- Home
- Medical news & Guidelines
- Anesthesiology
- Cardiology and CTVS
- Critical Care
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- ENT
- Gastroenterology
- Medicine
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Obstretics-Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics
- Pediatrics-Neonatology
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Surgery
- Urology
- Laboratory Medicine
- Diet
- Nursing
- Paramedical
- Physiotherapy
- Health news
- Fact Check
- Bone Health Fact Check
- Brain Health Fact Check
- Cancer Related Fact Check
- Child Care Fact Check
- Dental and oral health fact check
- Diabetes and metabolic health fact check
- Diet and Nutrition Fact Check
- Eye and ENT Care Fact Check
- Fitness fact check
- Gut health fact check
- Heart health fact check
- Kidney health fact check
- Medical education fact check
- Men's health fact check
- Respiratory fact check
- Skin and hair care fact check
- Vaccine and Immunization fact check
- Women's health fact check
- AYUSH
- State News
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Andhra Pradesh
- Arunachal Pradesh
- Assam
- Bihar
- Chandigarh
- Chattisgarh
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli
- Daman and Diu
- Delhi
- Goa
- Gujarat
- Haryana
- Himachal Pradesh
- Jammu & Kashmir
- Jharkhand
- Karnataka
- Kerala
- Ladakh
- Lakshadweep
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Manipur
- Meghalaya
- Mizoram
- Nagaland
- Odisha
- Puducherry
- Punjab
- Rajasthan
- Sikkim
- Tamil Nadu
- Telangana
- Tripura
- Uttar Pradesh
- Uttrakhand
- West Bengal
- Medical Education
- Industry
Symphyseal measurements may guide choice of suitable dental implant design
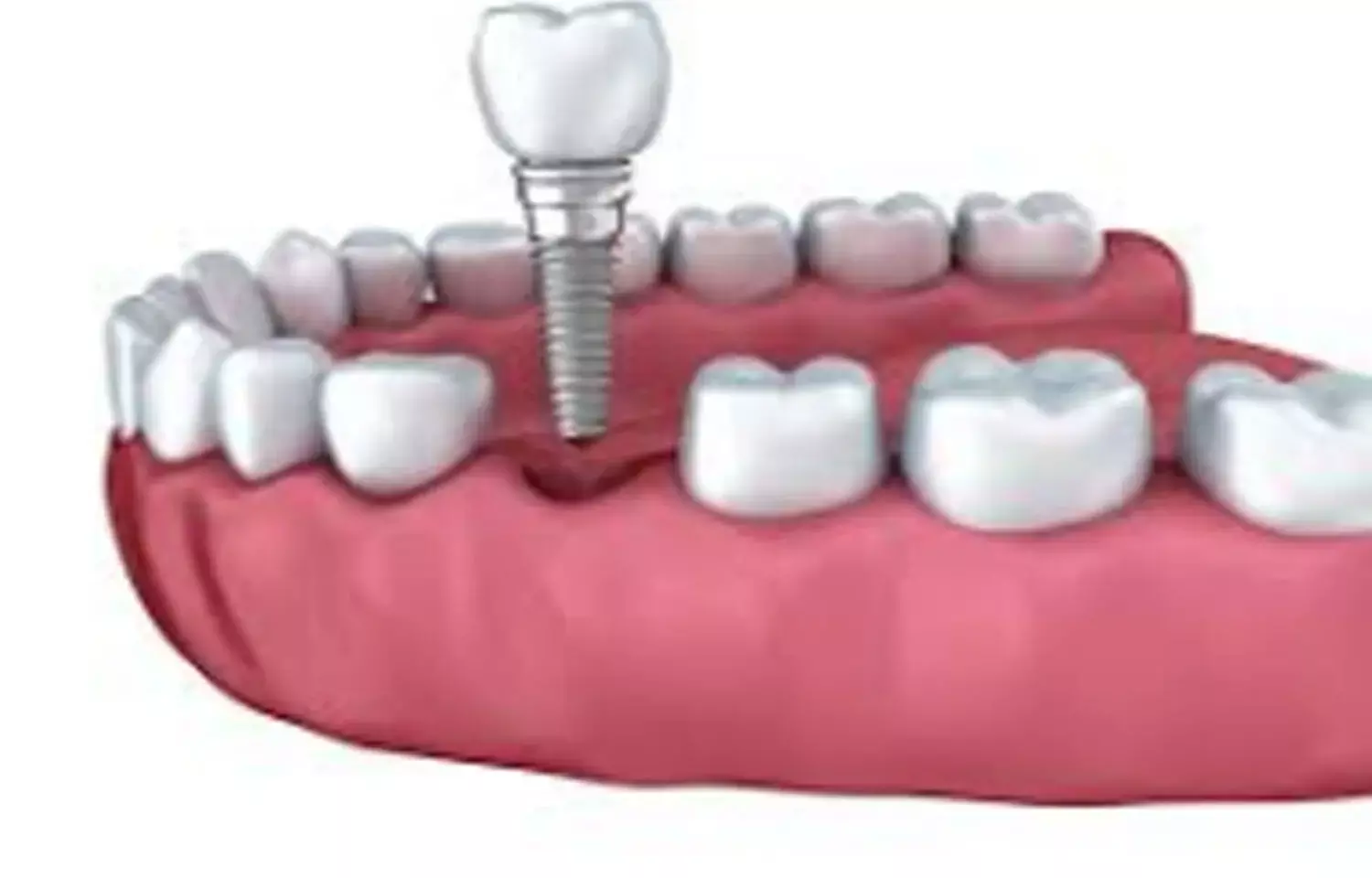
Investigators have recently noted that symphyseal measurements are parameters that reflect the symphysis bone characteristics and can guide the choice of a suitable implant design, as published in the Journal of Dental Sciences.
Overdenture with single symphyseal implant is one of the useful clinical approach for elderly edentulous patients. The loss of anterior mandibular teeth induces many changes of the symphysis, particularly regarding its shape and volume. These changes have been well described in the literature. They mainly occur during the first 6 months after tooth extractions, and often involve the loss of up to 50% of the initial volume.
Hence, Chloë Mense and colleagues from the Aix Marseille University, Marseille, France carried out this study to evaluate edentulous patients with regards to the relationship between dimensions, bone characteristics, cancellous densities, and cortical thickness of the mandibular symphyseal region using cone beam computed tomography (CBCT).
