- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Digital enhancements fails to improve radiographic detection of dental calculus: Study
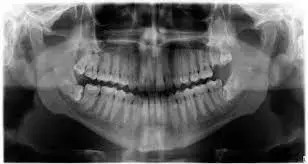
Digital enhancements are not tied with radiographic detection of dental calculus, according to a study published in the Journal of Periodontology.
The aim of this study was to determine if image enhancement improves a clinician's ability to identify the presence of calculus on digital radiographs.
Seventy-one hopeless teeth were collected from 34 patients. Teeth were stained with 1% methylene blue, the largest interproximal calculus deposit was scored, and photographs of each interproximal root surface were taken. The surface area of the calculus deposit was determined as a percentage of the total interproximal root surface area. Digital radiographs of teeth taken before extraction were modified using the following enhancements: auto-contrast, emboss, invert, and sharpen. The radiographic presence of calculus was determined by two examiners. Sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value (PPV), and negative predictive value (NPV) were calculated for each examiner and enhancement. A receiver operating characteristic curve was used to compare differences between the image enhancements in the detection of dental calculus. The kappa statistic was used to compare ratings between examiners.
The Results of the study are as follows:
None of the enhanced images was statistically superior to original images in identifying radiographic calculus (P > 0.05). The average sensitivity of digital radiography was 50%, average specificity was 82.2%, PPV was 94%, and NPV 23.2%. A threshold of >30% of interproximal root surface covered with calculus and increasing size of deposits were associated with improved detection (P < 0.05).
Thus, the researchers concluded that digital enhancements do not significantly improve radiographic detection of dental calculus. As an area of calculus on the root surface and size of calculus deposits increased, the sensitivity of detection also increased.
Reference:
A study named, "Accuracy of dental calculus detection using digital radiography and image manipulation" by Jenna C. Hyer et al. published in the Journal of Periodontology.
Dr. Shravani Dali has completed her BDS from Pravara institute of medical sciences, loni. Following which she extensively worked in the healthcare sector for 2+ years. She has been actively involved in writing blogs in field of health and wellness. Currently she is pursuing her Masters of public health-health administration from Tata institute of social sciences. She can be contacted at editorial@medicaldialogues.in.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


