- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Sevoflurane safe option for long-term sedation in ICU patients
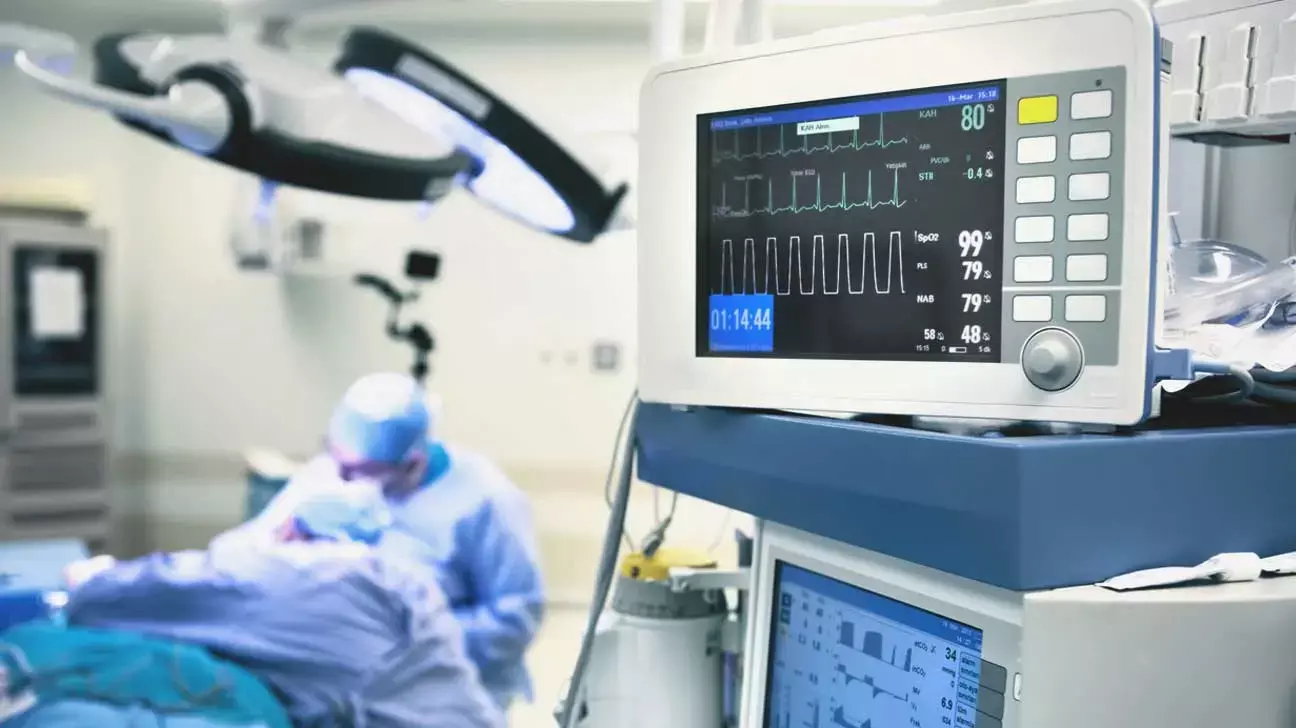
Sevoflurane safe option for long-term sedation in ICU patients suggests a new study published in the Journal of Critical Care
Volatile anesthetics are used more commonly for sedation in the intensive-care-unit (ICU). However, evidence for long-term use remains low. Therefore conducted a randomized controlled trial comparing sevoflurane with intravenous sedation with particular focus on efficacy and safety.
In this prospective, randomized-controlled phase-IIb monocentric clinical-trial ICU patients requiring at least 48 h of sedation were randomized to receive sevoflurane (S) or propofol/midazolam (P). Sedation quality was monitored using the Richmond-Agitation-Sedation-Scale. Following termination of sedation, the time to spontaneous breathing and extubation, opioid consumption, hemodynamics, ICU and hospital length of stay (LOS) and adverse events were recorded.
79 patients were eligible to randomization.
Sedation quality was comparable between sevoflurane (n = 39) and propofol (n = 40). However, the use of sevoflurane lead to a reduction in time to spontaneous breathing (26 min vs. 375 min, P < 0.001).
Patients sedated with propofol had lower opioid requirements (remifentanil:400 μg/h vs. 500 μg/h, P = 0.007; sufentanil:40 μg/h vs. 30 μg/h, P = 0.007) while hemodynamics, LOS or the occurrence of adverse events did not differ.
ICU patients sedated with sevoflurane >48 h may return to spontaneous breathing faster, while the quality of sedation is comparable to a propofol-based sedation regime. Sevoflurane might be considered to be safe for long-term sedation in this patient population, while being non-inferior compared to propofol.
Reference:
Jens Soukup, Peter Michel, Annett Christel, Gregor Alexander Schittek, Nana-Maria Wagner, Patrick Kellner,et al. Prolonged sedation with sevoflurane in comparison to intravenous sedation in critically ill patients – A randomized controlled trial,Journal of Critical Care, Volume 74,2023,154251, ISSN 0883-9441,https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcrc.2022.154251.
(https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0883944122002805)
Keywords:
Journal of Critical Care, Jens Soukup, Peter Michel, Annett Christel, Gregor Alexander Schittek, Nana-Maria Wagner, Patrick Kellner, Prolonged, sedation, sevoflurane,comparison, intravenous, sedation, critically ill patients
Dr. Shravani Dali has completed her BDS from Pravara institute of medical sciences, loni. Following which she extensively worked in the healthcare sector for 2+ years. She has been actively involved in writing blogs in field of health and wellness. Currently she is pursuing her Masters of public health-health administration from Tata institute of social sciences. She can be contacted at editorial@medicaldialogues.in.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


