- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Single bolus recombinant staphylokinase beneficial for STEMI patients undergoing PCI: Circulation
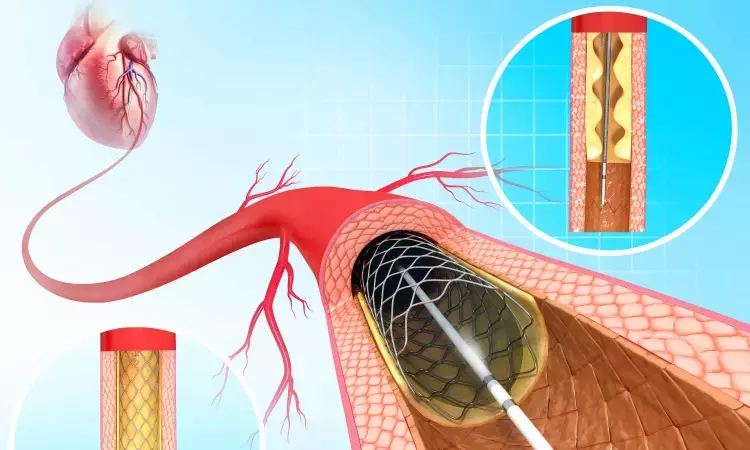
China: A single bolus recombinant staphylokinase (r-SAK) before percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) boosted patency of the infarct-related artery and decreased infarct size in some heart attack patients, a recent study published in Circulation: Cardiovascular Interventions has shown.
Time to reperfusion is critical in treating patients with ST-elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI). The benefit of adjunctive thrombolysis for patients with STEMI undergoing PCI within 120 minutes of presentation is uncertain. Therefore, Pengsheng Chen, Department of Cardiology, Xuzhou Central Hospital, Jiangsu, China (P.C.), and colleagues aimed to determine whether a single bolus recombinant staphylokinase before timely PCI leads to improved patency of the infarct-related artery and reduces the infarct size in patients presenting with ST-segment–elevation myocardial infarction.
For this purpose, the researchers conducted an open-label, prospective, multicenter, randomized study (OPTIMA-5). They enrolled patients aged 18 to 75 years who were within 12 hours of symptom onset of STEMI and expected to undergo PCI within 120 minutes.
Patients were administered loading doses of aspirin and ticagrelor and intravenous (IV) heparin and were randomized to receive a 5 mg bolus of r-SAK or normal saline intravenously before PCI.
The study's primary endpoint was Thrombolysis in Myocardial Infarction flow grade 2 to 3 or grade 3 in the infarct-related artery 60 minutes after thrombolysis. Cardiac magnetic resonance was used to detect infarct size five days after randomization. During the 30-day follow-up, the safety endpoint was major bleeding (Bleeding Academic Research Consortium ≥3).
283 patients were screened from 8 centres, and 200 were randomized (median age, 58.5 years; 14% female).
Based on the study, the researchers reported the following findings:
- The median symptom to thrombolysis time was 252.5 minutes and thrombolysis to coronary arteriography was 50.0 minutes.
- Patients randomized to r-SAK compared with normal saline more often had Thrombolysis in Myocardial Infarction flow grade 2 to 3 (69.0% versus 29.0%) and Thrombolysis in Myocardial Infarction flow grade 3 (51.0% versus 18.0%) and had smaller infarct size (21.91±10.84% versus 26.85±12.37%).
- There was no increase in major bleeding (r-SAK, 1.0% versus control, 3.0%).
"A single bolus r-SAK before primary PCI for ST-segment–-elevation myocardial infarction reduces infarct size and improves infarct-related artery patency without increasing major bleeding," the researchers concluded.
Reference:
The study titled, "Single Bolus r-SAK Before Primary PCI for ST-Segment–Elevation Myocardial Infarction," was published online in Circulation: Cardiovascular Interventions. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCINTERVENTIONS.123.013455
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


