- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Renal denervation benefits last upto 3 years in patients on BP medicines : SPYRAL HTN ON
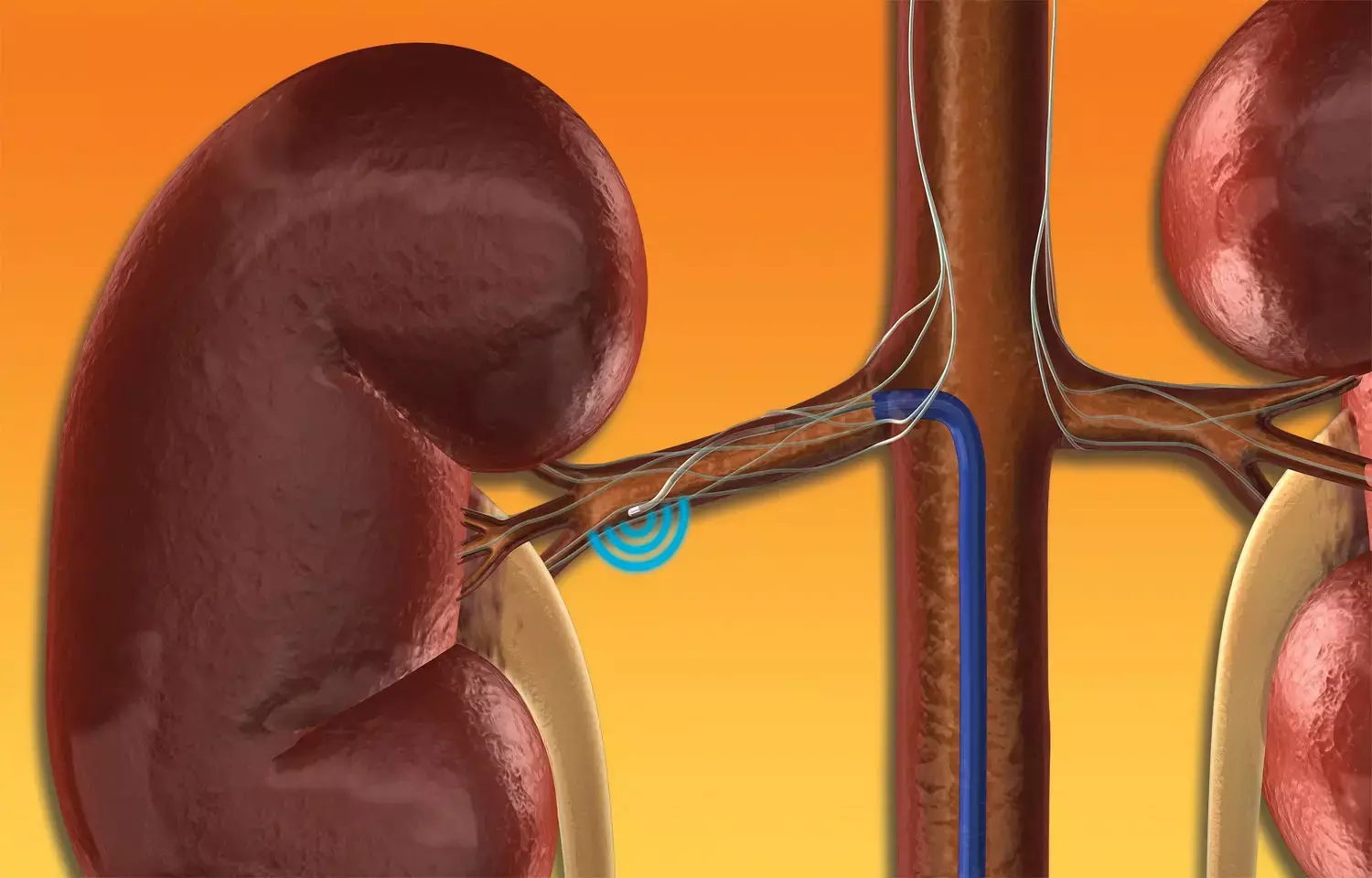
Germany: Results from pre-specified analysis of the SPYRAL HTN-ON MED study showed that renal denervation using Symplicity Spyral radiofrequency catheter gives additional reductions in blood pressure (BP) for up to 36 months in patients with high BP on medications. The study was published in the journal The Lancet on April 04, 2022.
