fluoroquinolone vs amoxicillin-based antibiotic treatment was associated with a higher relative and absolute 5-day risk of SCD
- Respiratory fluoroquinolone vs amoxicillin-based antibiotic treatment was not associated with the 5-day risk of fracture.
The researchers concluded that in this study, compared with amoxicillin-based antibiotic treatment, respiratory fluoroquinolone treatment was associated with a higher short-term risk of SCD among patients with hemodialysis-dependent kidney failure. This finding suggests that decisions between the use of respiratory fluoroquinolones and amoxicillin-based antibiotics should be individualized, with prescribers considering both the clinical benefits and potential cardiac risks.
Reference:
Analysis of Respiratory Fluoroquinolones and the Risk of Sudden Cardiac Death Among Patients Receiving Hemodialysis by Magdalene M. Assimon published in the JAMA Cardiol.
doi:10.1001/jamacardio.2021.4234
Dr. Shravani Dali has completed her BDS from Pravara institute of medical sciences, loni. Following which she extensively worked in the healthcare sector for 2+ years. She has been actively involved in writing blogs in field of health and wellness. Currently she is pursuing her Masters of public health-health administration from Tata institute of social sciences. She can be contacted at editorial@medicaldialogues.in.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


