- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Intravascular lithotripsy eases stent implantation in severely calcified lesions: JACC
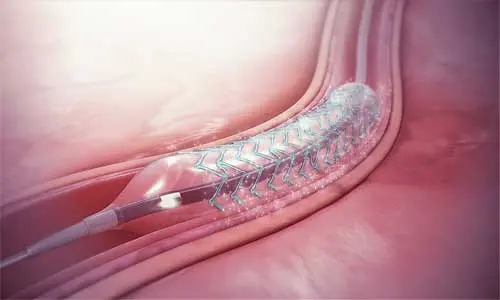
USA: Coronary intravascular lithotripsy (IVL) may facilitate successful stent implantation in severely calcified lesions, according to a recent study published in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology.
Calcification of the coronary arteries hinders stent delivery and expansion that leads to adverse outcomes. IVL delivers acoustic pressure waves that modify calcium hence optimizing stent deployment and enhancing vessel compliance.
Jonathan M. Hill, Royal Brompton Hospital, London, United Kingdom, and colleagues aimed to assess the safety and effectiveness of IVL in severely calcified de novo coronary lesions in this Disrupt CAD III -- a prospective, single-arm multicenter study designed for regulatory approval of coronary IVL.
The primary safety endpoint was freedom from major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE: cardiac death, myocardial infarction or target vessel revascularization) at 30 days. The primary effectiveness endpoint was a procedural success. Both endpoints were compared to a pre-specified performance goal (PG). The mechanism of calcium modification was assessed in an optical coherence tomography (OCT) sub-study.
The study enrolled a total of 431 patients at 47 sites in four countries.
Key findings of the study include:
- The primary safety endpoint of the 30-day freedom from MACE was 92.2%; the lower bound of the 95% confidence interval (CI) was 89.5% which exceeded the PG of 84.4%.
- The primary effectiveness endpoint of procedural success was 92.4%; the lower bound of the 95% CI was 90.2% which exceeded the PG of 83.4%.
- Mean calcified segment length was 47.9±18.8 mm, calcium angle was 292.5±76.5° and calcium thickness was 0.96±0.25 mm at the site of maximum calcification.
- OCT demonstrated multi-plane and longitudinal calcium fractures after IVL in 67.4% of lesions.
- Minimum stent area was 6.5 ± 2.1mm2 and was similar regardless of demonstrable fractures on OCT.
"Coronary IVL safely and effectively facilitated stent implantation in severely calcified lesions," concluded the authors.
"Intravascular Lithotripsy for Treatment of Severely Calcified Coronary Artery Disease: The Disrupt CAD III Study," is published in the journal JACC.
DOI: https://www.onlinejacc.org/content/early/2020/10/03/j.jacc.2020.09.603
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