Renal denervation has been reported to lower BP in the presence of antihypertensive medications; however, there is a lack of long-term safety and efficacy data from randomized trials of renal denervation. In the study, Prof Felix Mahfoud, Universitätsklinikum des Saarlandes, Saarland University, Homburg, Germany, and colleagues compared changes in blood pressure, antihypertensive drug use, and safety up to 36 months in renal denervation versus a sham control group in a randomized, single-blind, sham-controlled trial.
The study enrolled patients from 25 clinical centers in Germany, the USA, Japan, Australia, the UK, Austria, and Greece. Patients with uncontrolled hypertension and office systolic blood pressure between 150 mm Hg and 180 mm Hg and diastolic blood pressure of 90 mm Hg or higher were deemed eligible. Also, they had to have 24-h ambulatory systolic blood pressure between 140 mm Hg and less than 170 mm Hg, while taking one to three antihypertensive drugs with stable doses for at least 6 weeks.
Patients underwent renal angiography and were randomly assigned in a ratio of 1:1 to receive radiofrequency renal denervation or a sham control procedure. Treatment difference in mean 24-h systolic blood pressure at 6 months between the renal denervation group and the sham control group was the primary endpoint. Ambulatory and office blood pressure measurements for up to 36 months were used to assess long-term efficacy. Medication use was assessed using drug surveillance. Assessment of safety events was done for up to 36 months. An additional 260 patients are currently being randomly assigned as part of the SPYRAL HTN-ON MED Expansion trial.
Among 467 enrolled patients, 80 patients fulfilled the qualifying criteria between July 22, 2015, and June 14, 2017. They were randomly assigned to undergo renal denervation (n=38) or a sham control procedure (n=42).
Based on the study, the researchers reported the following findings:
- Mean ambulatory systolic and diastolic blood pressure were significantly reduced from baseline in the renal denervation group, and were significantly lower than the sham control group at 24 and 36 months, despite a similar treatment intensity of antihypertensive drugs.
- The medication burden at 36 months was 2·13 medications in the renal denervation group and 2·55 medications (2·19) in the sham control group.
- 24 (77%) of 31 patients in the renal denervation group and 25 (93%) of 27 patients in the sham control group adhered to medication at 36 months.
- At 36 months, the ambulatory systolic blood pressure reduction was −18·7 mm Hg for the renal denervation group (n=30) and −8·6 mm Hg (14·6) for the sham control group (n=32; adjusted treatment difference −10·0 mm Hg).
- Treatment differences between the renal denervation group and sham control group at 36 months were −5·9 mm Hg for mean ambulatory diastolic blood pressure, −11·0 mm Hg for morning systolic blood pressure, and −11·8 mm Hg for night-time systolic blood pressure.
- There were no short-term or long-term safety issues associated with renal denervation.
"Radiofrequency renal denervation versus sham control produces a clinically meaningful and lasting BP reduction up to 36 months of follow-up, independent of concomitant antihypertensive medications and without major safety events," wrote the authors. "Renal denervation could be used as an adjunctive treatment modality for the management of hypertension patients."
Reference:
The study titled, "Long-term efficacy and safety of renal denervation in the presence of antihypertensive drugs (SPYRAL HTN-ON MED): a randomised, sham-controlled trial," was published in The Lancet.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(22)00455-X
KEYWORDS: Lancet, renal denervation, antihypertensive drugs, Prof Felix Mahfoud, radiofrequency, hypertension, blood pressure, BP, medications, BP reduction
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


