- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Dietary Inflammatory Index Linked to Periodontitis in U.S. Adults: Study
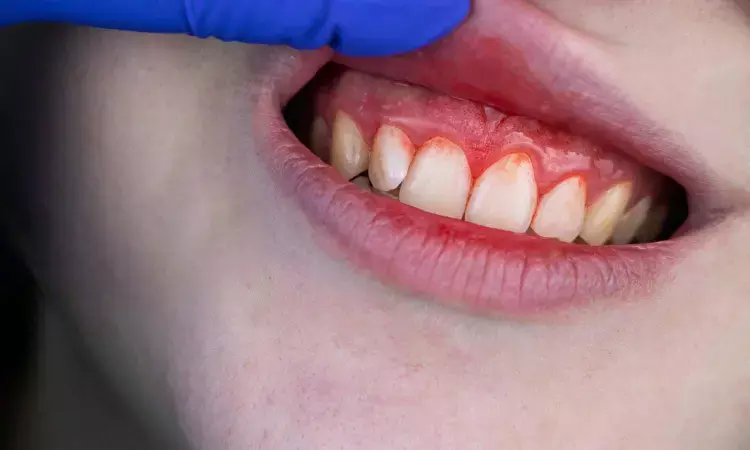
Researchers have found in a new study that higher Dietary Inflammatory Index (DII) scores were positively associated with prevalence of periodontitis among U.S. adults, highlighting the role of pro-inflammatory dietary patterns. Further findings also suggest a mechanistic link between biological aging, diet-induced inflammation, and periodontitis development.
Dietary patterns are associated with inflammatory states. However, there are few reports about its relationship with periodontitis and its mechanism. This study investigated the relationship between dietary inflammatory index (DII) and periodontitis, and the mediating role of biological aging in this relationship. Data from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey from 2009 to 2014 were utilized, including adults aged 20 years and above.
The relationship between DII and periodontitis was assessed using multivariate logistic regression analysis, and restricted cubic splines were employed to test for potential non-linear associations. Subgroup analyses were conducted to explore potential influencing factors related to DII and periodontitis. In addition, the mediating role of biological aging in dietary inflammatory indices and periodontitis was further explored. Results: A total of 10,096 participants were included in the study.
The results indicated a positive correlation between DII scores and the prevalence of periodontitis. In the fully adjusted model, participants in the highest DII quartile had a 23% higher risk of periodontitis compared to those in the lowest quartile (OR = 1.23, 95% CI: 1.01, 1.48, p = 0.04). Subgroup analysis consistently observed a positive correlation between DII and the risk of periodontitis across all subgroups. Mediation analyses suggest some direct and indirect effects of biological aging between a pro-inflammatory diet and periodontitis. DII scores were positively associated with the prevalence of periodontitis in U.S. adults, suggesting that dietary patterns may have a significant impact on the prevalence of periodontitis. It also provides further insight into the mechanistic link between biological aging-mediated DII and the development of periodontitis.
Reference:
Hua Haoyang , Xu Shencong , Wang Yifan , Zheng Yuanna , Xiang Fangyue. Association between dietary inflammatory index and periodontitis in American adults: exploring the mediating role of biological aging. Frontiers in Nutrition. Volume 12 - 2025. https://www.frontiersin.org/journals/nutrition/articles/10.3389/fnut.2025.1591830. DOI=10.3389/fnut.2025.1591830
Dr. Shravani Dali has completed her BDS from Pravara institute of medical sciences, loni. Following which she extensively worked in the healthcare sector for 2+ years. She has been actively involved in writing blogs in field of health and wellness. Currently she is pursuing her Masters of public health-health administration from Tata institute of social sciences. She can be contacted at editorial@medicaldialogues.in.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