The authors analyzed 103 CBCT from pre-implant investigations. All included patients were healthy without any disorders affecting bone metabolism. 13 measurements for each patient was performed: 9 of height, width, and thickness (mm) and 4 of density (Hounsfield Units; HU). Fisher's exact test was applied to examine the association between two categorical variables, the Pearson correlation coefficient to measure the strength of linear relationship between two quantitative variables. The two-sample Student's t-test was used to compare mean symphysis height between men and women, the paired Student's t-test to compare mean lingual and buccal cortical thickness. For all tests, the threshold of significance was fixed at 5%.
The results showed that men and women significantly differed with regards to mean total symphysis height (p = 0.004) and the distribution of Cawood and Howell classifications (p = 0.033). Symphysis height was negatively correlated with mean density of cancellous bone (r = −0.453, p < 0.001). Mean lingual cortical thickness significantly differed from mean vestibular thickness (p < 0.001, paired Student's t-test).
Therefore, the authors laid out the following conclusions-
- The reduction of symphyseal size is sex-related, with women showing greater reduction.
- The decrease of symphyseal height is accompanied by an increased density of the central and lower portion of cancellous bone, and the thickness of the lingual and lower parts of cortical bone.
- Symphysis size is an important parameter for selecting the design (form, thread, surface) of the implant to ensure optimal primary stability and quick osteointegration.
Dr. Nandita Mohan is a practicing pediatric dentist with more than 5 years of clinical work experience. Along with this, she is equally interested in keeping herself up to date about the latest developments in the field of medicine and dentistry which is the driving force for her to be in association with Medical Dialogues. She also has her name attached with many publications; both national and international. She has pursued her BDS from Rajiv Gandhi University of Health Sciences, Bangalore and later went to enter her dream specialty (MDS) in the Department of Pedodontics and Preventive Dentistry from Pt. B.D. Sharma University of Health Sciences. Through all the years of experience, her core interest in learning something new has never stopped. She can be contacted at editorial@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751
Dr Kamal Kant Kohli-MBBS, DTCD- a chest specialist with more than 30 years of practice and a flair for writing clinical articles, Dr Kamal Kant Kohli joined Medical Dialogues as a Chief Editor of Medical News. Besides writing articles, as an editor, he proofreads and verifies all the medical content published on Medical Dialogues including those coming from journals, studies,medical conferences,guidelines etc. Email: drkohli@medicaldialogues.in. Contact no. 011-43720751


