- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
SIGNALS score for in-hospital Neurological deterioration in Intracerebral hemorrhage
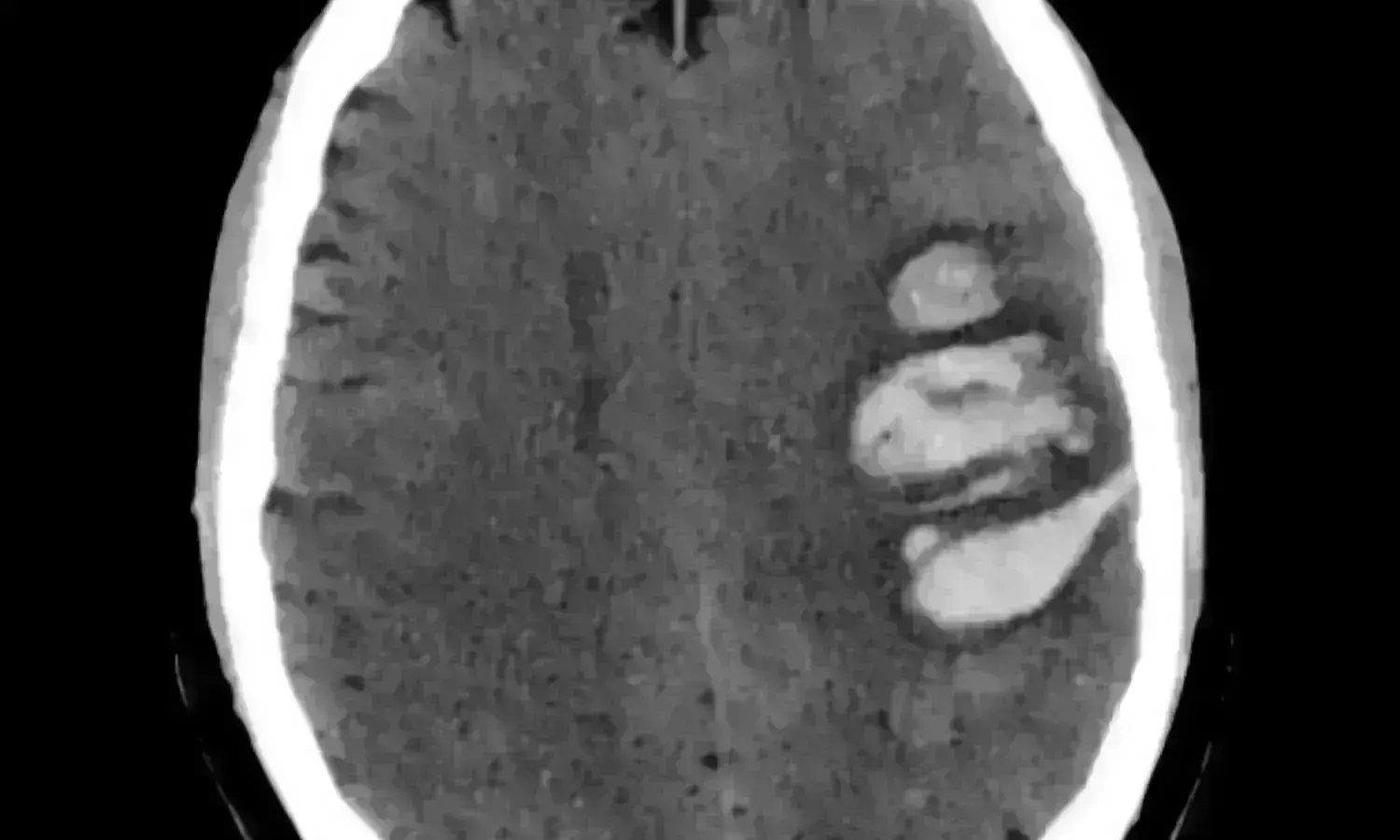
In patients with intracerebral hemorrhage, the SIGNALS score is reliable in predicting the risk of in-hospital neurological deterioration as per a study published in the "Journal of the American Heart Association."
Intracerebral hemorrhage is the most devastating and lethal form of stroke that occurs due to traumatic or non-traumatic causes. Management varies from medical to surgical options. Researchers from China conducted a study to develop a novel clinical score for neurological deterioration during hospitalization after intracerebral hemorrhage. They used data from the CHERRY (Chinese Cerebral Hemorrhage: Mechanism and Intervention) study. Eligible patients were randomly allocated into two groups. Two‐thirds were placed in the training cohort with 1027 patients and one‐third in the validation cohort with 515 patients. To identify factors associated with neurological deterioration like an increase in the National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale of ≥4 or death within 15 days after symptom onset, Multivariable logistic regression was used. Based on the regression coefficients from the logistic model, a prediction score was developed.
The site, size, gender, National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale, age, leukocyte, and sugar (SIGNALS) score was developed as a sum of individual points of 0–8. The points were as follows, based on:
Site | 1 point for infratentorial location |
Size | 3 points for >20 mL of supratentorial hematoma volume or 2 points for >10 mL of infratentorial hematoma volume |
Sex | 1 point for male sex |
National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale score | 1 point for >10 |
Age | 1 point for ≥70 years |
White blood cell | 1 point for>9.0×109/L |
Fasting blood glucose | 1 point>7.0 mmol/L |
Results:
The proportion of patients who suffered from neurological deterioration increased with higher SIGNALS scores, showing good discrimination and good calibration in the training cohort and the validation cohort.
Thus, the researchers concluded that the SIGNALS score reliably predicts the risk of in‐hospital neurological deterioration in patients with intracerebral hemorrhage.
For the full article, click here: https://doi.org/10.1161/JAHA.121.026379
He Q, Guo H, Bi R, et al. Prediction of Neurological Deterioration After Intracerebral Hemorrhage: The SIGNALS Score [published online ahead of print, 2022 Jul 20]. J Am Heart Assoc. 2022;e026379.
BDS, MDS
Dr.Niharika Harsha B (BDS,MDS) completed her BDS from Govt Dental College, Hyderabad and MDS from Dr.NTR University of health sciences(Now Kaloji Rao University). She has 4 years of private dental practice and worked for 2 years as Consultant Oral Radiologist at a Dental Imaging Centre in Hyderabad. She worked as Research Assistant and scientific writer in the development of Oral Anti cancer screening device with her seniors. She has a deep intriguing wish in writing highly engaging, captivating and informative medical content for a wider audience. She can be contacted at editorial@medicaldialogues.in.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751




