- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
EGCG may improve outcome of periodontal non-surgical periodontal treatment: Study
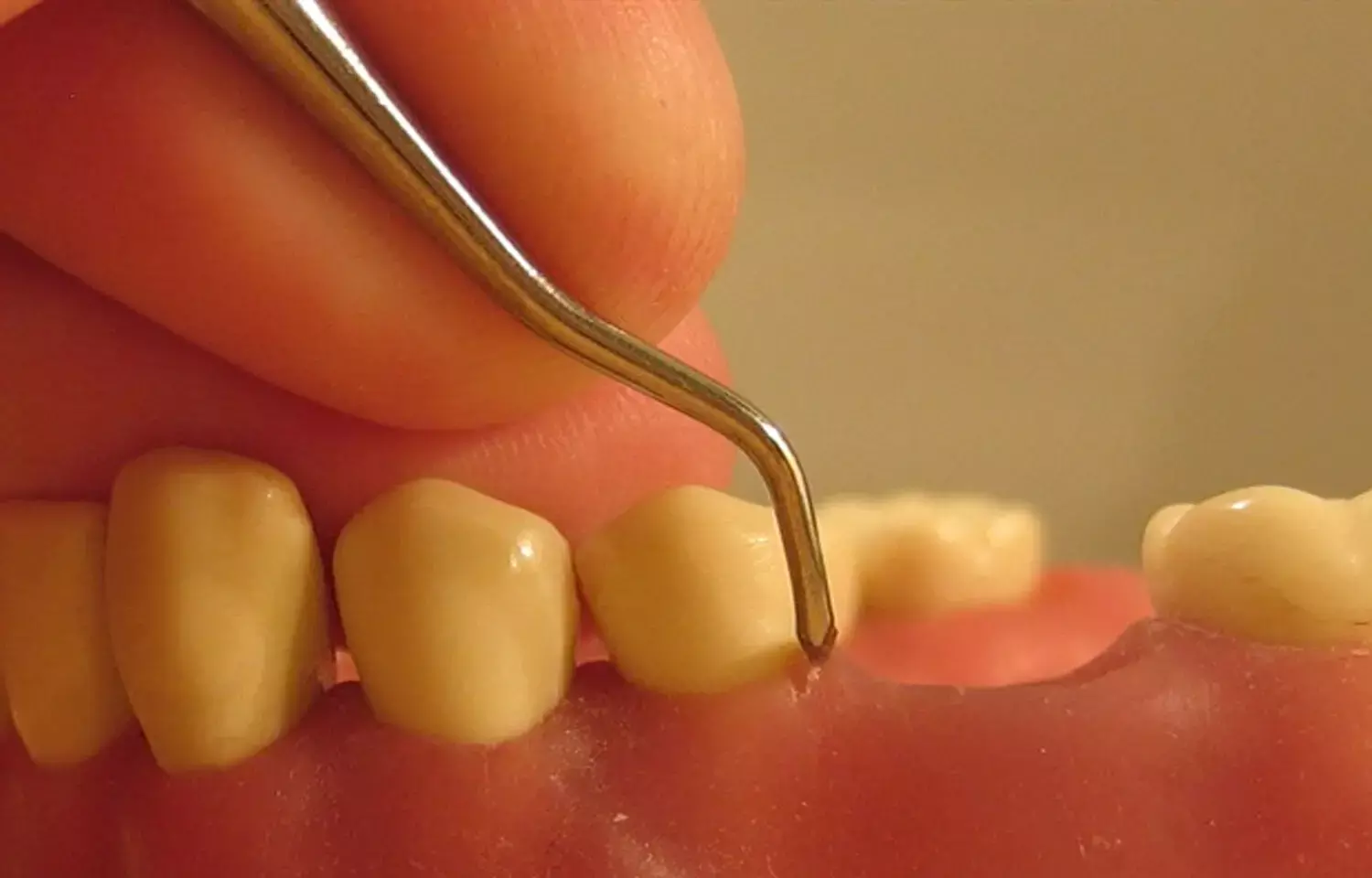
Researchers have observed that the purified Epigallocatechin Gallate showed the potential to improve the outcome of periodontal non-surgical treatment and the new-type scaler tip provided an alternative vehicle for subgingival medication.
The study is published in the BMC Oral Health Journal.
Epigallocatechin Gallate (EGCG) as green tea catechins possessed antibacterial and anti-inflammatory effects on periodontal disease. Green tea catechins extracted from Camellia sinesis have been reported to possess an antibacterial effect against gram-negative anaerobic rods. Mechanical debridement as scaling and root planing (SRP) has been repeatedly demonstrated to be effective to remove subgingival pathogens and lead to an improvement of periodontal status.
Therefore, Yanfeng Wang and colleagues from the Department of Periodontology, Peking University School and Hospital of Stomatology, National Engineering Laboratory for Digital and Material Technology of Stomatology, Beijing Key Laboratory of Digital Stomatology, Beijing, China conducted this study to evaluate the clinical and microbiological efficacy of scaling and root planing (SRP) using EGCG aqueous solution as coolants through a new-type ultrasonic scaler tip on chronic periodontitis.
This split-mouth, the randomized clinical trial included 20 patients (2 drop-outs) with chronic periodontitis and the maxillary contra-lateral sides were allocated into test and control groups randomly. Through the new-type scaler tip, 762 sites with probing depth (PD) ≥ 4 mm were treated by SRP using EGCG solution or distilled water as coolants respectively. Clinical parameters and red complex pathogens in the subgingival microbiome were evaluated at baseline, 3, and 6 months after treatments.
It was seen that during 6 months, the SRP plus EGCG medication contributed to additional PD reduction as 0.33 mm and gain of clinical attachment level as 0.3 mm compared with SRP alone, an approximate 8% more sites obtained PD reduction ≥ of 2 mm (p < 0.05). Meanwhile, the mean relative abundance of Tannerella forsythia was significantly lower in the combined treatment group (p < 0.05).
Hence, the authors concluded that "the purified EGCG showed the potential to improve the outcome of non-surgical periodontal treatment and the new-type scaler tip provided an alternative vehicle for subgingival medication."
Dr. Nandita Mohan is a practicing pediatric dentist with more than 5 years of clinical work experience. Along with this, she is equally interested in keeping herself up to date about the latest developments in the field of medicine and dentistry which is the driving force for her to be in association with Medical Dialogues. She also has her name attached with many publications; both national and international. She has pursued her BDS from Rajiv Gandhi University of Health Sciences, Bangalore and later went to enter her dream specialty (MDS) in the Department of Pedodontics and Preventive Dentistry from Pt. B.D. Sharma University of Health Sciences. Through all the years of experience, her core interest in learning something new has never stopped. She can be contacted at editorial@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


