- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Protein from mussel and stem cells may regenerate infarcted myocardium
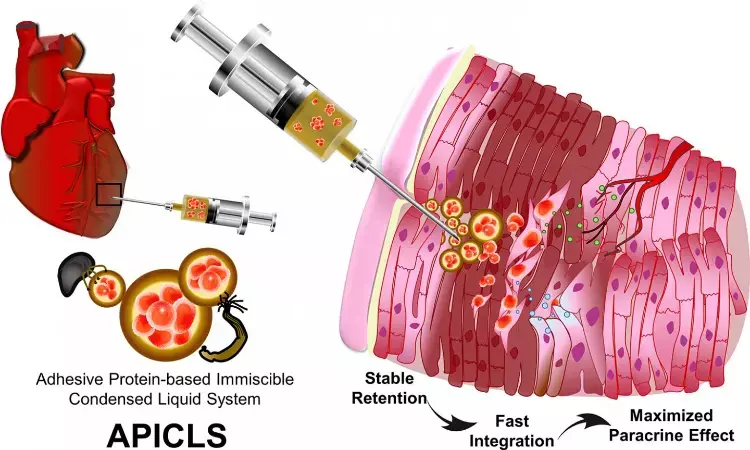 The unique physiochemical properties of APICLS allow transplanted MSCs to stably remain and to be rapidly integrated at the injected site, resulting in enhanced therapeutic efficacy through maximized paracrine effects. CREDIT Hyung Joon Cha (POSTECH)
The unique physiochemical properties of APICLS allow transplanted MSCs to stably remain and to be rapidly integrated at the injected site, resulting in enhanced therapeutic efficacy through maximized paracrine effects. CREDIT Hyung Joon Cha (POSTECH)The new study published in the Journal of Controlled Release suggests a promising assessment for direct stem cell injection strategy in patients of Myocardial Infarction.
Myocardial infarction is on the rise with an early mortality of about 30%.Therefore it is critical to have immediate and proactive treatment to prevent a heart attack.
Research team from South Korea has proposed an effective stem cell treatment system for myocardial infarction using harmless protein from mussel and stem cells.This may contribute to developing an efficient treatment of this fatal disease.The research has been published on the website of Journal of Controlled Release.
Prof. Hyung Joon Cha and Mr. Tae Yoon Park from Department of Chemical Engineering, POSTECH with Prof. Sung Bo Sim from Department of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery, Yeouido St. Mary's Hospital and Prof. Jongho Lee from Department of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery, Daejeon St. Mary's Hospital developed an 'adhesive protein-based immiscible condensed liquid system' (APICLS) that efficiently delivered the mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) to the damaged cardiac muscular tissues and enabled the transplantation prolonged. By employing the phase separation phenomenon of mussel adhesive protein, they were able to easily encapsulate the MSCs in the liquid coacervate. Especially, based on the mass production of bioengineered mussel adhesive protein, their newly suggested platform can be expected to be an innovative therapeutic system for myocardial infarction.
Heart is a vital organ that circulates blood while repeating contraction and relaxation of muscles by electrical signals. When blood vessels are clogged, oxygens and nutrients cannot be supplied to the heart and it brings severe damages to a muscle of the heart, causing infarcted myocardium with disruption of blood networks. This causes a necrosis on wall of the myocardium, resulting in cardiac wall thinning and this phenomenon is known as myocardial infarction. Because the heart cannot regenerate itself when it is damaged, there is no method for innovatively regenerating damaged heart muscles. As current therapeutic strategies, patients are treated with either mechanical device or heart transplantation.
Recently, there have been numbers of research proposing on transplanting exogenous stem cells into the damaged myocardium to help heart regeneration as a future treatment technique. However, transplanted stem cells have very low survival rate due to harsh environment of the heart. Even when the transplantation is successful, most of the stems cells soon die.
For a successful stem cell therapy on MI, there are two conditions required to survive in harsh environment of the damaged heart. First, the stem cells must be efficiently transplanted and remained into the thinned cardiac muscles. Secondly, transplanted stem cells must integrate rapidly into resident surrounding tissues to improve their viability by forming blood vessels. However, the current therapeutic methods so far cannot deliver injected stem cells to infarcted cardiac muscular tissues successfully, making it very difficult to maintain the transplantation.
The joint research team injected the MSCs encapsulated in APICLS into the thinned and infarcted cardiac muscular wall efficiently. They demonstrated in vivo feasibility through rat MI model that transplanted MSCs survived in the infarcted cardiac muscular tissues for a long time due to the mussel adhesive proteins with its unique characteristics of adhesiveness and angiogenesis and the efficacy of MSCs. Furthermore, the damaged heart muscles formed new blood vessels, prevented further apoptosis of existing cardiomyocytes, and regenerated the damaged cardiac wall by reducing fibrosis.
It is anticipated that the new stem cell delivery system proposed in this research will play an essential role in the stem cell therapeutic market as it used biocompatible materials which are harmless to humans.
"By using mussel adhesive proteins, we demonstrated with the MI rat model and proved its therapeutic efficacy as an efficient stem cell injection strategy. We gives a hope that it can also be successfully applied to chronic diseases and ischemic diseases that have similar environment," said Prof. Hyung Joon Cha who led the research.
In the meanwhile, this research was introduced as the most innovative technology found by POSTECH in the Most Innovative Universities 2019 by Reuters last year. It is also published on the website of Journal of Controlled Release, the world's most renowned journal in the field of drug delivery. This study was supported by the Marine BioMaterials Research Center grant funded by the Ministry of Oceans and Fisheries, Korea.
For further reference log on to :
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jconrel.2020.02.047
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


