- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Surface Smoothness of stainless steel orthodontic archwires not affected by Use of salbutamol inhalers in asthma patients: Study
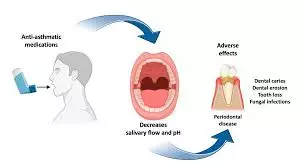
Smoothness of surface of stainless steel orthodontic archwires not affected by Use of salbutamol inhalers among asthma patients suggests a study published in the Clinical Dentistry.
This study aimed to compare the surface roughness and friction of different orthodontic archwires after exposure to salbutamol sulphate inhalation, an anti-asthmatic medication.
Orthodontic archwires (stainless-steel [StSt], nickel-titanium [NiTi], beta-titanium [β-Ti], and copper-NiTi [Cu-NiTi]) were equally divided into two groups. The exposed groups were subjected to 20 mg salbutamol sulphate for 21 days and kept in artificial saliva. The control groups were only kept in artificial saliva. Surface changes were visualized using scanning electron microscopy (SEM). The average surface roughness (Ra) was evaluated using atomic force microscopy (AFM), and friction resistance forces were assessed using a universal testing machine. Statistical analyses were performed using t-tests and ANOVA followed by post hoc tests. Results: Salbutamol sulphate did not change the surface roughness of StSt and NiTi archwires (p > .05).
However, the change in the surfaces of β-Ti and Cu-NiTi archwires was significant (p < .001). The frictional forces of exposed StSt, NiTi, and Cu-NiTi archwires did not change (p > .05). However, the frictional forces of β-Ti archwires increased significantly after exposure to salbutamol sulphate (p = .021). Brushing with fluoride after exposure to salbutamol sulphate increased the frictional forces of β-Ti only (p = .002). Salbutamol sulphate inhalation significantly affected the surface texture of β-Ti and Cu-NiTi orthodontic archwires and increased the friction of β-Ti archwires. These deteriorating effects were not detected on the surface of StSt and NiTi archwires. Therefore, we suggest that β-Ti and copper titanium archwires should be used cautiously in individuals under salbutamol sulphate inhalation treatment.
Reference:
Alemran MA, Abbassy MA, Bakry AS, Alsaggaf DH, Abuhaimed TS, Zawawi KH. The effect of salbutamol sulphate inhalation (an anti-asthmatic medication) on the surfaces of orthodontic Archwires. Orthod Craniofac Res. 2024; 27: 447-454. doi:10.1111/ocr.12749
Dr. Shravani Dali has completed her BDS from Pravara institute of medical sciences, loni. Following which she extensively worked in the healthcare sector for 2+ years. She has been actively involved in writing blogs in field of health and wellness. Currently she is pursuing her Masters of public health-health administration from Tata institute of social sciences. She can be contacted at editorial@medicaldialogues.in.
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


