- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
AI technology may significantly improve prediction of pulp exposure from radiographic information
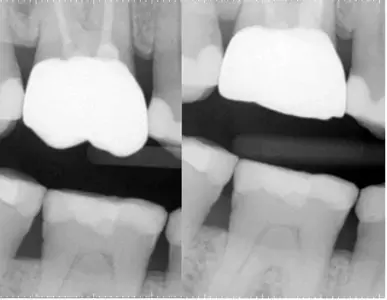
AI technology may significantly improve prediction of pulp exposure from radiographic information suggests a new study published in the Journal Of Dentistry.
The objective was to examine the effect of giving Artificial Intelligence (AI)-based radiographic information versus standard radiographic and clinical information to dental students on their pulp exposure prediction ability.
292 preoperative bitewing radiographs from patients previously treated were used. A multi-path neural network was implemented. The first path was a convolutional neural network (CNN) based on ResNet-50 architecture. The second path was a neural network trained on the distance between the pulp and lesion extracted from X-ray segmentations. Both paths merged and were followed by fully connected layers that predicted the probability of pulp exposure. A trial concerning the prediction of pulp exposure based on radiographic input and information on age and pain was conducted, involving 25 dental students. The data displayed was divided into 4 groups (G): GX-ray, GX-ray+clinical data, GX-ray+AI, GX-ray+clinical data+AI.
Results
The results showed that AI surpassed the performance of students in all groups with an F1-score of 0.71 (P < 0.001). The students’ F1-score in GX-ray+AI and GX-ray+clinical data+AI with model prediction (0.61 and 0.61 respectively) was slightly higher than the F1-score in GX-ray and GX-ray+clinical data (0.58 and 0.59 respectively) with a borderline statistical significance of P = 0.054.
Although the AI model had much better performance than all groups, the participants when given AI prediction, benefited only ‘slightly’. AI technology seems promising, but more explainable AI predictions along with a 'learning curve' are warranted.
Reference:
Shaqayeq Ramezanzade, Tudor Laurentiu Dascalu, Bulat Ibragimov, Azam Bakhshandeh, Lars Bjørndal. Prediction of pulp exposure before caries excavation using artificial intelligence: Deep learning-based image data versus standard dental radiographs,
Journal of Dentistry, Volume 138, 2023, 104732, ISSN 0300-5712, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jdent.2023.104732.
(https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0300571223003184)
Keywords:
AI, technology, may, significantly, improve, prediction, pulp, exposure, radiographic, Artificial intelligence; Endodontics; Pulpitis; Machine learning; Dental caries, information
Dr. Shravani Dali has completed her BDS from Pravara institute of medical sciences, loni. Following which she extensively worked in the healthcare sector for 2+ years. She has been actively involved in writing blogs in field of health and wellness. Currently she is pursuing her Masters of public health-health administration from Tata institute of social sciences. She can be contacted at editorial@medicaldialogues.in.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


