- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Attachment loss and periodontal inflamed surface area tied to HbA1c in T2DN patients
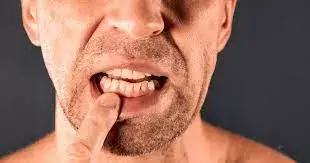
Clinical attachment loss and periodontal inflamed surface area are associated with glycemic status in patients with type 2 diabetic neuropathy according to a recent study published in the Journal of Periodontology.
The association between diabetic neuropathy with and without diabetic foot and periodontitis remains unaddressed in the literature. The present study was conducted to evaluate the frequency of patients with periodontitis and its severity, and to correlate clinical attachment loss (AL) and periodontal inflamed surface area (PISA) with HbA1c in Type 2 Diabetic Neuropathy (T2DN) patients with and without diabetic foot.
In this cross-sectional study, 310 patients with type 2 diabetic neuropathy (T2DN) were randomly selected, and the study comprised of 120 patients with type 2 diabetic neuropathy with diabetic foot and 155 patients with type 2 diabetic neuropathy without diabetic foot. All patients were assessed for periodontal parameters (bleeding on probing, probing depth, clinical attachment loss, oral hygiene index-simplified), plaque index, and PISA) and systemic parameters (HbA1c, fasting blood glucose, postprandial blood glucose, urinary albumin creatine ratio, erythrocyte sedimentation rate, and high-sensitivity C-reactive protein). Unpaired t-test and Chi-Square test were used to analyze quantitative data and qualitative data, respectively.
The results of the study are:
- The frequency of patients with periodontitis in patients with type 2 diabetic neuropathy with and without diabetic foot was 91.7% and 88.4%, respectively.
- The severity of periodontitis, periodontal inflamed surface area, and clinical attachment loss were higher in the diabetic foot group.
- Clinical attachment loss and periodontal inflamed surface area were significantly related to HbA1c in patients with type 2 diabetic neuropathy with and without diabetic foot.
Thus, the percentage of patients with periodontitis and the severity of periodontal destruction were high in type 2 diabetic neuropathy with diabetic foot. A significant correlation between periodontal inflamed surface area, and clinical attachment loss with glycemic status was found in patients with type 2 diabetic neuropathy with and without diabetic foot.
Reference:
Adhenkavil Radhakrishnan, Raji, et al. "Proportion and Severity of Periodontitis and Correlation of Periodontal Inflamed Surface Area With Glycemic Status in Patients With Type 2 Diabetic Neuropathy With and Without Diabetic Foot." Journal of Periodontology, vol. 93, no. 5, 2022, pp. 687-696.
Dr. Shravani Dali has completed her BDS from Pravara institute of medical sciences, loni. Following which she extensively worked in the healthcare sector for 2+ years. She has been actively involved in writing blogs in field of health and wellness. Currently she is pursuing her Masters of public health-health administration from Tata institute of social sciences. She can be contacted at editorial@medicaldialogues.in.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


