- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Earlier ECMO beneficial for patients with refractory cardiogenic shock: Study
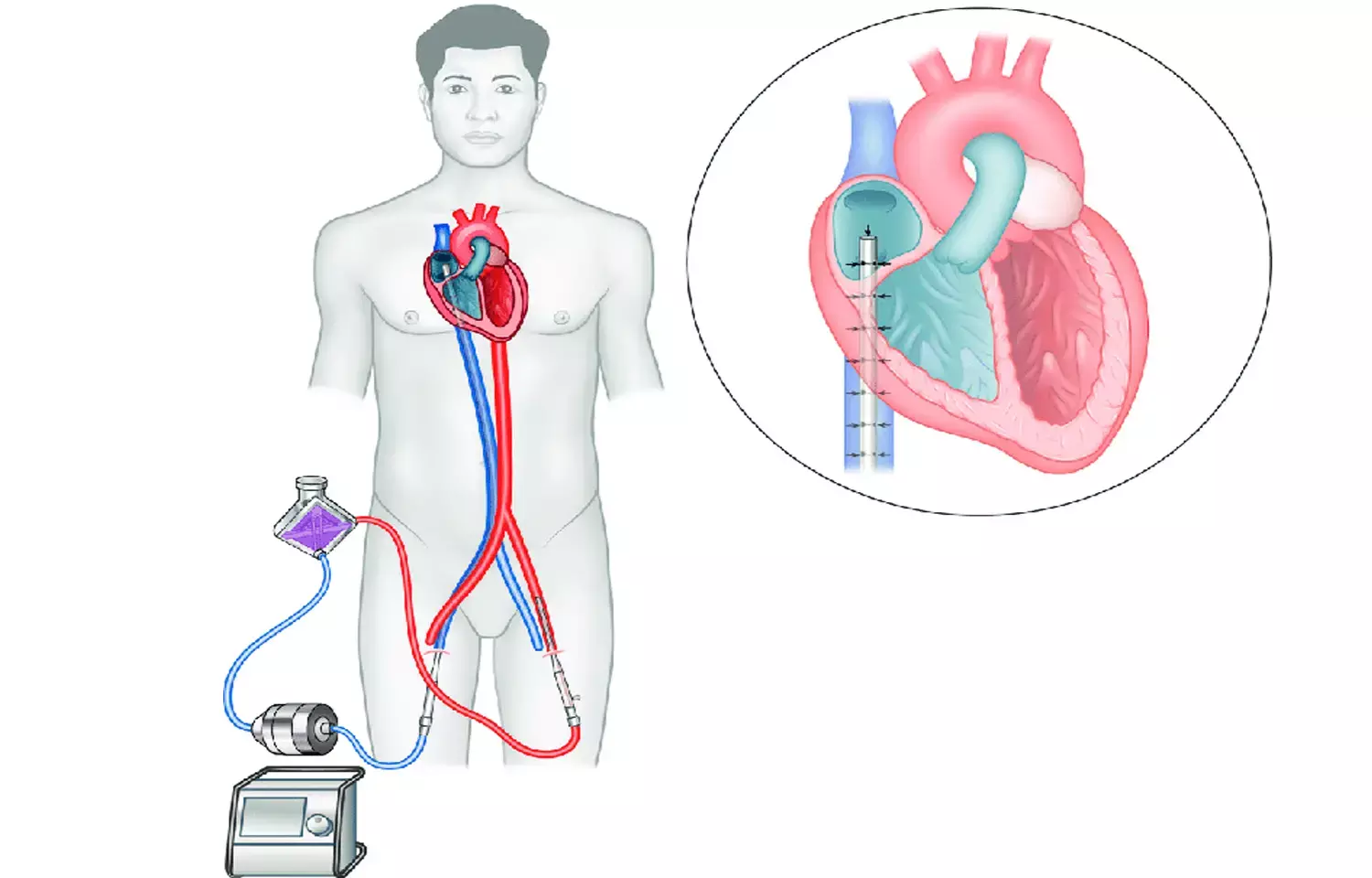
Seoul, Korea: Earlier extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO) support improves clinical outcomes in patients with refractory cardiogenic shock (CS), according to a recent study in the journal JACC: Cardiovascular Interventions.
The prognosis of refractory CS patients receiving ECMO remains poor. However, not much is known about the association between ECMO implantation timing and clinical outcomes in these patients. Considering this, Hyeok-Hee Lee, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea, and colleagues aimed to investigate whether earlier extracorporeal membrane oxygenation support is associated with improved clinical outcomes in patients with refractory cardiogenic shock.
For this purpose, the researchers identified 362 patients with refractory CS who underwent extracorporeal membrane oxygenation between January 2014 and December 2018 from a multicenter registry. The patients were divided into three groups depending on the tertiles of shock-to-ECMO time -- early, intermediate, and late ECMO.
Key findings of the study include:
- The overall 30-day the mortality rate was 40.9%.
- The risk for 30-day mortality was lower in the early group than in the late group (hazard ratio: 0.53).
- Early ECMO support was also associated with lower risk for in-hospital mortality, ECMO weaning failure, composite of all-cause mortality or rehospitalization for heart failure at 1 year, all-cause mortality at 1 year, and poor neurological outcome at discharge.
- The incidence of adverse events, including stroke, limb ischemia, ECMO-site bleeding, and gastrointestinal bleeding, did not differ significantly among the groups.
"Our findings show that earlier ECMO support was associated with improved clinical outcomes in patients with refractory CS," concluded the authors.
Reference:
The study titled, "Association Between Timing of Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation and Clinical Outcomes in Refractory Cardiogenic Shock," is published in the journal JACC: Cardiovascular Interventions.
DOI: https://www.jacc.org/doi/10.1016/j.jcin.2021.03.048
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


