- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Localized stage II/III periodontitis risk varies with metabolic biomarkers in young adults: Study
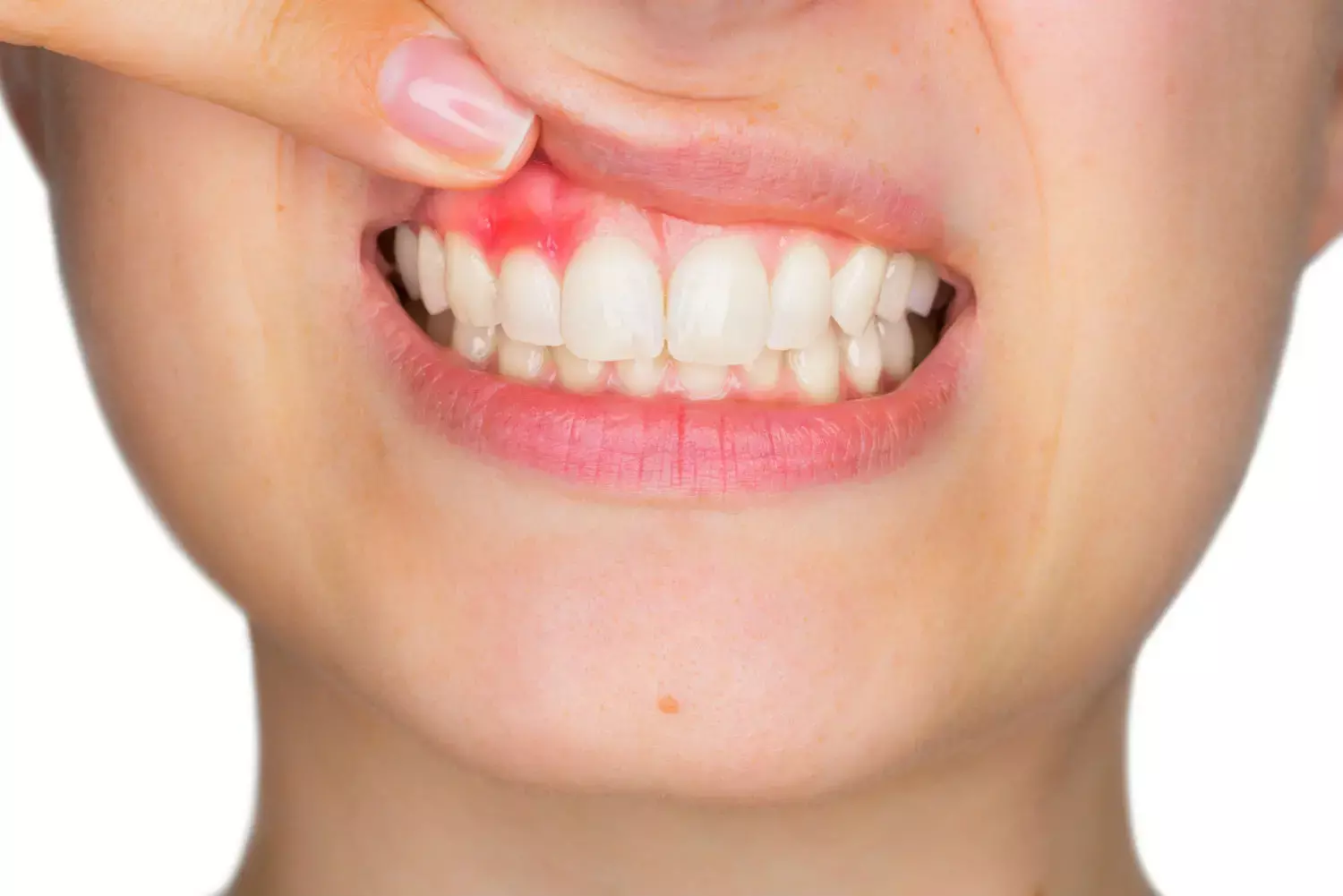
The risk of localized stage II/III periodontitis may vary with metabolic components in young adults, according to a study published in the Journal of Periodontology.
Periodontitis, also called gum disease, is a serious gum infection that damages the soft tissue and, without treatment, can destroy the bone that supports your teeth. Periodontitis can cause teeth to loosen or lead to tooth loss.
Periodontitis is common but largely preventable. It's usually the result of poor oral hygiene. Brushing at least twice a day, flossing daily and getting regular dental checkups can greatly improve your chances of successful treatment for periodontitis and can also reduce your chance of developing it.
A group of researchers from Taiwan conducted a study to investigate the associations between metabolic risk factors and periodontitis in young adults.
The study included 1,123 participants, aged 19-40 years in Taiwan. Metabolic syndrome components were defined by the International Diabetes Federation criteria. Localized periodontitis was graded to healthy (n =828) and stage II/III (n =295) according to the 2017 criteria of the world workshop. Multiple logistic regression analyses with adjustment for sex, age, betel nut consumption and smoking, were used to determine the associations.
The results of this study are as follows:
· Greater waist circumference, serum triglycerides and serum uric acid were associated with higher localized stage II/III periodontitis risk.
· There were no associations between total cholesterol, high-density lipoprotein and blood pressure.
· There was a non-linear association of fasting glucose with localized stage II/III periodontitis, where the turning point was 105 mg/dL.
Thus, the researchers concluded that the risks of localized stage II/III periodontitis vary with metabolic components, in which waist circumference, serum triglycerides and serum uric acid were the risk factors, whereas plasma glucose showed a non-linear relationship in young adults.
Reference:
A study titled, "Associations between metabolic biomarkers and localized stage II/III periodontitis in young adults: the CHIEF Oral Health" study by Tsai K et.a l published in the Journal of Clinical Periodontology.
https://doi.org/10.1111/jcpe.13555
Dr. Shravani Dali has completed her BDS from Pravara institute of medical sciences, loni. Following which she extensively worked in the healthcare sector for 2+ years. She has been actively involved in writing blogs in field of health and wellness. Currently she is pursuing her Masters of public health-health administration from Tata institute of social sciences. She can be contacted at editorial@medicaldialogues.in.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


