- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Ginge-Cal promising material for treatment of infected root canal when used as obturation material: Study
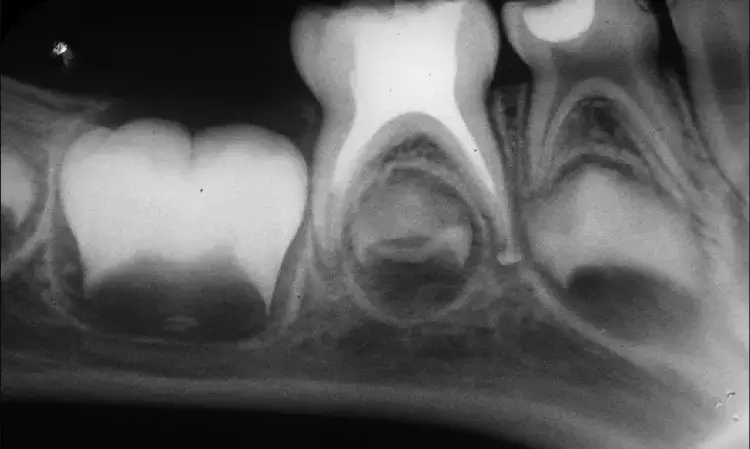
Ginge-Cal is a promising material for treating infected root canals when used as obturation material suggests a study published in the International Journal of Dentistry.
The tendency to use dental materials of plant origin is one of the prevailing trends in dentistry to reduce exposure to materials that could have some toxic impact in the long term. A study was done to evaluate the efficacy of calcium hydroxide combined with gingerols (Ginge-Cal) as a novel obturation material for treating infected primary teeth and decreasing the recurrence of infection. The study was conducted on 30 lower primary molars with infected pulp for children aged 4–8 years. The sample was randomly divided into two groups depending on the tested obturation material: Ginge-Cal group and the Metapex group. The evaluation was done by different parameters clinically and radiographically at various intervals up to 12 months.
Results. Based on chi-squared and McNamara’s test with a 5% significance level, the clinical results indicated that Ginge-Cal group was more effective than the Metapex group in reducing or eliminating pain () after 1 week, sensitivity to percussion () at 3 months of follow-up, purulent swelling () at 6 and 9 months of follow-up, fistula, and tooth mobility. The radiographic results, based on the periapical and furcation area radiolucency at 12 months of follow-up, favored Ginge-Cal group over the Metapex group (), (), respectively. There were no statistically significant differences in pathological root resorption and periodontal space. The differences within the Ginge-Cal group were directly influenced by the time intervals in a statistically significant manner, ranging from () to (). The success percentage was 87.5% for Ginge-Cal group and 64.3% for Metapex group. Ginge-Cal can be considered a promising material for treating the infected root canal when used as an obturation material for the infected root canal.
Reference:
Fathi A. Qasem, Salwa M. Awad, Rizk A. Elagamy, "Effectiveness of Calcium Hydroxide and Gingerols Mixture as a Novel Obturation Material for Infected Root in Primary Teeth: A Randomized Clinical Trial", International Journal of Dentistry, vol. 2024, Article ID 5528260, 10 pages, 2024. https://doi.org/10.1155/2024/5528260
Dr. Shravani Dali has completed her BDS from Pravara institute of medical sciences, loni. Following which she extensively worked in the healthcare sector for 2+ years. She has been actively involved in writing blogs in field of health and wellness. Currently she is pursuing her Masters of public health-health administration from Tata institute of social sciences. She can be contacted at editorial@medicaldialogues.in.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


