- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Apexification procedures tied to favorable tooth survival outcomes in necrotic immature permanent teeth
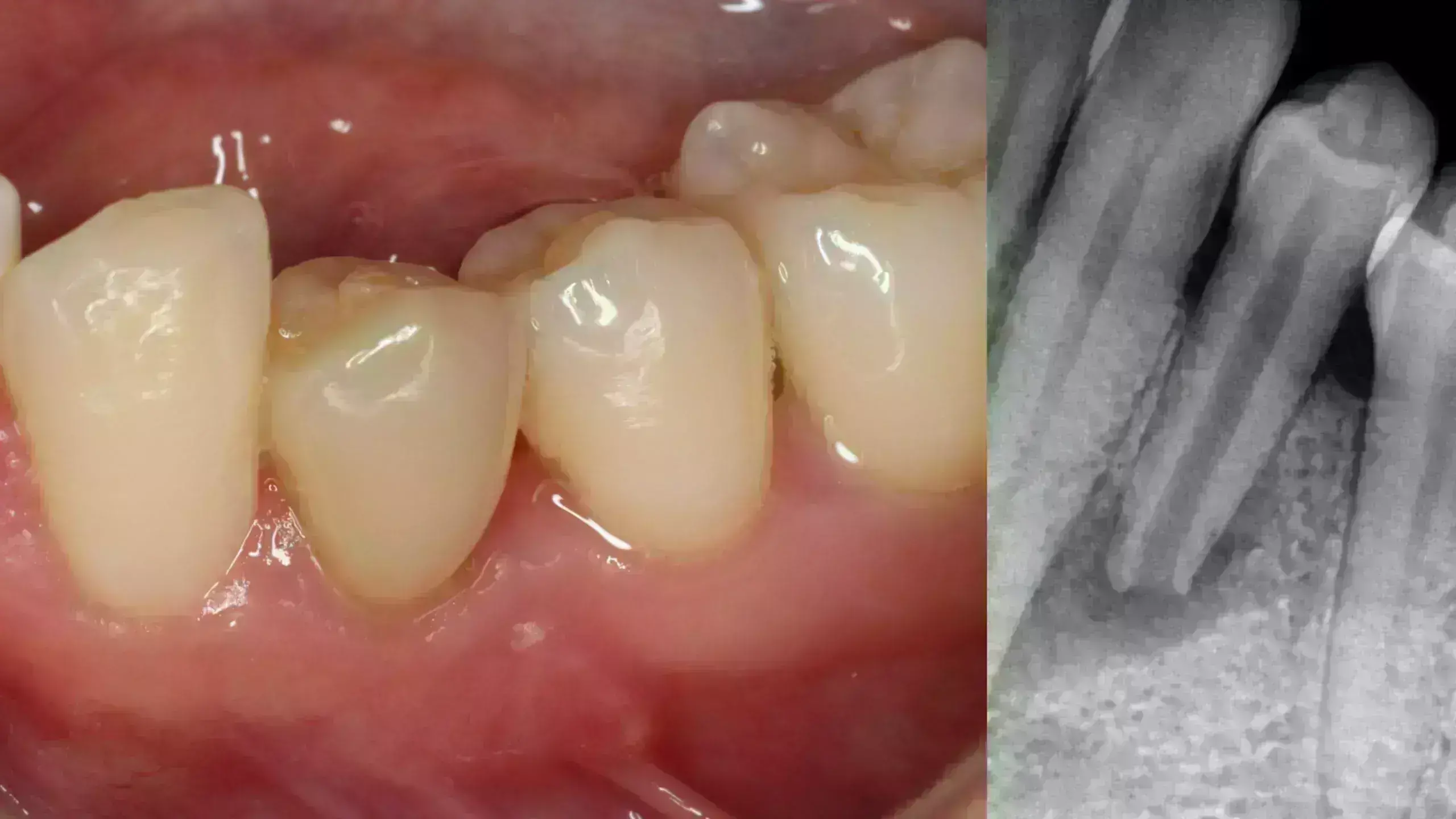
Apexification treatment may be indicated for immature permanent teeth after necrosis of the pulp, resulting from trauma or dental caries.
Apexification procedures are tied to favourable tooth survival outcomes in necrotic immature permanent teeth suggest a new study published in the Journal of Endodontics.
This epidemiological analysis used procedure codes from dental insurance claims data to identify apexification cases and evaluate survival at the tooth level.
Dental insurance claims data from New York State (2006–2019) and Massachusetts (2013–2018) were used in an observational, retrospective cohort study to evaluate the provision and treatment outcomes of apexification. Statistical analyses included Kaplan–Meier survival estimates and Cox proportional hazards regression. Cox proportional hazard regression was used to evaluate the hazard of adverse event occurrence by age, gender, tooth type, placement of a permanent restoration, and dental provider type. A sensitivity analysis evaluated potential bias in the survival estimates and adjusted hazard ratios (aHRs) due to differential loss to follow-up. Robust standard errors were used to account for potential dependence between teeth within an individual.
Results
The analytic cohort of 575 individuals included 632 teeth, with an average follow-up time of 64 months. The survival rates of apexification procedures were 95% at 1 year; 93% at 2 years; 90% at 3 years; and 86% at 5 years. Tooth retention following apexification was 98% at 1 year; 96% at 2 years; 95% at 3 years; and 90% at 5 years. Tooth type and subsequent placement of a permanent restoration were significant predictors of survival after apexification.
The procedural and tooth survival outcomes of apexification were high and comparable to studies that analyzed clinical data on tooth survival following apexification.p
Reference:
Apexification Outcomes in the United States: A Retrospective Cohort Study. Lorel E. Burns, Nihan Gencerliler, Kelly Terlizzi, Claudia Solis-Roman, Asgeir Sigurdsson, Heather T. Gold.
Open AccessPublished:July 27, 2023DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joen.2023.07.020
Keywords:
Apexification, procedures, tied, favourable, tooth, survival, outcomes, necrotic, immature, permanent teeth, Journal of Endodontics, Lorel E. Burns, Nihan Gencerliler, Kelly Terlizzi, Claudia Solis-Roman, Asgeir Sigurdsson, Heather T. Gold
Dr. Shravani Dali has completed her BDS from Pravara institute of medical sciences, loni. Following which she extensively worked in the healthcare sector for 2+ years. She has been actively involved in writing blogs in field of health and wellness. Currently she is pursuing her Masters of public health-health administration from Tata institute of social sciences. She can be contacted at editorial@medicaldialogues.in.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


