- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Digital Replication technique may accurately restore original crown morphology, suggests study
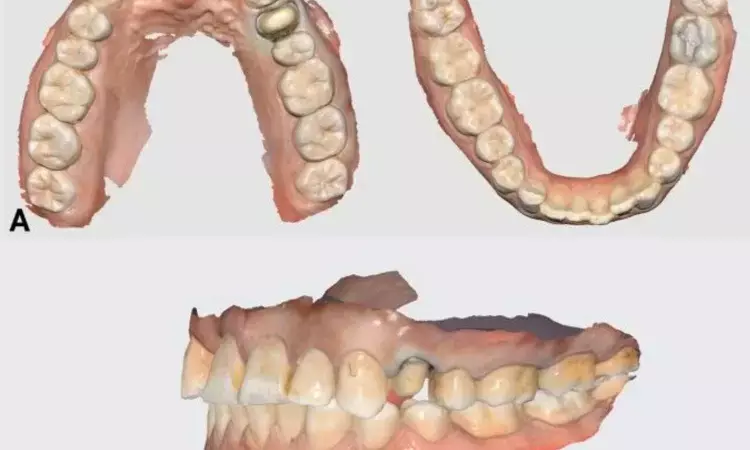
Researchers have found in a new study that Digital replication technique successfully restored the original crown morphology with high accuracy. However, the dimensional accuracy of all-ceramic crowns varied with the type of CAD/CAM porcelain material used, with lithium disilicate glass-ceramic demonstrating the most superior results.
The study aimed to evaluate the three-dimensional accuracy of computer-aided design and computer-aided manufacturing (CAD/CAM) in fabricating all-ceramic crowns using various cuttable materials, assessed through reverse engineering.
The original resin tooth morphology of the left maxillary mesial incisor and left maxillary first molar from a standard resin tooth model, along with the two corresponding prepared teeth, were scanned and imported into exocad software. The digitally reproduced crown morphology was utilized to fabricate crowns from cut porcelain-reinforced resin ceramic (Uh group, Upcera Hyramic), lithium disilicate glass-ceramic (e.max group, IPS e.max Cad), and zirconia ceramic (Ue group, Upcera Explore).
All specimens were subsequently rescanned, and the root mean square (RMS) values were calculated after overlaying with the original crown CAD data using the 3D analysis software Geomagic Studio 2013 to compare the dimensional accuracy. Results: Among the mesial incisor and first molar specimens, the e.max group demonstrated the highest dimensional accuracy of the all-ceramic crowns, followed by the Ue group, while the Uh group exhibited the lowest accuracy.
The differences in dimensional accuracy among the three groups were statistically significant (P < 0.05). The digital replication technique effectively restored the original crown morphology with a high degree of accuracy. For the same CAM pattern, the dimensional accuracy of all-ceramic crowns varied depending on the CAD/CAM porcelain material, with lithium disilicate glass-ceramic showing the superior results.
Reference:
Wang, H., Qu, W., Wang, T. et al. Accuracy analysis of all-ceramic crowns with different materials in CAD/CAM digital replication mode. BMC Oral Health 25, 491 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12903-025-05892-9
Dr. Shravani Dali has completed her BDS from Pravara institute of medical sciences, loni. Following which she extensively worked in the healthcare sector for 2+ years. She has been actively involved in writing blogs in field of health and wellness. Currently she is pursuing her Masters of public health-health administration from Tata institute of social sciences. She can be contacted at editorial@medicaldialogues.in.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


