- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Traditional Chinese Medicine Compound Tongxinluo Shows Promise in STEMI: JAMA
In a groundbreaking study conducted in China, a traditional Chinese medicine compound called Tongxinluo has shown promising results in improving clinical outcomes for patients with ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI). Tongxinluo has improved clinical outcomes for both a 1-month and 1-year duration.
The study results were published in the journal JAMA Network.
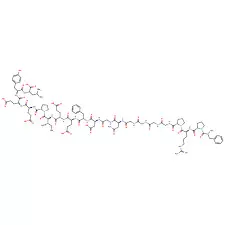
Acute ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI) is a major life-threatening condition affecting people worldwide. High risks of in-hospital mortality and recurrent cardiovascular events are faced by patients, despite reperfusion therapy and optimal medical management. Tongxinluo is a traditional Chinese medicine compound that is composed of powders and extracts from multiple plant and insect products. Previous in vitro and in vivo studies claimed the efficacy of Tongxinluo in improving myocardial infarction in STEMI patients. Hence, researchers conducted a Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial to investigate whether Tongxinluo could improve clinical outcomes in patients with ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI).
The study was carried out in 124 hospitals across China. It included patients who had experienced a STEMI within 24 hours of symptom onset and enrolled them between May 2019 and December 2020, with follow-up continuing until December 15, 2021. During the trial, patients were randomly assigned to one of two groups. Half received Tongxinluo, a traditional Chinese medicine compound, while the other half received a placebo. This treatment was administered orally for 12 months, with a loading dose of 2.08 grams immediately after randomization, followed by a maintenance dose of 1.04 grams, taken three times a day. Additionally, both groups received standard guideline-directed treatments for STEMI. The study's primary endpoint was to evaluate 30-day major adverse cardiac and cerebrovascular events (MACCEs). This composite endpoint included cardiac death, myocardial reinfarction, emergent coronary revascularization, and stroke.
Key Findings:
- The results were significant.
- Of the 3,797 patients who participated in the study, 3,777 were included in the primary analysis.
- The Tongxinluo group, which comprised 1,889 patients, demonstrated a 30-day MACCE rate of 3.4%, compared to the placebo group's rate of 5.2%. This represents a relative risk reduction of 36% (RR 0.64) and a risk difference of -1.8%.
- Further analysis of individual components of MACCEs revealed that the Tongxinluo group experienced significantly fewer cardiac deaths (3.0% vs. 4.2%) within the 30-day period.
- These positive outcomes continued beyond the initial 30-day period. At the one-year mark, the Tongxinluo group maintained lower rates of MACCEs (5.3% vs. 8.3%) and cardiac deaths (4.5% vs. 6.1%).
- The study also explored several secondary endpoints, such as 30-day stroke, major bleeding at 30 days and one year, one-year all-cause mortality, and in-stent thrombosis at various intervals. Interestingly, no significant differences were found in these secondary measures, suggesting that the benefits of Tongxinluo were primarily seen in reducing cardiac events.
- However, it is worth noting that the Tongxinluo group experienced more adverse drug reactions compared to the placebo group, primarily driven by gastrointestinal symptoms.
In conclusion, this study suggests that Tongxinluo, when used in addition to guideline-directed treatments for STEMI, significantly improves clinical outcomes, reducing the risk of MACCEs and cardiac death, both at 30 days and one year. While these findings are promising, further research is needed to understand the underlying mechanisms of Tongxinluo's effects on STEMI. Regulatory agencies and medical professionals will likely require more robust evidence before considering the integration of traditional Chinese medicine into standard medical practice for STEMI patients. This groundbreaking research offers hope for potential advancements in heart attack treatment, emphasizing the importance of exploring traditional medicine in conjunction with modern medical practices.
Further reading: Yang Y, Li X, Chen G, et al. Traditional Chinese Medicine Compound (Tongxinluo) and Clinical Outcomes of Patients With Acute Myocardial Infarction: The CTS-AMI Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA. 2023;330(16):1534–1545. doi:10.1001/jama.2023.19524
BDS, MDS
Dr.Niharika Harsha B (BDS,MDS) completed her BDS from Govt Dental College, Hyderabad and MDS from Dr.NTR University of health sciences(Now Kaloji Rao University). She has 4 years of private dental practice and worked for 2 years as Consultant Oral Radiologist at a Dental Imaging Centre in Hyderabad. She worked as Research Assistant and scientific writer in the development of Oral Anti cancer screening device with her seniors. She has a deep intriguing wish in writing highly engaging, captivating and informative medical content for a wider audience. She can be contacted at editorial@medicaldialogues.in.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751