- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Intravascular lithotripsy effective option for severely calcified peripheral lesions: Disrupt PAD III trial
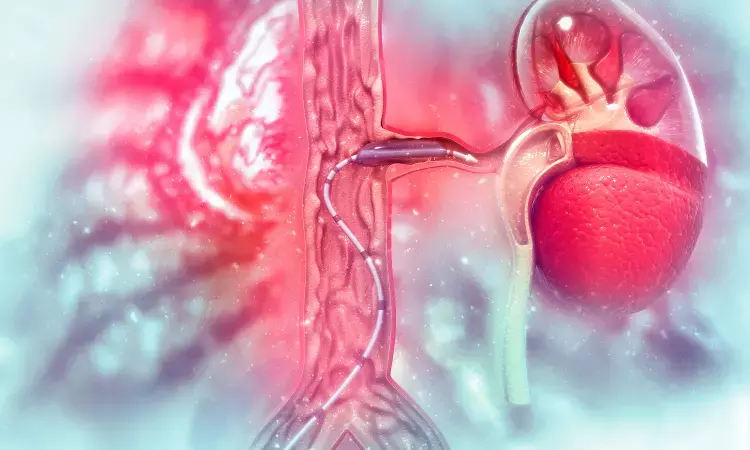
ATLANTA, GA: One year outcomes from the Disrupt PAD III Trial comparing intravascular lithotripsy (IVL) with a drug-coated balloon (DCB) to percutaneous transluminal angioplasty (PTA) with a DCB was presented today as late-breaking clinical research at the Society for Cardiovascular Angiography & Interventions (SCAI) 2022 Scientific Sessions. The results revealed consistent safety and effectiveness of IVL with durable patency.
Impacting approximately 6.5 million Americans over the age of 40, peripheral arterial disease (PAD) is the narrowing of the peripheral arteries that carry blood away from the heart to other parts of the body. PAD is caused by a buildup of fatty plaque in the arteries and treatment options can including lifestyle changes, medical therapy or surgery depending on the severity of the condition. However, patients with severe calcification are often left out of clinical trials.
The Disrupt PAD III study provides the largest randomized controlled evidence to guide endovascular treatment of severely calcified superficial femoral artery-pop lesions. Looking at 45 global sites, 306 SFA-pop lesions, and, greater than 80% of lesions were defined as severely calcified by the PARC definition with an average calcified length over 125mm. The goal of the study was to assess long-term primary patency (PP) in patients treated with IVL and DCB compared to patients treated with PTA with a DCB.
PP was defined as freedom from clinically driven target lesion revascularization (CD-TLR) by an independent Clinical Events Committee and freedom from restenosis determined by duplex ultrasound (DUS) as assessed by an independent core laboratory. Acute PTA failure requiring a stent during the index procedure was pre-specified per protocol as a loss of PP.
For IVL or PTA arms, PP follow-up is available in 80.4% and 83.7% of patients, respectively. Primary patency at one-year was significantly greater in the IVL arm (80.5% vs. 68.0%). The per protocol requirement for provisional stenting was significantly lower in the IVL group (4.6% vs 18.3%).
Freedom from CD-TLR (IVL: 95.7% vs PTA: 98.3%) and restenosis (IVL: 90.0% vs PTA: 88.8%) were similar between the two groups at 1-year. With IVL, severe complications and the need for additional interventions are reduced compared to PTA.
"This trial offers important new insights because patients with severe PAD are often excluded from trials, resulting in a very limited amount of randomized data to guide treatment," said William A. Gray, M.D., FSCAI, Lankenau Heart Institute/Main Line Health, Wynnewood, PA and lead author of the study. "The trial demonstrated the utility of IVL, rendering these challenging procedures safe and predictable.
This offers patients future treatment pathways without the potential long-term risk of adverse clinical events such as stent fracture and restenosis."
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


