- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Implant surface modifications additional risk factor for development of Peri-implantitis
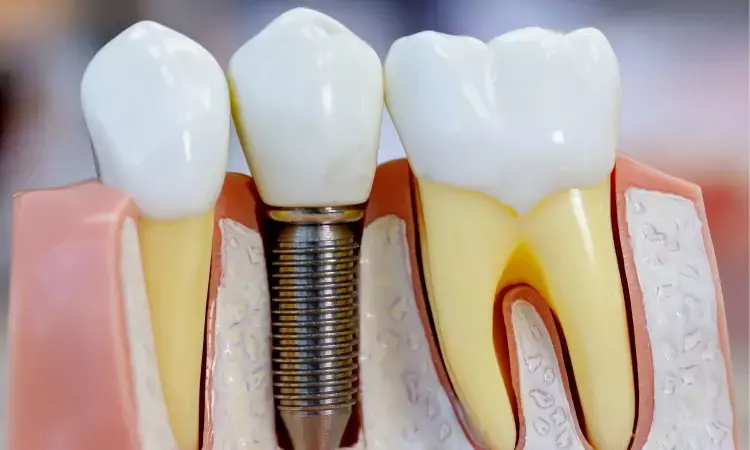
Around one in five dental implants are affected by Peri-implantitis (PI), with the disease often occurring as early as two years after functional loading.
A recent study published in the Journal of Periodontology has shown that the implant surface can differently influence the microbiome linked to the disease, implying that surface topography must be integrated into the multi-factorial causes of peri-implant diseases.
Given the limited understanding of the effect of implant surface modifications on the peri-implant microbiome, the main objective of the present study was to investigate the peri-implant communities in different surface types to gain insights into the influence of these surfaces on the development of PI.
One hundred six healthy individuals with anodized (AN), hydroxyapatite-coated (HA) or sandblasted acid-etched implants were recruited. These implants have been functional for more than six months and were categorized into healthy (H) or PI. Peri-implant biofilm was analyzed using 16S rRNA gene sequencing and compared between health/disease and HA/SLA/AN using community-level and taxa-level metrics.
Key Results of the study are:
- The healthy implants showed no significant variations in clustering, alpha- or beta-diversity due to surface modification.
- AN and HA surfaces displayed differences between health and PI.
- AN and HA surfaces differed in the magnitude and diversity of differences between health and PI.
- The abundances of six species from the genera Shuttleworthia, Scardovia, and Prevotella decreased in AN implants with PI. In comparison, 18 species from the genera Fretibacterium, Tannerella, Treponema, and Fusobacterium showed increased levels.
- In HA implants with PI, 20 species belonging to the genera Streptococcus, Lactobacillus, Veillonella, Rothia, and family Ruminococcaceae were depleted, and Peptostreptococcaceae, Atopobiaceae, Veillonellaceae, Porphyromonadaceae, Desulfobulbaceae, and order Synergistales were enriched.
Dental implants restore impaired dental function, and osseointegration is vital to implant success. Case selection is essential for determining the type of implant for each patient.
They said, “Our research indicates that the surface topography of implants can modify the microbiome associated with peri-implant disease, and the extent to which this occurs varies depending on the specific surface modifications. This finding highlights the complex causes of peri-implant diseases and suggests that the topography of the implant surface may directly or indirectly affect the likelihood of developing these diseases.”
The small sample size and cross-sectional study design were the limitations of the study.
Reference:
Khaled Sinjab et al. Impact of surface characteristics on the peri-implant microbiome in health and disease. Journal of Periodontology. https://doi.org/10.1002/JPER.23-0205
BDS, MDS in Periodontics and Implantology
Dr. Aditi Yadav is a BDS, MDS in Periodontics and Implantology. She has a clinical experience of 5 years as a laser dental surgeon. She also has a Diploma in clinical research and pharmacovigilance and is a Certified data scientist. She is currently working as a content developer in e-health services. Dr. Yadav has a keen interest in Medical Journalism and is actively involved in Medical Research writing.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


