- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
High BP and obesity have synergistic adverse effects on retinal vasculature in kids: Study
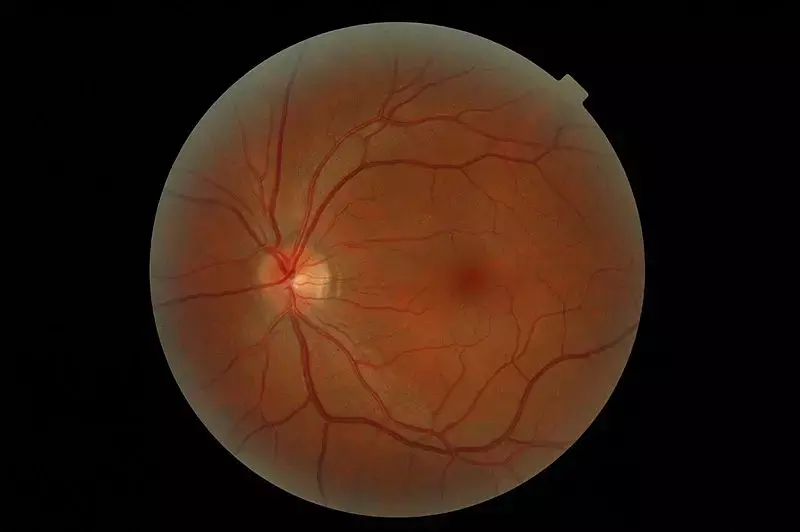
According to recent research, investigators have found out that there are potential synergistic or additive effects for both hypertensive BP and obesity on retinal vasculature in children.
The study is published in the Journal of American Heart Association.
High blood pressure (BP) and obesity are becoming increasingly prevalent among children globally. Although prior studies have shown their adverse impacts on macrovascular health, less is known about their effects on microvascular heath.
Hence, Agnes Ho and colleagues from the Department of Ophthalmology and Visual Sciences, , The Chinese University of Hong Kong, , Hong Kong, China conducted the study to evaluate the independent and synergistic effects of hypertensive BP and obesity on retinal vasculature in young children.
The authors studied a total of 1006 children aged 6 to 8 years. Quantitative retinal vascular parameters, including central retinal arteriolar and venular equivalents and retinal arteriolar and venular fractal dimensions, were measured from retinal photographs following a standardized protocol. BP and body mass index were categorized according to reference values from American Academy of Pediatrics and International Obesity Task Force guidelines respectively.
The following results were found-
- Children with hypertensive systolic BP had the narrowest central retinal arteriolar equivalents compared with children with either elevated or normotensive systolic BP (162.4, 164.6, and 167.1 µm; P‐trend <0.001).
- Increased standardized systolic BP was associated with narrower central retinal arteriolar equivalents (β=−2.276 µm, P<0.001), wider central retinal venular equivalents (1.177, P=0.007), and decreased arteriolar fractal dimensions (β=−0.004, P=0.034).
- Children with obesity had the smallest arteriolar fractal dimensions compared with children with overweightness and normal weight (1.211, 1.234, and 1.240; P‐trend=0.004).
- Children with both hypertensive BP and either overweightness or obesity had the narrowest central retinal arteriolar equivalents and smallest arteriolar Df (P‐trend<0.001 and P‐trend=0.007).
Therefore, the authors concluded that "the findings demonstrated the potential synergistic or additive effects for both hypertensive BP and obesity on retinal vasculature in children."
More proactive interventional approaches should be implemented in children with cardiovascular risk factors to prevent the development of microvascular impairments.
Dr. Nandita Mohan is a practicing pediatric dentist with more than 5 years of clinical work experience. Along with this, she is equally interested in keeping herself up to date about the latest developments in the field of medicine and dentistry which is the driving force for her to be in association with Medical Dialogues. She also has her name attached with many publications; both national and international. She has pursued her BDS from Rajiv Gandhi University of Health Sciences, Bangalore and later went to enter her dream specialty (MDS) in the Department of Pedodontics and Preventive Dentistry from Pt. B.D. Sharma University of Health Sciences. Through all the years of experience, her core interest in learning something new has never stopped. She can be contacted at editorial@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


