- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Pulsed-field ablation device allows simple and safe single-shot pulmonary vein isolation in AF: 5 S Study
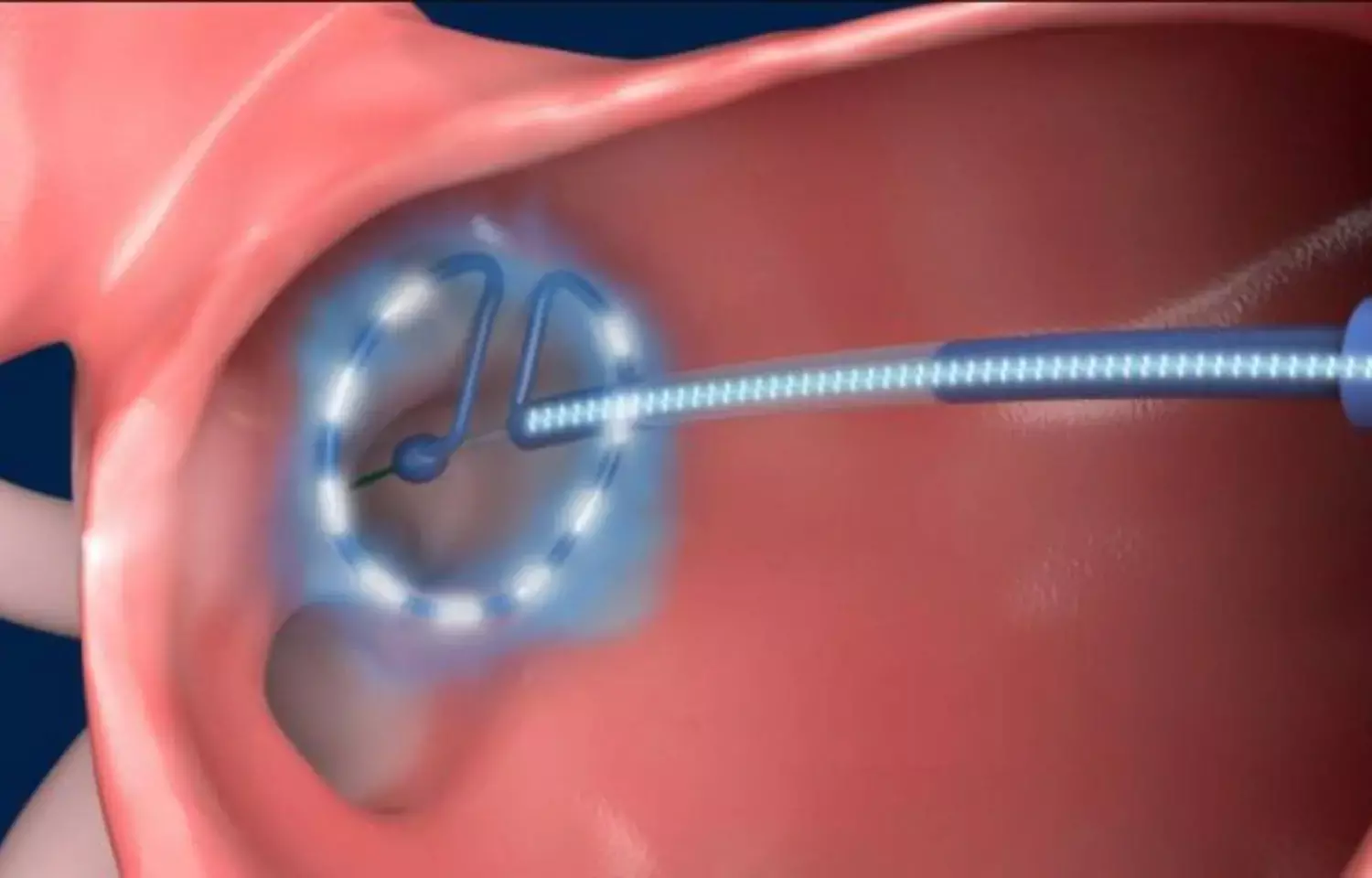
Germany: The pulsed-field ablation device allows for simple and safe single-shot pulmonary vein isolation (PVI) by utilizing standard sedation protocols, a recent study in Circulation: Arrhythmia and Electrophysiology has found. However, to further validate and assess the performance characteristics of pulse-field ablation for PVI, large prospective trials are required.
Pulsed-field ablation represents an energy source for the ablation of cardiac arrhythmias including atrial fibrillation. Boris Schmidt, Cardiovascular Center Bethanien, Germany, and colleagues, therefore, aimed to describe the adoption and the process of streamlining procedures with a new ablation technology.
For this purpose, all-comer atrial fibrillation patients (n=191; mean age 69±12 years) underwent catheter ablation with a pulsed-field ablation device through the exclusive use of analog-sedation. In the validation phase (n=25), a comparison was made between device electrogram quality and a circular mapping catheter to assess pulmonary vein isolation, and esophageal temperature monitoring was used. In the streamline phase (n=166), a single-catheter approach was implemented.
In 53 patients, postprocedural cerebral magnetic resonance imaging was performed. Esophageal endoscopy was performed on 52 patients on day 1 after the procedure. Follow-up was performed using 72 hours Holter ECGs.
The study led to the following findings:
- On a pulmonary vein basis, the pulmonary vein isolation rate was 100% including a single shot isolation rate of 99.5%.
- The electrogram information of the pulsed-field ablation catheter and the circular mapping catheter was 100% congruent.
- Neither esophageal temperature rises nor esophageal thermal injury was observed.
- Two minor strokes occurred, presumable due to air embolism during catheter exchanges through the large bore sheath (13.8 F ID).
- In the streamline phase, reduced procedure times (46±14 versus 38±13 minutes), no further strokes, and a low incidence of silent cerebral injury (10/53 patients; 19%) were noted.
- During short-term follow-up, 17/191 patients (9%) had an atrial tachyarrhythmia recurrence.
"The pulsed-field ablation device allows for simple and safe single-shot pulmonary vein isolation using standard sedation protocols," the researchers wrote. "Procedural speed and efficacy are remarkable and streamlining measures have added safety."
Reference:
The study titled, "5 S Study: Safe and Simple Single Shot Pulmonary Vein Isolation With Pulsed Field Ablation Using Sedation," was published in Circulation: Arrhythmia and Electrophysiology.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


