- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Regenerative endodontic procedures may help detect root canal calcification
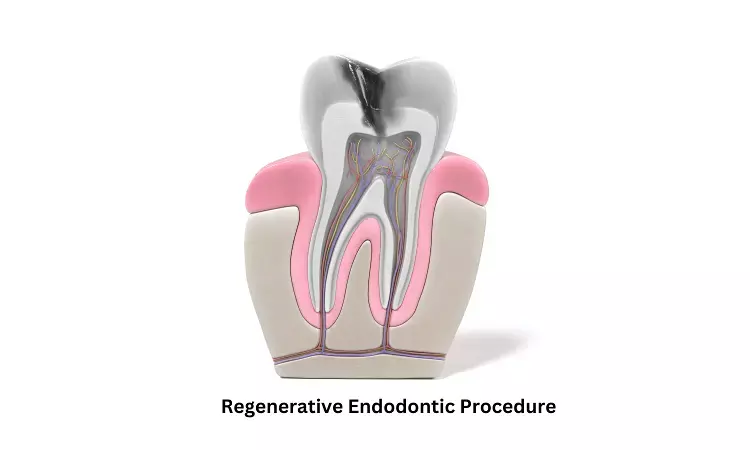
A recent retrospective study by Xijun Jiang and team, reveals that teeth treated with regenerative endodontic procedures (REP) had a relatively high probability of root canal calcification detection over a long time. The study says occurrence of calcification is related to the use of calcium hydroxide paste but does not affect the long-term prognosis of teeth.
The study findings is published in International Journal of Pediatric Dentistry.
Regenerative endodontic treatment is a procedure designed to replace damaged pulp tissue with viable tissue which restores the normal function of the pulp-dentin structure. After regenerative endodontic treatment, continued root development and hard tissue deposition on the dentinal wall can occur under ideal circumstances
Researchers aimed to evaluate the characteristics of root canal calcification after regenerative endodontic procedures (REPs) during long-term follow-up.
Jiang's team collected Data of children who underwent REPs and were followed up for more than 3 years in the Department of Pediatric Dentistry, Peking University School and Hospital of Stomatology, Beijing, China, from January 2013 to January 2019. All the patients were treated by the protocol of REPs based on the AAE (American Association of Endodontists) protocol.
The key findings of the study are:
•A total of 91 teeth of 54 boys and 37 girls (average age 10.4 ± 1.9 years) with follow-up duration > 3 years were included.
•The follow-up duration ranged from 36-92 months (average, 53.2 ± 13.4 months). The prevalence, contributing factors, and long-term prognoses of root canal calcification after REPs were discussed.
•The incidence of root canal calcification was 78% (71/91).
•The use of calcium hydroxide paste was significantly correlated with the occurrence of root canal calcification (p < 0.05).
• Some teeth showed aggravation of calcification with time, however, not all teeth showed calcification after longer follow-up duration.
Xijun Jiang and team concluded that "Teeth treated with REPs had a relatively high probability of root canal calcification detection during the long-term follow-up. The occurrence of calcification is related to the use of calcium hydroxide paste but does not affect the long-term prognosis of teeth."
Reference: Xijun Jiang, Yunfei Dai, He Liu; "Evaluation of the characteristics of root canal calcification after regenerative endodontic procedures: A retrospective cohort study over 3 years" DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/ipd.13039.
MSc. Neuroscience
Niveditha Subramani a MSc. Neuroscience (Faculty of Medicine) graduate from University of Madras, Chennai. Ambitious in Neuro research having worked in motor diseases and neuron apoptosis is interested in more of new upcoming research and their advancement in field of medicine. She has an engrossed skill towards writing and her roles at Medical dialogue include Sr. Content writer. Her news covers new discoveries and updates in field of medicine. She can be reached at editorial@medicaldialogues.in
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


