- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Smoking intensity and implant- and patient-related variables may increase risk of peri-implantitis
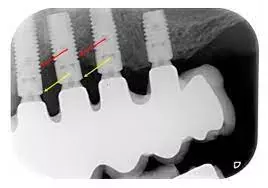
Smoking intensity and implant- and patient-related variables linked to increased risk of peri-implantitis suggests a new study published in the Clinical Oral Implants Research.
A study was done to determine the association between tobacco and peri-implant diseases in a sample of patients who had received implant-supported restorations in a university dental clinic. Furthermore, the study aimed to investigate patient- and implant-related variables associated with peri-implant diseases.
The present retrospective study analyzed data from 117 patients treated with implant-supported restorations from 2001 to 2013. A total of 450 implants were evaluated. Patients were selected from an electronic database, and patient- and implant-related variables were evaluated. Detailed information regarding the smoking history (i.e., smoking status, lifetime cumulative dose, duration of exposure, intensity of the habit, and smoking cessation) was recorded. The primary study outcome was peri-implant status [i.e., health (H), peri-implant mucositis (PM) and peri-implantitis (PI)]. Univariate and multinomial regression models comparing PM and PI versus peri-implant health were conducted.
Results
A total of 117 subjects [55 (47%) females and 62 (53%) males] with a mean age at examination of 64.2 years (SD 11.6) and rehabilitated with 450 implants were included. The average number of implants per patient was 4.6 (SD 3.3) with a mean time in function of 8.0 years (SD 1.9). Fifty-six patients (47.9%) were non-smokers, 42 (35.9%) were former-smokers, and 19 (16.2%) were current-smokers. Thirty-nine subjects (33.4%) were H, whereas 41 (35%) and 37 (31.6%) exhibited PM and PI, respectively. At implant level, the corresponding values were 142 (31.6%), 230 (51.1%) and 78 (17.3%). In the multinomial regression model, significant associations for peri-implant diseases were observed for the mean number of implants per patient (p = .016), function time (p = .048), implants placed simultaneously with guided bone regeneration (p = .016), implant surface (p = .020), keratinized mucosa at the buccal aspect (p = .032), and access to interproximal hygiene (p < .001). In addition, ever smokers >23 pack-years exhibited a significantly higher risk for peri-implantitis (p = .002). Finally, the multinomial regression analysis revealed that subjects who had stopped smoking more than 21 years before the last examination presented a significantly lower risk of peri-implant diseases than a smoking cessation of ≤21 years (p = .028).
Smoke intensity was associated with an increased risk of the development of peri-implantitis. Moreover, the risk of peri-implant diseases might be similar in those subjects who had stopped smoking for more than 21 years with respect to never-smokers.
Reference:
Martinez-Amargant, J., de Tapia, B., Pascual, A., Takamoli, J., Esquinas, C., Nart, J., & Valles, C. (2023). Association between smoking and peri-implant diseases: A retrospective study. Clinical Oral Implants Research, 00, 1–14. https://doi.org/10.1111/clr.14147
Keywords:
Smoking, intensity, implant, patient-related, variables, linked, increased risk, peri-implantitis, Martinez-Amargant, J., de Tapia, B., Pascual, A., Takamoli, J., Esquinas, C., Nart, J., & Valles, C, Clinical Oral Implants Research
Dr. Shravani Dali has completed her BDS from Pravara institute of medical sciences, loni. Following which she extensively worked in the healthcare sector for 2+ years. She has been actively involved in writing blogs in field of health and wellness. Currently she is pursuing her Masters of public health-health administration from Tata institute of social sciences. She can be contacted at editorial@medicaldialogues.in.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


