- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
LBB pacing shows greater EF improvement than BiV-CRT in NICMP patients, JACC study
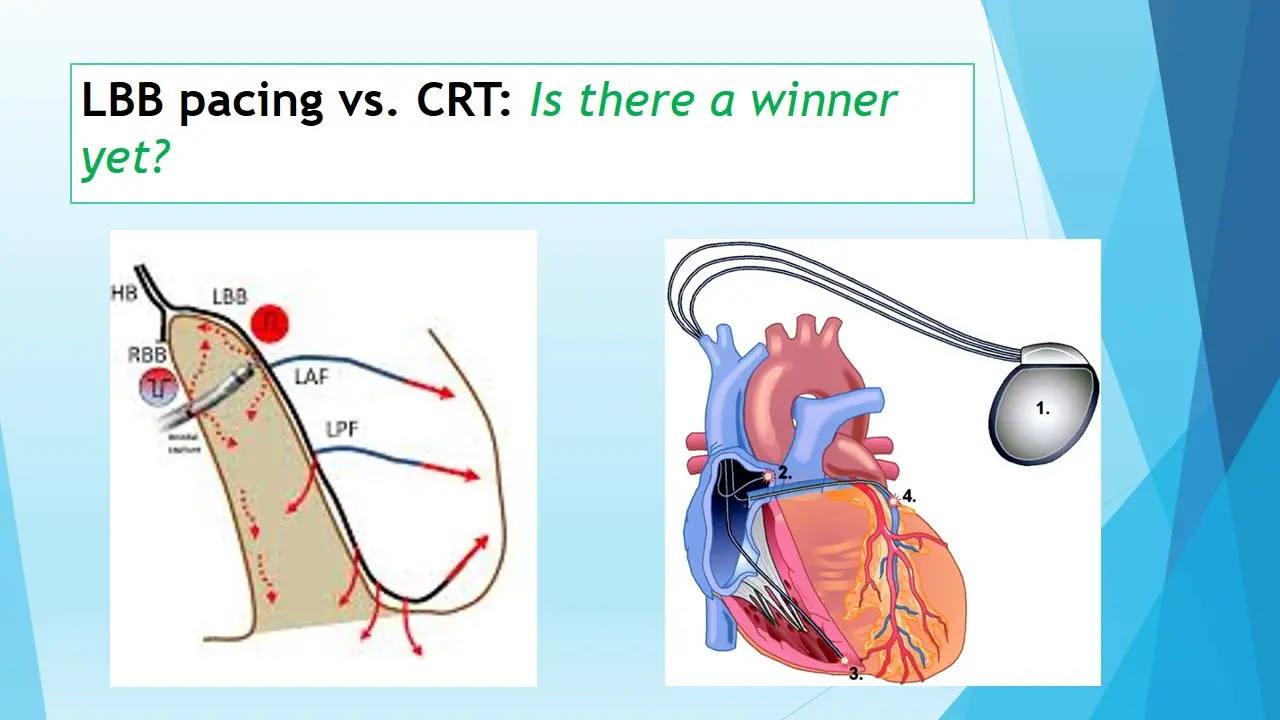
Left bundle branch pacing (LBBP) is the latest conduction system pacing technique that is capable of correcting intrinsic LBBB. In the first ever randomized comparison of this novel technique with the conventional method of biventricular pacing with CRT, authors Wang et al have shown that patients undergoing LBB pacing show better improvement in EF and other echo parameters like end-systolic volume when compared to those receiving biventricular pacing (BiVP) CRT over a 6 month follow up in nonischemic cardiomyopathy patients.
The results of the LBBB-RESYNC trial were recently published in JACC.
Shortcomings of CRT:
Despite its established mortality benefit in heart failure patients, CRT is underused and has a nonresponder rate of 30% to 50%. Possible explanations for suboptimal response include the nonphysiologic electrical resynchronization between an epicardial wavefront from the coronary sinus (CS) lead and the right ventricle endocardium, suboptimal lead position, presence of LV scar, and latency due to localized conduction delay.
Engaging the conduction system with His corrective and/or left bundle branch pacing (LBBP) has been shown to be an effective and feasible alternative to BVP in several studies. The authors of LBB-RESYNC trial sought to compare the efficacy of LBBP-CRT with BiVP-CRT in patients with heart failure and reduced left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF).
In this prospective, randomized trial of patients with NICMP and LBBB with 6-month preplanned follow-up. Crossovers were allowed if LBBP or BiVP were unsuccessful. The primary endpoint was the difference in LVEF improvement between 2 groups. The secondary endpoints included changes in echocardiographic measurements, N-terminal pro–B-type natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP), New York Heart Association functional class, 6-minute walk distance, QRS duration, and CRT response.
At 6-month follow-up, patients with LBBP resulted in a greater improvement in LVEF (a difference of 5.6%), LV end systolic volumes, and NT-proBNP compared with BVP. In addition, on-treatment analysis showed significantly narrower paced QRS in the LBBP group (129.1 ± 12.2 ms vs 140.1 ± 11.0 ms). Importantly, there were fewer crossovers in LBBP compared with BVP (2 vs 4).
Promising as it is, this study still leaves open several questions mainly with regard to applicability of LBBP in situations like patients with ischemic cardiomyopathy (ICM), septal scar, or conduction system disease, which is multilevel or diffuse in nature that is neither completely corrected by HBP/LBBP nor responds to CS pacing.
As a bailout strategy for BVP in patients with failed CS lead placement, LBBP was shown to be a viable alternative with significant QRS narrowing as well as positive clinical and echocardiographic response. In BVP nonresponders, the outcomes, however, are still suboptimal.
How will our practice change in future?
"The future of cardiac pacing and resynchronization lies in understanding the mechanisms that result in the dyssynchronous myocardial activation and selecting the appropriate modality. Therein, we shall see the transition in practice where focal LBBB can be treated with LBBP and the more complex conduction system disease may be addressed with His or left bundle pacing optimized CRT", suggest Vijayaraman et al in an accompanying editorial.
Randomized trials are needed to compare the long-term effects of LBBP and BiV pacing on functional status and survival in patients with heart failure and LBBB.
Source: JACC
1. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2022 Sep, 80 (13) 1205–1216
2. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2022 Sep, 80 (13) 1217–1219
MBBS, MD , DM Cardiology
Dr Abhimanyu Uppal completed his M. B. B. S and M. D. in internal medicine from the SMS Medical College in Jaipur. He got selected for D. M. Cardiology course in the prestigious G. B. Pant Institute, New Delhi in 2017. After completing his D. M. Degree he continues to work as Post DM senior resident in G. B. pant hospital. He is actively involved in various research activities of the department and has assisted and performed a multitude of cardiac procedures under the guidance of esteemed faculty of this Institute. He can be contacted at editorial@medicaldialogues.in.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


