- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Digital technique may help manufacture Removable partial denture frameworks accurately: Study
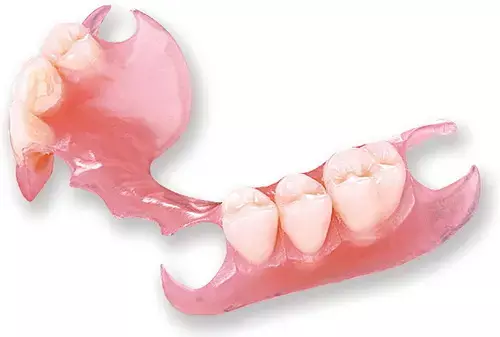
Digital technique for Removable partial denture (RPD) frameworks is accurate, suggests a study published in the Journal of Prosthetic Dentistry.
Removable partial dentures (RPDs) are traditionally made by casting, a complex, error-prone, and time-consuming process. Computer-aided design and computer-aided manufacturing (CAD-CAM) RPD systems may simplify the clinical steps and minimize errors; however, the accuracy of CAD-CAM RPD systems is unclear.
A team of researchers conducted a study to determine whether CAD-CAM systems are accurate for the manufacturing of Removable partial denture (RPD) frameworks.
A literature search was conducted through Medline-PubMed, Scopus, Lilacs, Web of Science, and Cochrane Library databases using specific keywords for articles published up to November 2019. Three reviewers obtained data and compared the results. All studies evaluated the framework accuracy or fit of prostheses fabricated with conventional and digital techniques.
The results of the study are as follows:
- A total of 7 articles, 2 clinical studies, and 5 in vitro studies that complied with the inclusion criteria were evaluated.
- One in vitro study compared indirect (extraoral) and direct (intraoral) scanning for partially edentulous ridges and shows that digital scans were better than conventional impressions in terms of trueness.
- In the other studies included, although the frameworks analyzed had clinically acceptable discrepancies (<311 μm), the material influenced the fit.
- Polyetheretherketone (PEEK) showed better fit than traditional metal cast RPDs. Co-Cr alloy RPDs produced by rapid prototyping exhibited the highest discrepancies when produced by sintering laser melting.
Thus, the researchers concluded that the digital technique for RPD frameworks is accurate. In the studies included, the analyzed frameworks had clinically acceptable gaps, but the results were heterogeneous among studies because the articles used different measurement methods with small sample sizes. Few studies discussed the long-term clinical performance. The digital technique for Removable partial denture (RPD) frameworks was accurate because the misfits and mismatches found in in vitro and clinical studies were within the acceptable clinical limit for RPDs.
Reference:
Accuracy of CAD-CAM systems for removable partial denture framework fabrication: A systematic review by Ana LarisseCarneiro Pereira et al published in The Journal of Prosthetic Dentistry
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.prosdent.2020.01.003
Dr. Shravani Dali has completed her BDS from Pravara institute of medical sciences, loni. Following which she extensively worked in the healthcare sector for 2+ years. She has been actively involved in writing blogs in field of health and wellness. Currently she is pursuing her Masters of public health-health administration from Tata institute of social sciences. She can be contacted at editorial@medicaldialogues.in.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


