- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Selection of cast and wrought-wire clasps for removable partial dentures: Guideline
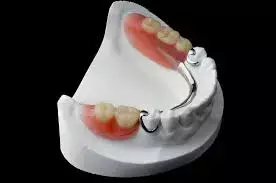
A set of guidelines for the selection of cast and wrought-wire clasps for suggested that combinations of clasp material and undercut that would exert the maximum retentive force without deformation were the most effective, as published in the International Dental Journal.
The aim of this study was to establish guidelines for the selection of cast and wrought-wire clasps for removable partial dentures (RPDs) that would be appropriate for clinically encountered undercuts and facial curvatures.
Randomly selected discarded casts were collected and 30 premolars and 30 molars were surveyed, sectioned to a line representing the clasp and scanned using a flatbed scanner. The average clasp curvature and length for each group was determined and a three-dimensional model was printed, to which wrought wire clasps of 0.9- and 1.0-mm diameter were adapted. Standard wax clasp patterns were adapted and cast in a stellite alloy. Each clasp was deformed beyond its proportional limit; and the forces exerted at that limit and at deflections of 0.25 mm, 0.5 mm, and 0.75 mm were measured, and a safety limit was calculated that would ensure elastic deformation at the required undercuts.
Results:
A table was produced with guidelines for those clasps that would provide the highest retentive force within the proposed safety limit. The highest forces were provided by cast clasps in a 0.25-mm undercut. Wrought round wire of 1-mm diameter provided the next highest retentive forces, in a 0.25-mm undercut for premolar clasps arms and 0.5-mm for molar clasps.
The results provide valid guidelines for the use of combinations of clasp material and undercut that would exert the maximum retentive force without deformation for both short (premolar) as well as long (molar) clasps, for wrought and cast clasps.
Reference:
Guidelines for the choice of circumferential wrought wire and cast clasp arms for removable partial dentures by C. Peter Owen et al published in the International Dental Journal.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.identj.2021.01.005
Dr. Shravani Dali has completed her BDS from Pravara institute of medical sciences, loni. Following which she extensively worked in the healthcare sector for 2+ years. She has been actively involved in writing blogs in field of health and wellness. Currently she is pursuing her Masters of public health-health administration from Tata institute of social sciences. She can be contacted at editorial@medicaldialogues.in.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


