- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Immediate Implant Placement With Loading more beneficial in midfacial mucosal level in maxillary esthetic area
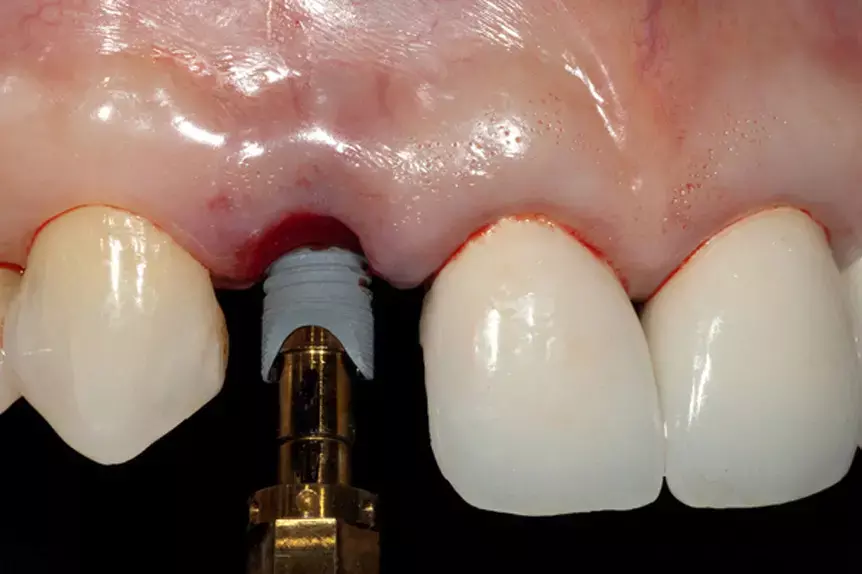
Immediate Implant Placement With Immediate Loading Offers Greater Benefits in the midfacial mucosal level in the maxillary esthetic area suggests a new study published in The International Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial implants.
The study was conducted to determine whether immediate implant placement and loading renders different outcomes from delayed loading with respect to midfacial mucosal level in the maxillary esthetic area.
A literature search was conducted in four electronic databases (PubMed, Web of Science, Embase, and Cochrane), identifying eligible clinical studies published prior to December 2021. Only randomized controlled trials (RCTs) comparing immediate implant placement with or without immediate loading in the maxillary esthetic zone with a mean follow-up of at least 12 months were selected for qualitative analysis and meta-analysis. The Cochrane Risk of Bias tool was adopted to assess the quality of the evidence. The heterogeneity between the pooled literature was analyzed through the chi-square test (P < .05) and quantified by the I2 index. A mixed-effects model was applied if it appeared that there was noteworthy heterogeneity; otherwise, a random-effects model was chosen. For continuous outcomes, the estimate of relative effect was presented to display the standardized mean differences (SMDs) and 95% CIs. For dichotomous variables, the Mantel-Haenszel statistical method was applied with effect sizes expressed as risk ratios (RRs) and 95% CIs.
Results:
Out of 5,553 records, 8 RCTs were involved, providing data for 324 immediately placed implants (immediate implants subjected to immediate loading [IPIL]: 163; immediate implants subjected to delayed loading [IPDL]: 161) that had been in function within 12 to 60 months. Meta-analyses revealed significantly lower midfacial mucosal level changes for IPIL compared with IPDL, pointing to 0.48 mm (95% CI: –0.84 to –0.12; P = .01), as well as more significant papillary recession after IPDL (SMD –0.16; 95% CI: –0.31 to 0.00; P = .04). The differences regarding implant survival and marginal bone loss between the two loading groups showed no statistical significance. The result of meta-analyses revealed similar plaque score (SMD 0.03; 95% CI: –0.22 to 0.29; P = .79) and probing depth (SMD –0.09; 95% CI: –0.23 to 0.05; P = .21) for IPIL and IPDL. On the other hand, IPIL induced a trend toward more bleeding on probing (SMD 0.22; 95% CI: 0.01 to 0.42; P = .04) and less change in facial ridge dimension (SMD 0.94; 95% CI: –1.49 to –0.39; P < .01).
After a follow-up ranging from 12 to 60 months, midfacial mucosa level change was 0.48 mm lower following IPIL compared with IPDL. Immediate implant placement and loading is conducive to the preservation of physiologic soft and hard tissue architecture, appearing to offer considerable benefits in the anterior zone. In summary, IPIL should be considered in the esthetic zone if the primary implant stability permits.
Reference:
Rao Qin, MS/Yue Chen, MS/Chong Han, MS/Dongchao Wu, MS/Feiyan Yu, PhD/Dongning He. Immediate Implant Placement With or Without Immediate provisionalization in the Maxillary Esthetic Zone: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. The International Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial implants. DOI: 10.11607/jomi.10112
Keywords:
Immediate, Implant, Placement, Immediate, Loading, Offers, Greater, Benefits, midfacial, mucosal level, maxillary esthetic area, Rao Qin, MS/Yue Chen, MS/Chong Han, MS/Dongchao Wu, MS/Feiyan Yu, PhD/Dongning He,The International Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial implants.
Dr. Shravani Dali has completed her BDS from Pravara institute of medical sciences, loni. Following which she extensively worked in the healthcare sector for 2+ years. She has been actively involved in writing blogs in field of health and wellness. Currently she is pursuing her Masters of public health-health administration from Tata institute of social sciences. She can be contacted at editorial@medicaldialogues.in.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


