- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Among patients with Down syndrome occurrence of malocclusion higher, may need more interceptive orthodontic procedures
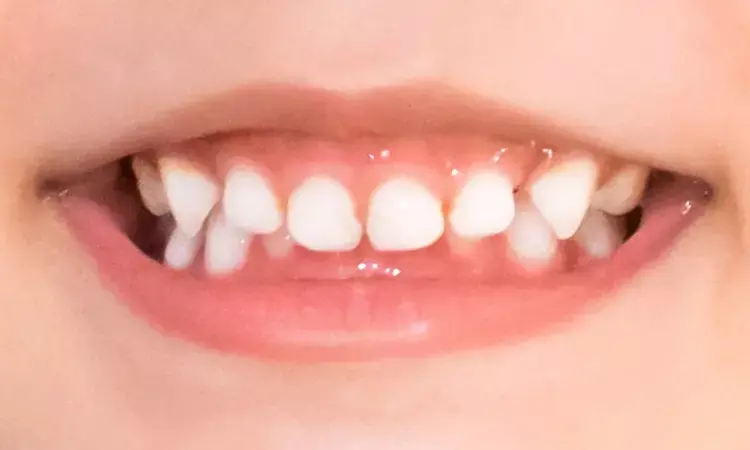
Among patients with Down syndrome occurrence of malocclusion was higher implying a higher need for orthodontic treatments than for NS subjects. Therefore patients with Down syndrome may require more preventive and interceptive orthodontic procedures to improve dental health suggests a new study published in the Special Care in Dentistry.
A study was done to evaluate the prevalence and significance of the malocclusion traits and orthodontic treatment needs of Down syndrome (DS) subjects with matched non-syndromic (NS) controls.
This cross-sectional study involved 222 subjects (50% DS, 50% NS) who were matched by gender and age. The casts were digitized into three-dimensional images. These images were used alongside the ten occlusal characteristics of the Dental Aesthetic Index (DAI) to determine malocclusion severity and the need for orthodontic treatment.
Results
There were 58 (52.3%) females and 53 (47.7%) males with a mean age of 18.4 ± 8.4 years in both groups. The most common and significant (p < .05) malocclusion traits among the DS subjects were missing teeth (56.2%), incisal spacing segments (73.0%), anterior maxillary irregularity (95.5%), mandibular overjet (36.0%), and full cusp deviation of the molar relationship (61.3%). On the other hand, increased maxillary overjet (69.3%) is a more significant (p < .05) trait amongst NS subjects. There were 85 (76.6%) DS subjects who presented severe malocclusion, which implies a highly orthodontic treatment need (DAI > 30). The DS showed some impact of malocclusion traits components of the DAI.
The occurrence of malocclusion was higher in DS, implying a higher need for orthodontic treatments than for NS subjects
Reference:
Syed Mohamed, AMF, Wei, TZ, Sean, CJ, Rosli, TI. Comparison of the malocclusion and orthodontic treatment needs of Down syndrome and non-syndromic subjects by using the dental aesthetics index. Spec Care Dentist. 2023; 43: 554–560. https://doi.org/10.1111/scd.12790
Keywords:
Patients, Down, syndrome, require, more, preventive, interceptive, orthodontic, procedures, improve health, Syed Mohamed, AMF, Wei, TZ, Sean, CJ, Rosli, TI, Special Care in Dentistry
Dr. Shravani Dali has completed her BDS from Pravara institute of medical sciences, loni. Following which she extensively worked in the healthcare sector for 2+ years. She has been actively involved in writing blogs in field of health and wellness. Currently she is pursuing her Masters of public health-health administration from Tata institute of social sciences. She can be contacted at editorial@medicaldialogues.in.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


