- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Needling vs Non-Needling Therapies: New Meta-Analysis Reveals Most Effective Treatment for TMD Pain
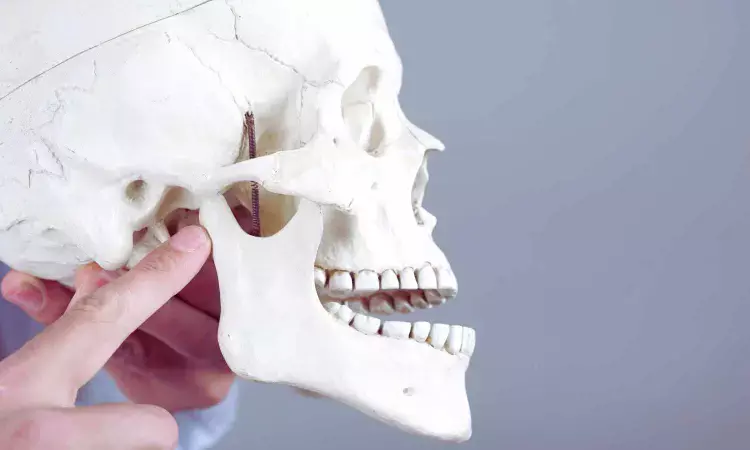
China: Researchers from Wuhan University have conducted a comprehensive Bayesian network meta-analysis comparing needling and non-needling therapies for temporomandibular disorders (TMD), offering new insights into which interventions deliver the most meaningful pain relief and functional improvement.
- A total of 37 randomized controlled trials with 2,581 participants were included in the analysis.
- Dry needling therapy (DNT) emerged as the most effective treatment for reducing pain, showing the greatest decrease in VAS pain scores with a mean difference of –1.61 compared to controls.
- The analgesic effect of DNT was stronger than that of traditional acupuncture and pharmacologic injection therapy.
- Both DNT and acupuncture-based combined therapy (ACT) achieved pain reduction levels that surpassed the minimal clinically important difference for TMD, indicating meaningful clinical benefit.
- ACT, which combines acupuncture with additional therapeutic modalities, showed the best overall functional improvement among all interventions.
- ACT reduced pain indices more effectively than traditional acupuncture and demonstrated the highest treatment efficacy rate, nearly doubling the improvement seen in control groups.
- ACT provided slight improvements in disability measures compared to traditional acupuncture, though the difference was minimal.
- None of the therapies evaluated—including DNT, ACT, and TAT—produced significant improvements in maximal mouth opening.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


