- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Partial pulpotomy better in terms of clinical and radiographic treatment outcome
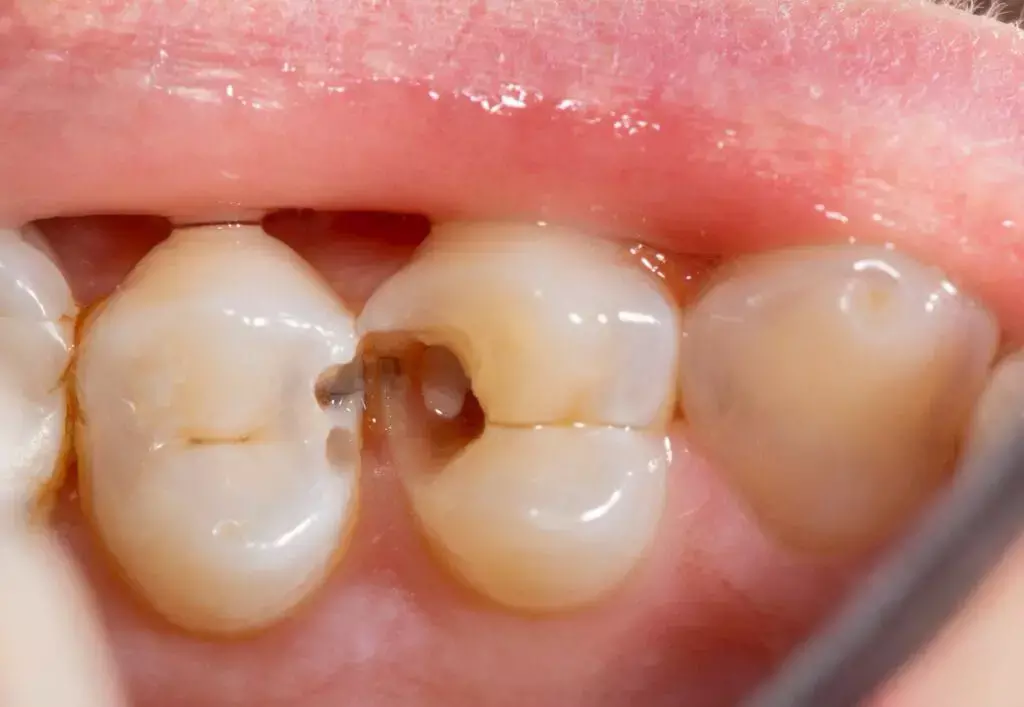
Partial pulpotomy showed comparable results to full pulpotomy in terms of clinical/radiographic treatment outcome suggests a recent study published in the International Endodontic Journal.
A study was conducted to assess and compare the clinical and radiographic outcome of partial pulpotomy and full pulpotomy using Biodentine in cariously exposed mature molar teeth with symptoms indicative of irreversible pulpitis This study is a an unicentric, double-arm, randomised superiority clinical trial with parallel experimental groups.
Fifty mature permanent molar teeth with carious exposures with symptoms indicative of irreversible pulpitis were randomly allocated equally into two groups.
Partial Pulpotomy (PP) and Full Pulpotomy (FP) was performed in the first and second group respectively following standardised protocols.
Exposed pulp tissue was removed up to a depth of 2-3 mm for partial pulpotomy whereas complete coronal pulp tissue was removed up to the level of root orifices for full pulpotomy. Haemostasis was achieved with placement of 2.5% sodium hypochlorite-moistened cotton pellets placed on amputated pulp tissue for a maximum of 10 minutes.
Biodentine was used as the pulp capping material.
Pain scores were evaluated using 11-point visual analogue scale (VAS) pre-operatively, at 24 hours, 48 hours and 7th day after the intervention(s).
Clinical and radiographic evaluation was done at 3 months, 6 months and 1 year.
The data was statistically analysed using chi-square test, Mann-Whitney U test, Friedman's test and Wilcoxon signed-rank test.
The significance level was predetermined at p<0.05.
Cumulative survival probabilities were assessed at 12 months using Kaplan Meier analysis.
Results:
Intra-group analysis of pain scores revealed significant reduction in pain scores pre-operatively and at 24 hours, 48 hours and 7th day in both the groups.
However, the difference in the pain score(s) reduction between both the groups was not statistically significant at any time interval (p > 0.05).
At 1 year follow up, the success rate was 88% (22/25) and 91.6% (22/24) for PP and FP respectively (p>0.05).
Jassal, A., Nawal, R.R., Yadav, S., Talwar, S., Yadav, S. and Duncan, H.F. (2022), Outcome of partial and full pulpotomy in cariously-exposed mature molars with symptoms indicative of irreversible pulpitis: A randomized controlled trial. Int Endod J. Accepted Author Manuscript. https://doi.org/10.1111/iej.13872
Dr. Shravani Dali has completed her BDS from Pravara institute of medical sciences, loni. Following which she extensively worked in the healthcare sector for 2+ years. She has been actively involved in writing blogs in field of health and wellness. Currently she is pursuing her Masters of public health-health administration from Tata institute of social sciences. She can be contacted at editorial@medicaldialogues.in.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


