- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Higher Rates of Carotid Artery Calcification and Pulp Stones Found in Diabetics: Study
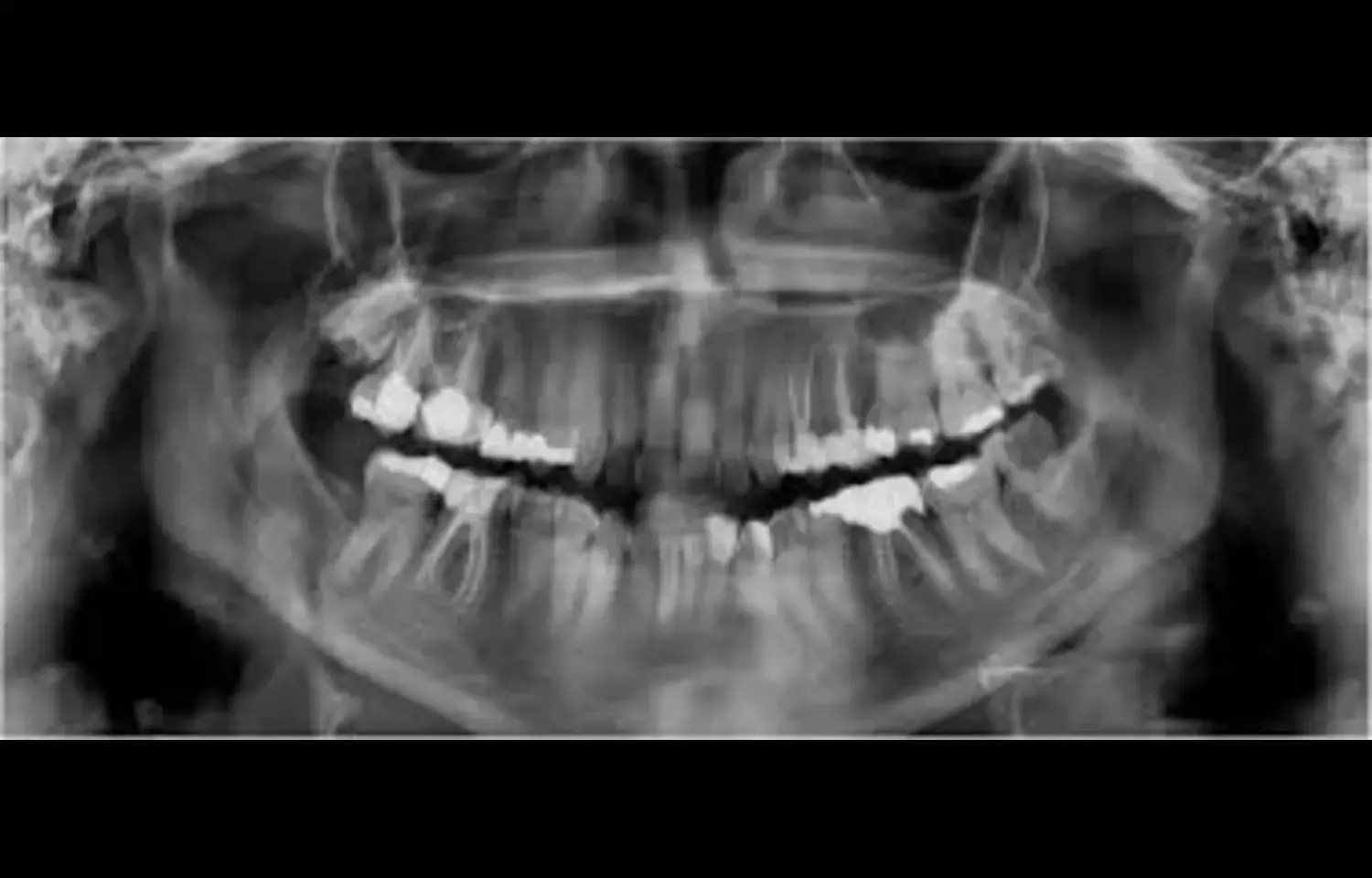
A new retrospective observational study published in BMC Endocrine Disorders reports that individuals with diabetes mellitus have significantly higher rates of carotid artery calcifications (CACs) and dental pulp stones compared to non-diabetic controls, based on routine panoramic radiographs.
Among 107 diabetic patients, 41.1% showed evidence of CACs versus only 14% in 300 healthy individuals—a relative risk (RR) of 2.60 (P < 0.05). Similarly, pulp stones were present in 38.3% of diabetics compared to 21.3% of controls, translating to an RR of 1.8 (95% CI: 1.3–2.48, P < 0.05) mdpi.com+4bmcendocrdisord.biomedcentral.com+4pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov+4. These findings suggest that panoramic radiographic screening—commonly used in dental practices—can reveal incidental signs of systemic calcification and dental pulp changes, making it a practical tool for early risk detection.
Detecting CACs may signal underlying atherosclerosis and increased cardiovascular risk, while pulp stones may correlate with chronic inflammation and metabolic disturbances present in diabetes mdpi.com. Given the accessibility of panoramic imaging and its ability to capture both jaw structures and adjacent cervical anatomy, the study recommends incorporating it into routine dental examinations for diabetic patients.
Early identification of these radiographic markers could prompt timely referral to endocrinologists or cardiologists for preventive strategies, including tighter glycemic control and cardiovascular risk management. While the cross-sectional design limits causal inferences, the statistically significant associations underline the need for further longitudinal research. For now, panoramic radiography could offer dual diagnostic value—monitoring dental health and flagging potential systemic complications in one scan.
Dr. Shravani Dali has completed her BDS from Pravara institute of medical sciences, loni. Following which she extensively worked in the healthcare sector for 2+ years. She has been actively involved in writing blogs in field of health and wellness. Currently she is pursuing her Masters of public health-health administration from Tata institute of social sciences. She can be contacted at editorial@medicaldialogues.in.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


