- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Ferromagnetic/paramagnetic orthodontic wires may create artefacts during MRI due to local alteration of magnetic field homogeneity: Study
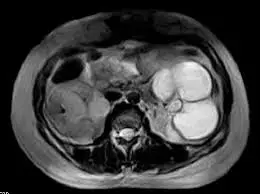
Ferromagnetic/paramagnetic orthodontic wires may create artefacts during MRI due to local alteration of magnetic field homogeneity suggests a study published in the Dentomaxillofacial Radiology.
A study was done to evaluate magnetic susceptibility artefacts produced by orthodontic wires on MRI and the influence of wire properties and MRI image sequences on the magnitude of the artefact. Arch form orthodontic wires [four stainless steels (SS), one cobalt chromium (CC) alloy, 13 titanium (Ti) alloys] were embedded in a polyester phantom, and scanned using a 1.5-T superconducting magnet scanner with an eight-channel phased-array coil. All wires were scanned with T1-weighted spin echo (SE) and gradient echo (GRE) sequences according to the American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM) F2119-07 standard. The phantom also scanned other eight sequences. Artefacts were measured using the ASTM F2119-07 definition and OsiriX software. Artefact volume was analysed according to metal composition, wire length, number of wires, wire thickness, and imaging sequence as factors.
Results: With SE/GRE, black/white artefacts volumes from all SS wires were significantly larger than those produced by CC and Ti wires (P < .01). With the GRE, the black artefacts volume was the highest with the SS wires. With the SE, the black artefacts volume was small, whereas white artefacts were noticeable. The cranio-caudal extent of the artefacts was significantly longer with SS wires (P < .01). Although a direct relationship of wire length, number of wires, and wire thickness with artefact volume was noted, these factors did not influence artefact extension in the cranio-caudal direction. Ferromagnetic/paramagnetic orthodontic wires create artefacts due to local alteration of magnetic field homogeneity. The SS-type wires produced the largest artefacts followed by CC and Ti.
Reference:
Yuri Iwamoto, Hiroaki Shimamoto, Doaa Felemban, Tomoyuki Terai, Sven Kreiborg, Sanjay M Mallya, Fan-pei Gloria Yang, Chihiro Tanikawa, Shumei Murakami, MRI susceptibility artefacts caused by orthodontic wire, Dentomaxillofacial Radiology, 2024;, twae023, https://doi.org/10.1093/dmfr/twae023
Dr. Shravani Dali has completed her BDS from Pravara institute of medical sciences, loni. Following which she extensively worked in the healthcare sector for 2+ years. She has been actively involved in writing blogs in field of health and wellness. Currently she is pursuing her Masters of public health-health administration from Tata institute of social sciences. She can be contacted at editorial@medicaldialogues.in.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


