- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Novel post-closure technique reduces vascular complications related to Impella CP removal
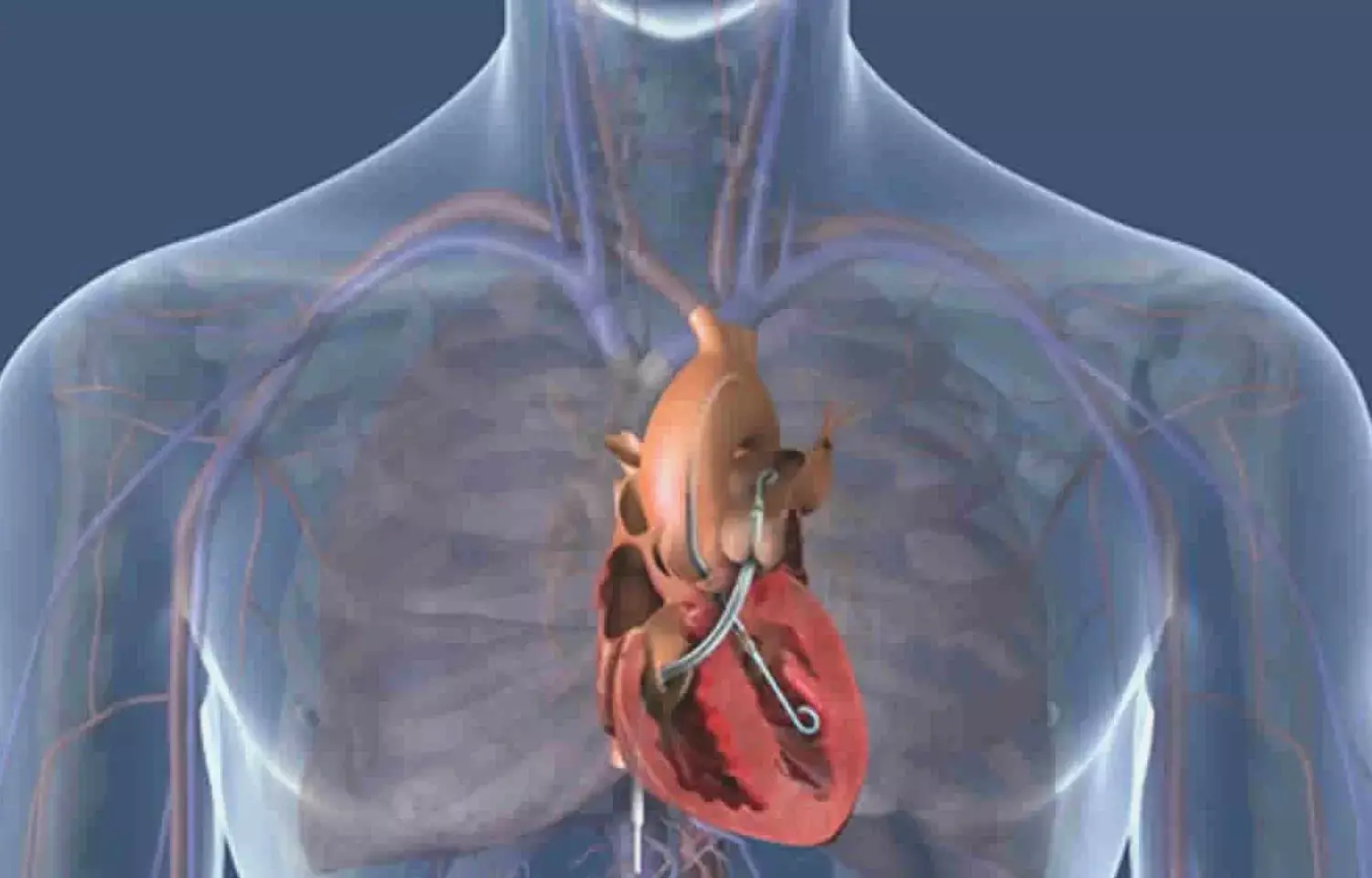
USA: A novel post-closure technique for removal of next-generation Impella CP and immediate hemostasis may reduce vascular complications tied to devise removal and may improve clinical outcomes in these patients, the researchers claim in a new study.
"The post-closure technique uses the side port of the next generation Impella CP to introduce a 0.035″ guidewire to maintain femoral vascular access," the researchers explain in their study published in the journal Cardiovascular Revascularization Medicine.
"The Impella CP is removed, a 14F sheath is placed and a second 0.035″ wire is introduced through the 14F sheath in an over-the-wire, rapid exchange fashion," they wrote. "This allows for a double-wire approach to deploy two suture-mediated closure devices at the time of the extraction of the device of immediate hemostasis in the cath lab."
In an over-the-wire, rapid exchange fashion, the Impella CP is removed, a 14F sheath is placed and a second 0.035″ wire introduced through the 14F sheath, which allows for a double-wire approach to deploy two suture-mediated closure devices at the time of device extraction for immediate hemostasis in the cardiac catheterization lab
There has been an exponential growth in the use of percutaneous mechanical circulatory support. Vascular complications remain a growing concern and there are no best practices for device removal. In the study, Colin S.Hirst, Ascension Saint John Heart and Vascular Institute, Ascension Saint John Hospital, Detroit, MI, USA, and colleagues describe a novel post-closure technique for the next generation Impella CP removal and immediate hemostasis. They aimed to determine if the post-closure technique reduces access site adverse vascular events (AVE) and bleeding when compared to manual compression upon device removal of the next generation Impella CP.
For this purpose, the researchers conducted a single-center, retrospective, exploratory analysis of 11 consecutive patients receiving an Impella CP for either high-risk PCI or cardiogenic shock and then referred for post-closure. They were compared to 20 patients receiving manual compression for Impella CP removal between 2017 and 2019. The mean age range was 62.7–65.4 years and 50–65% were male.
Salient findings of the study include:
- The average duration of Impella CP treatment ranged from 3.4 to 5.2 days.
- Patients referred for post-closure had significantly lower rates of all-cause adverse vascular events (0% versus 40%; n = 0/11 versus n = 8/20).
- There was no significant difference in BARC 3 or greater bleeding, transfusion requirement, hospitalization duration or intensive care duration between removal strategies.
"The novel post-closure technique significantly decreases vascular complications associated with device removal and may improve clinical outcomes for these critically ill patients," the authors concluded.
Reference:
Hirst CS, Thayer KL, Harwani N, Kapur NK. Post-closure technique to reduce vascular complications related to Impella CP. Cardiovasc Revasc Med. 2021 Nov 3:S1553-8389(21)00686-2. doi: 10.1016/j.carrev.2021.10.008. Epub ahead of print. PMID: 34810113.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


