- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Standard anti-infective mechanical treatment may reduce peri-implant mucositis
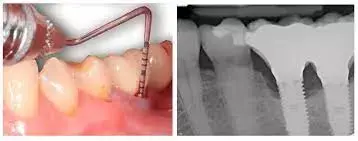
Standard anti-infective mechanical treatment may reduce peri-implant mucositis suggests a new study published in the Journal of Periodontology.
Peri-implant mucositis (PIM) is a pathological precursor of peri-implantitis, but its pattern of conversion to peri-implantitis is unclear and complicated to diagnose clinically, while none of the available protocols yield complete disease resolution. The aim of this study was the evaluation of PIM responsiveness to standard anti-infective mechanical treatment (AIMT) at clinical and biomarker levels, and estimation of the diagnostic capacity of bone markers as surrogate endpoints and predictors.
Systemically healthy outpatients presenting one implant exhibiting clinical signs of inflammation confined within the soft tissue (PIM) and one healthy control (HC) implant at a non-adjacent position were included. Clinical parameters and peri-implant crevicular fluid samples were collected baseline and 6 months following mechanical therapy, to assess the levels of RANKL, OPG, and IGFBP2. PIM clustering was performed using machine learning algorithms.
Results
Overall, 38 patients met the inclusion criteria. Therapy resulted in the reduction of all clinical and biological indicators, but respective values remained significantly higher compared to HC. Clinical examination noted 30% disease resolution at the 6-month follow-up, while 43% showed no active bone resorption. OPG showed positive prognostic value for treatment outcome, while the clustering based on active bone resorption did not differ in terms of therapeutic effectiveness.
AIMT is effective in reducing the clinical and biological indicators of PIM, but complete clinical resolution was achieved in only 30% of the cases. Around one third of PIM patients exhibited active bone resorption bellow clinical detectability that was not associated with disease progression and poor treatment responsiveness.
Reference:
Rakic M, Tatic Z, Radovanovic S, Petkovic-Curcin A, Vojvodic D, Monje A. Resolution of peri-implant mucositis following standard treatment: A prospective split-mouth study. J Periodontol. 2023; 1-11. https://doi.org/10.1002/JPER.23-0507
Keywords:
Standard, anti-infective, mechanical, treatment, may, reduce, peri-implant, mucositis,Rakic M, Tatic Z, Radovanovic S, Petkovic-Curcin A, Vojvodic D, Monje A, Journal of periodontology
Dr. Shravani Dali has completed her BDS from Pravara institute of medical sciences, loni. Following which she extensively worked in the healthcare sector for 2+ years. She has been actively involved in writing blogs in field of health and wellness. Currently she is pursuing her Masters of public health-health administration from Tata institute of social sciences. She can be contacted at editorial@medicaldialogues.in.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


