- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Salivary and peri-implant crevicular fluid biomarkers promising predictors of peri-implant disease conditions: Study
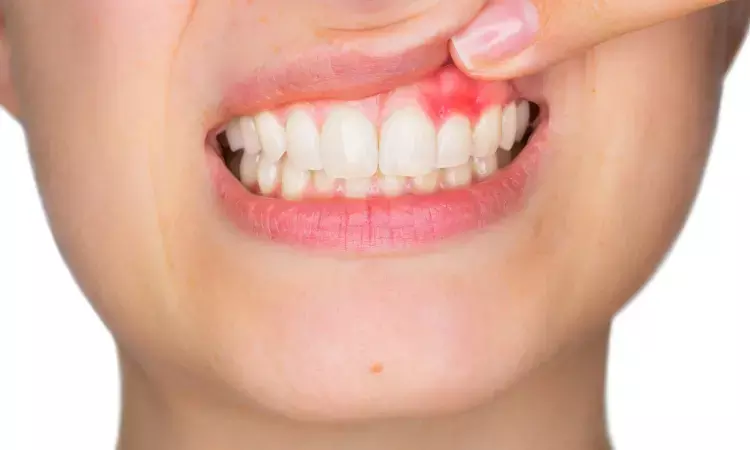
Lithuania: A recent systematic review published in The International Journal of Oral & Maxillofacial Implants assessed the recent evidence (2017–2022) to identify salivary and peri-implant crevicular fluid biomarkers with potential prognostic and diagnostic capabilities for peri-implant disease conditions.
The study found that of all 49 biomarkers evaluated, IL-1β and RANKL were promising as biomarkers of peri-implant disease conditions; however, the researchers suggest the need for clinical studies with a robust methodology to strengthen the evidence base.
"RANKL and IL-1β have the highest diagnostic significance in assessing peri-implant inflammatory conditions, as differences were observed between all three groups (HI < PIM < PI), the researchers wrote.
The study was conducted by Vykintas Pliavga, Lithuanian University of Health Sciences, Kaunas, Lithuania, and colleagues to summarize the latest scientific literature regarding the concentrations of biomarkers in saliva and peri-implant crevicular fluid (PICF) of healthy implant (HI) patients and patients with peri-implant mucositis (PIM) and peri-implantitis (PI).
For this purpose, the researchers performed a literature review according to PRISMA guidelines. The following online databases were used: ScienceDirect, PubMed MEDLINE, and Cochrane Library. A combination of keywords was used, and selection criteria were applied. Selected articles were published between 2017 and 2022, written in English, and conducted in humans. The articles investigated the levels of saliva and PICF biomarkers in peri-implantitis patients and compared them to healthy implant/peri-implant mucositis patients.
The researchers selected 16 publications comprising 1,117 patients with 1,346 implants.
Following were the key findings:
- Qualitative analysis revealed 49 different biomarkers, the levels of which were compared between groups.
- After evaluating the most frequently studied biomarkers, significantly higher values of IL-1β, RANKL, sRANKL, IL-6, TNF-α, TNFSF12, MMP2, and MMP8 levels were observed in the PI group than in the HI group.
- Of the above-listed biomarkers, IL-1β and RANKL demonstrated the highest diagnostic significance as their levels differed among the three groups, with the highest levels in the peri-implantitis group, followed by the peri-implant mucositis group and the lowest levels in the healthy group.
"Of the 49 biomarkers evaluated, RANKL and IL-1β have potentially the highest diagnostic significance in assessing peri-implant inflammatory conditions, as differences were observed between all three groups (HI < PIM < PI), but data from current publications were not adequate to provide strong evidence," the researchers concluded.
Reference:
Pliavga V, Peceliunaite G, Daugela P, Leketas M, Gervickas A, Juodzbalys G. Peri-implantitis Diagnosis and Prognosis Using Biomarkers: A Systematic Literature Review. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2023 Dec 12;38(6):1095-1105. doi: 10.11607/jomi.10353. PMID: 38085740.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


